| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2141606
![]()
SOLAR POWER PLANT
Name of applicant: Agroindustrial Corporation alternative agriculture "Russian peasant"
Name of the inventor: Sparrows RN .; Ogneva EG .; Ivliev SA .; Prokhorov ZP .; Fedorov VA
The name of the patentee: Agroindustrial Corporation alternative agriculture "Russian peasant"
Address for correspondence:. 143900, Moscow region, Balashikha-8 ul.Yu.Fuchika, 7, kv.14, fire EG
Starting date of the patent: 1996.06.20
The invention relates to the conversion of solar radiation into electrical energy needed to power various consumers: space ships, farms and individual farms and individual buildings, vehicles for different purposes, etc. The solar power plant comprising a radiation receiver with a focussing device 1, the semiconductor converter 2 current collectors 3, 4 feeding electricity to the consumer, the cooling system 2 transmitters is formed as a closed circuit with an evaporator, the steam generator 5, the pump 7 and the radiator 6. In the installed steam circuit 8 turbine coupled to an electric generator 9. instead, the turbine can be used in a steam engine, but instead of individual turbines and electric - turbogenerator or thermoelectric generator. The current collectors 10 are connected to said device pantographs converters, which improves installation efficiency.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of converting solar radiation into electrical energy and can be used to power various consumers: space ships, farms and individual buildings, vehicles for different purposes, etc.
There are solar power plants with a radiation focus on semiconductors, system of cooling and receiving power (see. The SU, auth. St. Of N 868 109, M. Cl. The F 03 G 7/02, H 01 L 31/00, 1981).
The use of such systems can improve the density of radiation on semiconductor converters, gain greater power density and lower the unit cost of the installation. The use of these plants cooling system Semiconductor intensively is heated by radiation and ohmic heat generated flowing current, ensures reliable operation due to heat dissipation into the environment.
However, it is useless thermal energy is lost, the loss of 88% is achieved for silicon cells and 76% for GaAs converters.
Known and solar power plant (SPP), containing the radiation detector with focusing devices, semiconductor converters with output power of consumers and their cooling system (see., Eg, the German application N 2750679, M. Cl. Of H 01 L 31/00, 1979) .
The disadvantages of the known SPP include the same as described above.
The object of the invention is useful to use these losses.
The solution of this problem the technical result, manifested in the increase in the radiation density converters, increasing the power density can be obtained by reducing the cost of installation and increase efficiency.
Said technical result is achieved in that the solar power plant comprising a radiation receiver with a focussing device and semiconductor transducers pantographs, the inventive cooling system converters designed as a closed circuit with an evaporator, a steam generator, a pump and a radiator, wherein in said circuit mounted device for converting thermal energy into electrical energy, which are connected to current collectors of trolleys semiconductor transducers. Apparatus for converting thermal energy into electrical energy can be accomplished in a steam turbine connected to an electric generator. You can use instead of the steam turbine of the steam engine or thermoelectric.
The prior art SEU, and a solar power plant, in which the mirror system using solar rays collected into bundles and sent to a steam boiler. The resulting steam is used to drive the turbine generator. Instead, the boiler is sometimes used thermoelectric. These plants use the cycle steam boiler - turbine - generator (see Polytechnic Dictionary -.. M .: Soviet encyclopedia -. 1977. - S.461 and Soviet Encyclopedic Dictionary -.. M .: Soviet encyclopedia -. 1989. - S. 1253).
It should be noted, however, that the known installations allow both receive electricity. In the claimed invention, the turbine is driven by means of a diverter system cooling heat converters and due to this additional power can be obtained, which together with the core increases the efficiency of the installation. This is a key moment in the present invention.
Of known prior art and SPP, which is used to wind the engine (see. SU, SU, N 1687113, F 03 D 9/02, 1991) along with solar panels. The solar power plant generates electricity during the day and transmits the current to the static converter and the wind engine (HP) generates electricity in the presence of wind during both day and night, and transmits it to the static converter. SPP and HP can work both together and separately.
In the claimed invention, an additional power source is made otherwise than in the known device.
Thus, the compounds of the prior art sequence (of communication) known structural elements and their performance has been detected. Therefore, we can conclude the novelty of the claimed SPP and its inventive step. As for the industrial application, it will be apparent from the following description of the operation of EMS.
Brief Description of the drawing, which shows a diagram of a solar power plant.
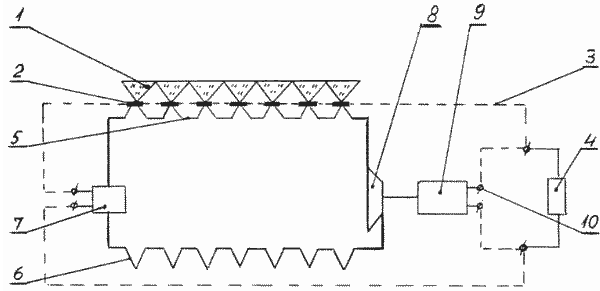
The installation comprises a focusing device 1, the semiconductor converter 2 current collectors 3, 4 connected to the consumer converters 2 are cooled using the built-in steam generator them evaporator 5, in which the closed circuit to a radiator 7 6 mounted electric liquid supply and a steam turbine 8. Instead of the latter a steam engine may be used. The steam turbine 8 is connected to an electric generator 9, current collectors 10 that are connected to the current collectors 3 semiconductor converters 2. Therefore generator 9 operates simultaneously with semiconductor converters 2. Instead of a steam turbine and electric generator turbine generator may be used, or thermoelectric.
POWER INSTALLATION WORKS AS FOLLOWS
Solar radiation is focused on semiconductor devices 1, two transducers which produces the current flowing through the current collectors 3 and the user feeds the motor pump 7, which delivers liquid working fluid (water, air, ammonia, etc.) to the evaporator, the steam generator 5, which removes heat two converters from spent on evaporation of the liquid working fluid and the superheat (if necessary). Steam is supplied to the turbine 8 (steam engine or turbine generator, or thermoelectric) that rotates the generator 9, and runs on 4 consumer of electricity, as well as semiconductor converters 2.
After expansion in the turbine (engine), the exhaust steam is condensed in the radiator 6 to a liquid which is pumped back to the evaporator 7, the steam generator 5, etc.
When extending, for example, saturated steam at a temperature of 200 o C it adiabatic operation is 26% of the heat extracted from the semiconductor converter, if condensed liquid temperature is 50 o C, which corresponds to 82% of the efficiency of the ideal Carnot cycle. If the losses in turbine adiabatic operation is 35%, there will be obtained an efficient thermal energy conversion efficiency of 17%.
The most suitable semi-conductor converters for t = 200 o C are gallium arsenide, can withstand a temperature (for silicon cells t = 50 o C).
When the efficiency of the converter 24% of the total efficiency of the power plant will be up to 37%:
![]()
1.54 times that in a higher efficiency of the semiconductor converter. In this case the specific power at power plants, and m the receiver is increased 1.54 times.
CLAIM
- Solar power plant comprising a radiation receiver with focusing devices, semiconductor transducers pantographs and cooling system converters, wherein the cooling system converters designed as a closed circuit with the evaporator - a steam generator, a pump and a radiator, wherein in said circuit mounted device for converting thermal energy into electrical energy, which are connected to current collectors of trolleys semiconductor transducers.
- Apparatus according to claim 1, characterized in that the device for converting thermal energy of a closed loop cooling semiconductor converters designed as a steam turbine connected to an electric generator.
- Apparatus according to claim 1, characterized in that the device for converting thermal energy of a closed loop cooling semiconductor converters designed as a steam engine, connected to an electric or thermoelectric.
print version
Publication date 19.11.2006gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.