| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2269629
![]()
CONSTRUCTION ROOF OF ANGARA
The name of the inventor: Yuri Dmitrievich Morozov (RU); Teplyakov Albert Alekseevich (RU); Nechay Igor Alekseevich (RU); Lyagaeva Olga Sergeevna
The name of the patent owner: Open Joint-Stock Company GIPRONIIAVIAPROM (RU)
Address for correspondence: 127083, Moscow, ul. Verhnyaya Maslivka, 20, JSC "GIPRONIIAVIAPROM"
Date of commencement of the patent: 2003.10.29
The invention relates to construction, in particular to roof structures of industrial buildings and structures, in particular to hangar roof structures, and can be used in the construction of large-span hangars in subtropical and tropical climatic zones of different countries. The invention is aimed at ensuring the reliability and durability of roof operation in the conditions of active infrared radiation and intensive solar radiation by preventing the breach of waterproofing roofing leakage and ensuring its ventilation. The essence of the invention is that the roof structure of the hangar includes a waterproof roofing carpet, profiled metal flooring and thermal insulation . In this case, the profiled metal deck is installed on the upper rungs, and the rest of the roof, including the waterproofing roofing carpet and the heat insulation plates, is located on the metal grids, each grid is attached to the wall of the run at the point of interface of this wall with the inner surface of the lower rung shelf. In this case, an air gap is provided between the deck and the waterproofing carpet.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to construction, in particular to roof structures of industrial buildings and structures, in particular to hangar roof structures, and can be used in the construction of large-span hangars in subtropical and tropical climatic zones of different countries.
Known construction of the roof, used in mass construction. It consists of a gravel protective layer, a waterproofing roofing carpet, thermal insulation and a profiled metal flooring, to which the thermal insulation is adhered with bitumen [1]. This construction is the closest in technical essence and achievable results to the present invention.
However, the use of the aforementioned known roof construction in the construction of large-span hangars in countries with a hot tropical and subtropical climate is inexpedient, because in the conditions of active infrared radiation and intense solar radiation, the operation of this roof will be short-lived, Waterproof roofing carpet made of roofing material, under the influence of high temperatures and intense solar radiation is destroyed, resulting in a broken roof integrity. Infringement of tightness leads to impossibility of creation in a hangar of the microclimate necessary for service of the expensive equipment of wide-body aircraft according to the international norms of ICAO (International Civil Aviation Organization).
The invention is aimed at ensuring the reliability and durability of roof operation in conditions of active infrared radiation and intense solar radiation due to the prevention of breach of the waterproofing roofing hermeticity and its ventilation.
This is achieved by the fact that the roof structure of the hangar includes a waterproof roofing carpet, profiled metal flooring and thermal insulation. In this case, the profiled metal deck is installed on the upper shelves of the passes, and the rest of the roof, including the waterproofing roofing carpet and the heat insulation plates, is located on the metal grids, each of which is attached to the wall of the run at the interface of this wall with the inner surface of the lower rung shelf. In this case, an air gap is provided between the abovementioned deck and the waterproofing carpet ( ![]() ), The value of which is determined by the following relationship:
), The value of which is determined by the following relationship:
![]() = H- (a + b + c + d)
= H- (a + b + c + d)
Where: h is the height of the run for a particular construction area;
A - thickness of the waterproof roofing carpet;
B - thickness of thermal insulation boards;
C is the thickness of the metal mesh;
D is the thickness of the flange of the run plus the radius r of the mating of the flange wall with the inner surface of the lower flange of the run.
The aforementioned set of essential features distinguishing the invention from the closest analogue makes it possible to obtain a technical result in the implementation of the invention, namely to prevent a breach of the waterproofing roofing impermeability and to ensure its ventilation.
Due to the achievement of the technical result that can be obtained by practicing the invention, the reliability and durability of roof operation is assured, i. E. The task for which the invention is directed is solved.
The essence of the invention is explained in the drawings, where
 |
 |
1 shows a variant of a roof in plan.
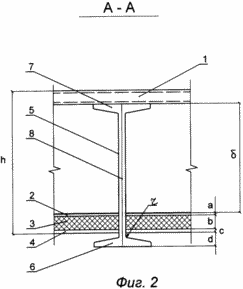
FIG. 2 is a sectional view of AA in FIG. 1. FIG.
The positions on the drawings indicate: special profiled metal flooring - 1 for roofs operated in countries with tropical climate, waterproof roofing carpet - 2, plates, thermal insulation - 3, metal mesh - 4, run - 5, air gap " ![]() ", The lower run shelf is 6, the upper run shelf is 7, the run wall is 8, the radius" r "of the interface of the wall 8 of the run 5 is with the inner surface of the bottom 6 of the run shelf 5.
", The lower run shelf is 6, the upper run shelf is 7, the run wall is 8, the radius" r "of the interface of the wall 8 of the run 5 is with the inner surface of the bottom 6 of the run shelf 5.
The structure of the roof of the hangar includes a waterproof roofing carpet 2, a profiled metal floor 1 and heat insulation plates 3, a profiled metal floor 1 is installed on the upper shelves of the runs 5 and the rest of the roof including the waterproof roofing carpet 2 and the insulation plate 3 is located on the metal nets 4, Each of which is attached to the wall of the run at the junction point of the wall 8 with the surface of the lower flange of the run 6, with an air gap "between the above-mentioned deck and the waterproofing carpet" ![]() ", And the interface of the wall with the surface of the lower rung shelf is formed by the radius" r ".
", And the interface of the wall with the surface of the lower rung shelf is formed by the radius" r ".
The roof structure of the hangar works as follows. Under the influence of active infrared radiation and intense solar radiation, the profiled metal floor 1 is heated to high temperatures (up to 100 ° C). Air from the outside, passing through the air gap " ![]() ", Protects the waterproof roofing carpet 2 from the destructive effect of the heated metal deck 1. Due to this, the microclimate necessary for repair and preventive maintenance with expensive aircraft equipment is maintained inside the hangar. Prevention of breach of watertightness of the waterproofing roofing carpet and ensuring its ventilation through the air gap "
", Protects the waterproof roofing carpet 2 from the destructive effect of the heated metal deck 1. Due to this, the microclimate necessary for repair and preventive maintenance with expensive aircraft equipment is maintained inside the hangar. Prevention of breach of watertightness of the waterproofing roofing carpet and ensuring its ventilation through the air gap " ![]() "Helps to increase the reliability and durability of roof operation.
"Helps to increase the reliability and durability of roof operation.
INFORMATION SOURCES
1. Gosstroy USSR, All-Union Research Institute of Information on Construction and Architecture. Construction and architecture. Series IV. Industrial complexes, buildings and structures. Issue 1. Roofs of industrial buildings. Moscow. 1984, page 8, Fig. 1a.
CLAIM
The construction of the roof of the hangar includes a waterproof roofing carpet, profiled metal flooring and heat insulation plates, a profiled metal floor is installed on the upper shelves of the girders, and the rest of the roof, including a waterproof roofing carpet and heat insulation boards, is located on metal grids, each of which is attached to the wall of the girder The interface of the runner wall with the surface of the lower run flange, which is formed by a radius r, with an air gap between the above deck and the waterproofing carpet.
print version
Date of publication 01/21/2007




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.