| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2034742
![]()
SOLAR POWER PLANT AND METHOD FOR ITS OPERATION
Name of the inventor: Bratuta AMY GOODMAN .; Brodsky VL .; Simonenko AS
The name of the patentee: Kharkov Polytechnical Institute; Institute "Ukrkranenergo"
Address for correspondence:
Starting date of the patent: 1990.07.03
The invention relates to the aerostat technology, in particular, to solar power plants placed on tethered aircraft lighter than air. The purpose of the invention - to simplify operation. The apparatus comprises a field of solar cells 1, the nodes for their attachment 2 aircraft 3 and 4, lighter than air, turning mechanisms field of solar cells 5, flexible rod 6, the vertical movement mechanisms 7 and 8 of the aircraft. Field of the solar cell 1 is mounted between the aircraft 3 and 4. The distance between the axes of the mechanisms 7 and 8 vertical movement aircraft 3 and 4 satisfies the inequality B ![]() L-2h min where L - length of the field of solar cells 1; h m - minimum height Field arrangement of solar cells 1, which made installation, commissioning and maintenance of power plants. The method includes the operation of a solar power plant of its placing on the tethered flying machines 3 and 4 and rise to a height that exceeds the maximum height of clouds to the region. Aircraft 3 and 4 have a long axis along the line east-west. Orienting field of solar cells 1 on the sun by rotating it about an axis which is set at an angle
L-2h min where L - length of the field of solar cells 1; h m - minimum height Field arrangement of solar cells 1, which made installation, commissioning and maintenance of power plants. The method includes the operation of a solar power plant of its placing on the tethered flying machines 3 and 4 and rise to a height that exceeds the maximum height of clouds to the region. Aircraft 3 and 4 have a long axis along the line east-west. Orienting field of solar cells 1 on the sun by rotating it about an axis which is set at an angle ![]() Equal latitude location of the power plant, aircraft separation by 3 and 4 in height.
Equal latitude location of the power plant, aircraft separation by 3 and 4 in height.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the aerostat technology, in particular, to solar power plants placed on tethered balloons, to generate electricity using a renewable, alternative and environmentally friendly source of energy of the sun, and can be used anywhere in the world, including in the cloud and icy areas, both in stand-alone mode or in conjunction with other existing power plants.
Known solar power plant, comprising a tethered aircraft lighter than air with flexible rods and mechanisms of vertical movement, the field of solar cells with their fixing and rotation mechanism nodes.
Known and the method of operation of solar power plants [1] in which it is placed on a tethered aircraft lighter than air and rises to a height that exceeds the maximum height of clouds to the region, and orient the field of solar cells to the sun by its rotation.
The disadvantage of solar power and a method of operation is the complexity of the operation.
The invention aims to simplify the operation.
This is achieved by the fact that in the known solar power field of solar cells mounted between the aircraft and the distance between the axes of the vertical displacement of the mechanisms of aircraft satisfies b ![]() L 2h min where L of the length of the solar cell, h min minimum height Field arrangement of solar cells, which made installation, commissioning and maintenance of power plants.
L 2h min where L of the length of the solar cell, h min minimum height Field arrangement of solar cells, which made installation, commissioning and maintenance of power plants.
In addition, the known method of operation of solar power a craft long axes along the line east-west, and the rotation of the field of solar cells is carried out around this axis, which is mounted at an angle ![]() equal to the geographical latitude of the location of the power plant by the diversity of aircraft height units.
equal to the geographical latitude of the location of the power plant by the diversity of aircraft height units.
 |
 |
 |
 |
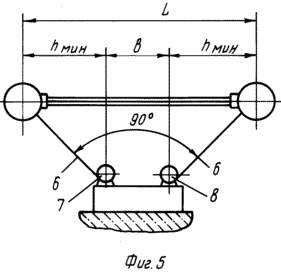 | |
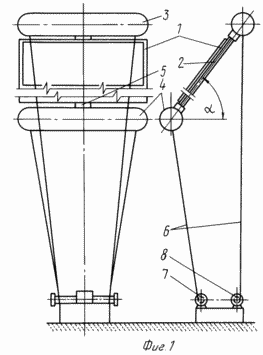
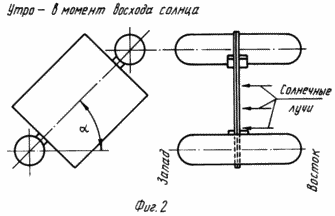
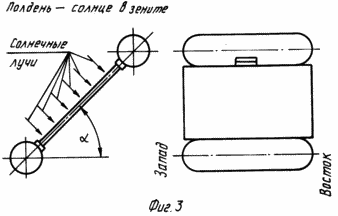
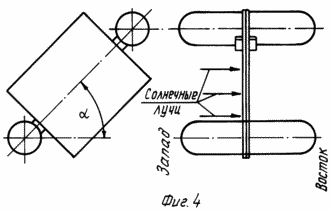
FIG. 1 shows a solar plant, general view; FIG. 2 orientation power of the sunrise; FIG. 3 However, in the afternoon; FIG. 4 is the same as at the time of sunset; FIG. 5 flexible linkage arrangement for mounting the field of solar cells.
The apparatus comprises a field of solar batteries 1, 2 sites for attachment of upper 3 and lower 4, lighter than air aircraft, rotating device 5, flexible rod 6, the mechanism 7, the lower vertical movement mechanism of the aircraft and vertical movement of the upper 8 of the aircraft.
Field 1, mounted together with the structure 2 on the ground, is attached to the aircraft 3 and 4 by the rotary device 3 and 5. Apparatuses four flexible rods 6 are connected with the mechanisms 7 and 8.
WORK UNIT AS FOLLOWS
Field 1, structure 2, apparatus 5 while rotating mechanisms 7 and 8 in the direction of increasing the length of rods 6 are raised in the air. Symmetrical and simultaneous lifting devices 3 and 4 is carried out as long as the box 1 is above the maximum height of clouds to the region. After reaching the specified height mechanism 7 stops, stopping the rise of the machine 4. The mechanism 8 continues to work towards increasing the length of the rods 6 of the machine 3 and the rise of this apparatus. Lifting apparatus 3 is made as long as the line connecting the apparatus to the axis 3 and 4, forms an angle ![]() with the horizon equal to the latitude placement power.
with the horizon equal to the latitude placement power.
Accommodation arrangements 7 and 8 on the ground is such that the long axis of the apparatus 3 and 4 are directed through the east-west direction and the distance between the axes of the mechanisms 7 and 8 is chosen such that b ![]() L 2h min.
L 2h min.
To transfer the generated solar power electricity used flexible rod 6. After the lifting of the field 11 and structure 2 in the design position when the line drawn through the axis of the apparatus 3 and 4 forms an angle ![]() with the horizon, 5 devices made them turn in such a position that the sun's rays fell on the field 1 at an angle close to 90 °.
with the horizon, 5 devices made them turn in such a position that the sun's rays fell on the field 1 at an angle close to 90 °.
If at the time of sunrise Field 1 is oriented to the east (see. FIG. 2), then the afternoon field devices 5 1 rotates at an angle of 90 ° (see. Fig. 3). At the time of sunset field 1 occupies a vertical position (see. FIG. 4) different from the one shown in FIG. 2 position so that the sun's rays fall on the field 1 at a right angle to the west. During the night a half days Field 1 and structure 2 takes place in the direction from west to east, preparing the power plant to work at sunrise.
The lifting force of the upper aircraft P wa 0,5 m (1 + sin ![]() ) And lower P NA 0,5 m cos
) And lower P NA 0,5 m cos ![]() Manufacturing apparatus at the upper lift lesser 0,5 m (1 + sin), does not allow to raise the air box 1, structure 2 and actuator 5 to a height providing the desired angle
Manufacturing apparatus at the upper lift lesser 0,5 m (1 + sin), does not allow to raise the air box 1, structure 2 and actuator 5 to a height providing the desired angle ![]() Similarly, production and lower the aircraft to lift less 0,5 · m · cos
Similarly, production and lower the aircraft to lift less 0,5 · m · cos ![]() Does not allow to raise the field 1 and the mechanism of structure 2 with an angle 5
Does not allow to raise the field 1 and the mechanism of structure 2 with an angle 5 ![]() (M weight of the device).
(M weight of the device).
If you lift the upper unit has a power reserve, the angle ![]() is greater than a predetermined, which is undesirable because sunlight will fall on one field at an angle different from the target.
is greater than a predetermined, which is undesirable because sunlight will fall on one field at an angle different from the target.
In the case of the location of aircraft in such a way that their long axis is not oriented on an east-west line, the sun's rays will fall on the field 1 at an angle different from the angle of 90 °, which does not allow power plants with maximum efficiency.
If the distance between the axes of the vertical movement mechanism will be higher than the value ![]() 2 hmin, then the angle between the rods 6, with a minimum height of one field is smaller than the angle
2 hmin, then the angle between the rods 6, with a minimum height of one field is smaller than the angle ![]() 90, which is permissible.
90, which is permissible.
The use of flexible rods, not only for the vertical movement, but also for the transmission of electricity generated to consumers, reduces metal consumption power due to the lack of special conductors.
Solar power can be operated with rechargeable batteries that will store excess electricity generated and give it to customers in the dark, or in combination with ground-based power plants, covering the load in the dark.
CLAIM
1. The solar power plant comprising a tethered lighter-than-air aircraft with flexible rods, and vertical movement mechanisms, the field of solar cells and their attachment and rotation mechanisms nodes, characterized in that, to simplify the operation, the field of solar cells are mounted between the aircraft and the distance between the axes of vertical movement of aircraft mechanisms satisfies
b ![]() L 2h min,
L 2h min,
where L is the length of the field of solar cells;
h min minimum height Field solar cell arrangement, which performed installation, commissioning and maintenance of power plants.
2. A method of operating a solar power plant, in which it is placed on a tethered aircraft lighter than air and rises to a height that exceeds the maximum height of clouds to the region, and orient the field of solar cells to the sun, by its rotation, characterized in that the aircraft has a long axis on the east-west line, and the rotation of the field of solar cells is carried out around this axis, which is mounted at an angle ![]() Equal to the geographical latitude of the location of the power plant by the diversity of aircraft height units.
Equal to the geographical latitude of the location of the power plant by the diversity of aircraft height units.
print version
Publication date 12.01.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.