| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2258292
![]()
METHOD OF SUPPLYING LOAD DOWN
The name of the inventor: Korotkikh V.V. (RU); Khartov V.V. (RU); Evens G.D.
The name of the patent holder: the Federal State Unitary Enterprise "Scientific and Production Association of Applied Mechanics named after Academician MF Reshetnev"
Address for correspondence: 662972, Krasnoyarsk Territory, Zheleznogorsk, ul. Lenina, 52, ZATO Zheleznogorsk, FSUE "NPO of Applied Mechanics named after Academician MF Reshetnev", R.P. Turkenichu
Date of commencement of the patent: 2003.05.07
The present invention relates to the electrical industry and can be used in the creation of autonomous power supply systems. A method for supplying a DC load from a source of limited power, for example a solar battery, and a secondary power source, such as a battery, is provided, which consists in stabilizing the load voltage and reconciling the operation of the primary and secondary power sources. The technical result of the proposed invention is to increase the efficiency of using electric power sources. This is achieved by stabilizing the "n" voltage values, first stabilizing the maximum voltage level, and stabilizing the remaining (n-1) voltage levels from the first level of the stabilized voltage to the series stabilized converters. In addition, the coordination of the work of primary and secondary sources of electricity is carried out only at the first level of voltage stabilization. In addition, the stabilization of the voltage at the first level is carried out by a shunt stabilized converter or a short-circuited stabilized converter. In this case, when the voltage is stabilized at the first level by a serially or short-circuited stabilized transducer, extreme control of the primary source of limited power is used.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to the electrical industry and can be used in the creation of autonomous power supply systems.
At present, the process of creating coherent satellites of the Earth with a large output power (10-25 kW) and a long (10-15 years) service life is underway in space technology.
This task, with respect to an autonomous power supply system, can be solved only if the specific energy characteristics of primary electric power sources (mainly solar batteries) are increased, secondary electric power sources (mainly battery batteries) and an automation system that matches the work of these sources with ensuring a stable voltage at the inputs Consumers of electricity.
When creating an automation system that provides a stable voltage at the inputs of electricity consumers, it is necessary to solve an important task - this is to reduce the loss of electricity on the way from electricity sources to consumers.
A method of supplying a load with a constant stable voltage is known, which is realized by the device according to the author. Svid. No. 127153.
According to this method, the load is supplied from the solar and battery batteries through the serial and discharge stabilized converters, and the accumulation of the excess energy of the solar battery in the battery is via the charging stabilized converter.
A method of supplying a load with a constant stable voltage is known, which is realized by the device according to the author. Svid. №77724.
Unlike the previous one, it uses a different principle of solar energy conversion implemented by a shunt stabilized converter.
Otherwise, these known ways of feeding loads are similar.
In more detail, similar methods (systems) of DC load power supply are described in "Power Supply Systems for Spacecraft, Novosibirsk, VO" Nauka ", 1994." [1].
The closest technical solution is the method of supplying the load with a direct current, described in the author's certificate No. 215364 or in [1] (see Chapter 2, paragraph 2.5), which is chosen as a prototype.
The known method provides for increasing the capacity of the autonomous power supply system by installing additional modules ensuring their uniform loading.
The disadvantage of the known method is the low efficiency of using electric power sources.
In the overwhelming majority of cases, the autonomous power supply system forms one level of the output stabilized voltage, for example, in [1] (see Chapter 7) this voltage in the nominal value is 27 V.
At the same time, not all consumers of electric power use this voltage rating as part of on-board equipment, and consequently, they have their own stabilized converters in their composition. At the same time, if there is a need for a higher voltage, converters with booster elements are used, the efficiency of which is much lower.
In addition, in the circuits of electric power sources there are a number of elements that cause ohmic losses of electric power. For example, in the circuit of the primary source of electricity, the solar battery, there is a resistance of the cable line, the transient resistance of the connectors, the transient resistance of the current collector of the rotary device. The total value of the voltage drop across the listed elements is 1.5-2.5 V, and the current loss (for example) of 100 A will be 150-250 W, which is equivalent to 1-2 meters of the square area of the solar battery.
It should be noted that power losses also occur on the control keys of serial converters or on diodes of short-circuited converters (about 0.4-0.6 V).
It is obvious that the loss of electricity is directly proportional to the current flowing. If the voltage is doubled (hence, the current is halved at the same power), the losses will be halved.
The aim of the proposed invention is to increase the efficiency of using electric power sources.
The goal is achieved by stabilizing the "n" voltage values, first stabilizing the maximum voltage level, and stabilizing the remaining (n-1) voltage levels from the first level of the stabilized voltage to the series stabilized converters. In addition, the coordination of the operation of primary and secondary power sources is carried out only at the first level of voltage stabilization, and the stabilization of the voltage at the first level is performed by a shunt stabilized converter or a short-circuited stabilized converter.
Indeed, the stabilization of several output voltage ratings makes it possible to reduce power losses and, consequently, to increase the efficiency of using electric power sources.
This is achieved by reducing the electric current transmission of electricity by increasing the level of the stabilized voltage.
The main electricity consumer is the on-board repeater ("payload").
At the same time, it is quite logical that a high enough input voltage is required to ensure its high specific characteristics (hence, competitiveness).
The remaining consumers of electricity (orientation system, thermal control system, command-measuring system, telemetry system and so on) account for 20-30% of the total electricity consumption. These consumers of electricity are more conservative, as they use unified elements in their composition, and low consumption makes it unnecessary to increase the input voltage. Therefore, their input voltage is lower, mainly 27 V [1].
However, the transmission of electricity from a higher voltage level to a lower level is carried out by correspondingly smaller currents, which again reduces the energy losses.
In addition, the use of a battery with a charging and discharge converter only at the first (highest) level of voltage stabilization and reduces power losses for the same reasons.
The method provides for using as the stabilized converter for the first level of voltage stabilization three main converters: serial, shunt and short-circuited, but, in principle, another type of stabilized converter can be used.
The choice of a particular type of stabilized converter is carried out by the developer of the autonomous power supply system based on specific initial data on the parameters of the primary source of limited power, the level of the element base used, and so on.
As for the three basic types of stabilized transducers indicated here, the following can be noted.
Serial and short-circuited stabilized converters can operate in the mode of extreme power regulation of the primary power source, but they have power loss elements (transistors, diodes) in their composition (in a direct electric power transmission circuit).
The shunt stabilized converter of such elements does not have, but can not work in the regime of extreme regulation of the primary source of limited power.
The figure shows a functional diagram of an autonomous power supply system, explaining the work of the proposed method.
In this case, an option is considered when a shunt stabilized converter is used at the first level of voltage stabilization, although in principle, a series or short-circuited stabilized voltage converters can be used. In this case, the operation of an autonomous power supply system will be similar.
The essence of the proposed method can be explained on the device depicted in the figure.
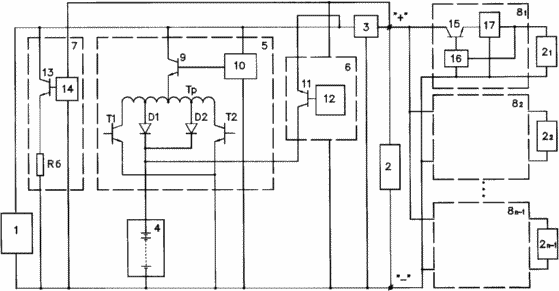
The device comprises a solar battery 1 connected to a load 2 through an output filter 3, a battery 4 connected via a charging converter 5 to a solar battery 1, and via a discharge converter 6 to the input of an output filter, a shunt voltage converter 7 with a ballast resistance R6, Solar battery 1. In addition, to the terminals "+" and "-" of load 2, there are connected (n-1) serial converters 8 1 , 8 2 , ... 8 n-1 , to which the loads are connected 2 1 , 2 1 , ... 2 n-1 .
The charging converter consists of a control switch 9 controlled by a control circuit 10, a booster node executed on a transformer Tp, transistors T1 and T2, a rectifier on diodes D1 and D2.
The discharge converter 6 consists of a control key 11 controlled by a control circuit 12.
The shunt voltage converter 7 consists of a control key 13 controlled by a control circuit 14 and a ballast resistance R6.
Serial converters 8 1 , 8 2 , ... 8 n-1 consist of control keys 15 controlled by control circuits 16 and output filters 17.
The control circuits of the converters 10, 12, 14, 16 are made in the form of pulse width modulators, the input is connected to the buses of the stabilized voltage.
DEVICE WORKS AS FOLLOWING
During operation, the battery 4 works mainly in the storage mode and periodic recharging from the solar battery 1 through the charging stabilized converter 5. This mode of operation allows it to be kept in readiness for emergency situations (loss of orientation to the sun) or for the passage of regular shadow areas Orbits.
The load 2 is supplied by the solar battery 1 through the filter 3, and the voltage stabilization is performed by the shunt stabilized converter 7.
When the shadow areas of the orbit pass, or when the orientation is disturbed, the load 2 is supplied from the storage battery 4 through the discharge converter 6.
Serial converters 8 1 , 8 2 , ... 8 n-1 constantly operate in the same mode from a stable high voltage.
Thus, the proposed method makes it possible to increase the efficiency of the use of electric power sources, which increases the specific energy characteristics of the autonomous power supply system as a whole.
CLAIM
1. A method of supplying a DC load from a power source, such as a solar battery, and a secondary power source, for example a battery, comprising stabilizing the voltage on the load and reconciling the operation of the primary and secondary power sources, characterized in that n voltage ratings are stabilized, First stabilize the voltage on the load having the maximum supply voltage, and stabilize the voltage of the remaining (n-1) loads from the first-load power buses with series stabilized converters, while the primary voltage level and the secondary source are reconciled only at the first level of voltage stabilization.
2. A method according to claim 1, characterized in that the voltage stabilization at the first level is performed by a shunt stabilized transducer.
3. The method according to claim 1, characterized in that the voltage stabilization at the first level is carried out by a short-circuited stabilized converter.
print version
Date of publication 03.02.2007gg




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.