| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2199704
![]()
HELIUM ENERGY INSTALLATION
The name of the inventor: Sobolev VM; Titov N.F .; Golovchenko AI; Ryzhenkov A.Ya.; Malenkov AG; Zhukova E.V.
The name of the patent holder: Sobolev Valerian Markovich ; Titov Nikolay Fedorovich; Golovchenko Alexander Ivanovich; Ryzhenkov Anatoly Yakovlevich; Malenkov Andrey Georgievich; Zhukova Elena Valerianovna
Address for correspondence: 400005, Volgograd, Lenin Avenue, 88, office.313
Date of commencement of the patent: 2001.04.12
Purpose: to provide electricity and heat to industrial and residential objects, including separately standing buildings and their parts, for example, mansards. Essence: three independent energy removal systems are used in the installation: obtaining electricity from collector emitters; obtaining thermal energy through forced convection of the air medium heated in a confined space under the aerodynamic fairing; and transferring heat energy to the consumption zone by the working body enclosed Into the closed system of the internal supply of the coolant. The technical result is achieved by the fact that the efficiency of the installation is enhanced by the use of heat and electricity accumulators that allow to store solar heat in the heat-consuming period (in summer) and use it in the heat-deficient period (in winter) due to the constructive execution of the light receiving trap providing maximum selection of the solar Energy, falling on the aperture area of the mirror, by installing an electric heater and an additional local ballast inductor-heat radiator in the light receiving trap, and by using a mirror lavsan film with devices that regulate its tension, which minimizes the diffraction of light on its microroughnesses And the associated opening and defocusing of the light spot on the surface of the heat pipe and the input aperture of the light receiving trap.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of autonomous power supply and can be used, in particular, to provide electric power and heat to free-standing buildings and parts thereof, for example, mansards.
A solar plant with a solar collector is known, containing in parallel installed pipelines, connected respectively to the inlet and outlet manifolds of the circulating coolant. The solar collector is mounted on a supporting structure and can rotate relative to two mutually perpendicular axes by means of a drive mechanism. The solar collector includes helio concentrators with reflectors having a cylindrical parabolic shape of the envelope surface, in the focus of which pipelines are located. The end sections of the inlet and outlet pipelines are located along the vertical axis of the solar installation and are fixed motionless with respect to the supporting structure. With the inlet and outlet manifolds, the respective pipelines are connected by several hinge assemblies that rotate the solar collector relative to the two axes (US Pat. No. 4,934,324 of 1990, NCI 126/448).
A solar power plant is known comprising a fixed mirror spherical concentrator inclined at an angle equal to the latitude of the place and a power generation circuit having a main and additional heat exchangers and a turbine with an electric generator, the heat exchangers being installed in the region of the concentrator's quasi-focus on a farm rotating around the center of curvature of the concentrator. A turbine with an electric generator is installed in the center of the sphere or at the top of the support tower, or on the surface of the earth at the base of the tower and at the same time is connected to the heat exchanger by a flexible or articulated pipeline. The stationary spherical concentrator is made in the form of a cut from the hemisphere with an aperture angle of 150 ° in the plane of the local meridian (Russian patent 2034204 from 1995, MKI F 24 J 2/10).
A solar plant with a hyperfocal tracking solar collector is known, the reflecting surface of which is located above the earth's surface and mounted on a mobile supporting structure that allows tracking the visible movement of the Sun. The tracking system allows you to constantly keep the focal line in a horizontal position. In the focal zone of the collector an elongated receiver of solar radiation is installed, which converts it into heat. The elongate housing can be rotated about its longitudinal axis. The thermal insulation layer is fixed on the receiver body to reduce heat losses to the environment. The concentrated flux of solar radiation enters the receiver cavity through the downward aperture of the receiver, the receiver is equipped with an equalizing system that keeps it in a horizontal position and provides orientation down the aperture of the receiver during current movements of the reflective surface (US Patent No. 5,353,637 of 1993, NCI 126/696).
A solar plant with a parabolic reflector consisting of separate cells located on a polygonal frame is known. The receiver in the focal region of the reflector has a body formed by an outer elongated tubular casing with closed end portions. The outer surface of the receiver body in cross section has the shape of a polygon, similar to the individual cells of the reflector. Inside the casing, a coil is mounted, through which the heated water circulates. When passing through the coil, the water heats up and evaporates. The cavity of the receiver casing is filled with a heat transfer medium, by means of which the heat from the casing walls is transferred to the coil (US Pat. No. 4,599,995 from 1986, NCI 126/438).
The closest analogue adopted for the prototype is the solar power plant, intended primarily for transport systems, containing a mounted helio-concentrator mounted on the frame with a reflector having a cylindrical parabolic shape of the envelope surface, the focus of which is the energy block associated with the energy consumption zone and the support-rotary platform . The support-swivel platform has a pivot drive around the axis for horizontal tracking of the Sun. The power unit includes a steam boiler installed in the focus of the mirror and connected through a piping system to the vehicle's energy consumption zone. The solar system is controlled by an electronic system for monitoring the position of the Sun (Russian patent 1774137 of 1992, MKI F 24 J 2/38).
The drawback of all the analogues described above, including the prototype, is the limited use of their energy capabilities, expressed in the fact that in the process of work only a part of the generated energy is taken from them.
The object of the present invention is to increase the efficiency of the device and to improve the thermodynamic parameters of the solar concentrator.
This problem is solved by the fact that the solar energy installation contains a helio-concentrator mounted on the frame with a reflector having a cylindrical parabolic shape of the envelope surface, in the focus of which the energy block associated with the energy consumption zone and the support-rotary platform are located. The power unit and the cylinder-parabolic reflector are hermetically sealed with an aerodynamic fairing. The power unit is equipped with a heat pipe filled with a working fluid of the heat carrier with a tunnel-type light-receiving mirror trap mounted in it and a block of electricity generating emitter collectors. In the energy consumption zone, a heat radiator, a heat accumulator and an electric power battery connected to a block of emitter-collectors are mounted. The heat pipe is connected to the heat radiator by a closed transport channel for the working fluid, which forms the internal coolant supply system. The solar power plant is additionally equipped with a convective forced air exchange system, made in the form of a closed path connecting the air volume, limited by a reflector and an aerodynamic fairing, to a heat accumulator.
The heat radiator can be made in the form of a coil. The light receiving mirror trap of the tunnel type is made with wedge-shaped mirror walls covered from the outside by thermal insulation. The light receiving mirror trap is additionally equipped with a ballast inductor-radiator of heat. The convective forced air exchange system can be equipped with a fan mounted at the outlet of the aerodynamic fairing with the possibility of forcing heated air into the energy consumption zone. In the light receiving mirror trap built in an electric heater, installed with the ability to work in a joint thermodynamic cycle with a ballast inductor-emitter. The heat accumulator is provided with a two-circuit coolant system with the possibility of air heat transfer from the internal coolant supply system to the external domestic coolant circuit of the energy consumption zone. The envelope surface of the reflector is formed by a lattice frame, over which a reflective mirror film is stretched from the curved outer side, installed with the help of lamellas and tension screws and protected from the outside by glass-cloth coating. The light receiving trap, the heat pipe, the internal coolant supply system and the convective forced air exchange system are covered with thermal insulation. The mirror film can be made of lavsan, and the fairing is made of polycarbonate panels. The frame of the support-rotary platform is designed horizontally on the corner and the azimuthal angle of the single axis of rotation of the reflector, collinear in the installation of the installation on the North Star.
A comparative analysis of the claimed invention with a prototype shows that it is distinguished by the fact that the power unit and the cylinder-parabolic reflector are hermetically sealed by an aerodynamic fairing. The power unit is equipped with a heat pipe filled with a working fluid of the heat carrier with a tunnel-type light-receiving mirror trap mounted in it and a block of electricity generating emitter collectors. In the energy consumption zone, a heat radiator, a heat accumulator and an electric power battery connected to a block of emitter-collectors are mounted. The heat pipe is connected to the heat radiator by a closed transport channel for the working fluid, which forms the internal coolant supply system.
The solar power plant is additionally equipped with a convective forced air exchange system, made in the form of a closed path connecting the air volume, limited by a reflector and an aerodynamic fairing, to a heat accumulator. The heat radiator can be made in the form of a coil. The light receiving mirror trap of the tunnel type is made with wedge-shaped mirror walls covered from the outside by thermal insulation. The light receiving mirror trap is additionally equipped with a ballast inductor-radiator of heat. The convective forced air exchange system can be equipped with a fan mounted at the outlet of the aerodynamic fairing with the possibility of forcing heated air into the energy consumption zone. In the light receiving mirror trap built in an electric heater, installed with the ability to work in a joint thermodynamic cycle with a ballast inductor-emitter. The heat accumulator is provided with a two-circuit coolant system with the possibility of air heat transfer from the internal coolant supply system to the external domestic coolant circuit of the energy consumption zone. The envelope surface of the reflector is formed by a lattice frame, over which a reflective mirror film is stretched from the curved outer side, installed with the help of lamellas and tension screws and protected from the outside by glass-cloth coating. The light receiving trap, the heat pipe, the internal coolant supply system and the convective forced air exchange system are covered with thermal insulation. The mirror film can be made of lavsan, and the fairing is made of polycarbonate panels. The frame of the support-rotary platform is designed horizontally on the corner and the azimuthal angle of the single axis of rotation of the reflector, collinear in the installation of the installation on the North Star.
The analysis shows the presence of novelty in the claimed device.
A comparison of the proposed solar power plant with other known technical solutions of the same purpose shows that in this installation there are essentially three independent energy removal systems: the generation of electricity from the collector emitters, the generation of thermal energy by forced convection of the air medium heated in a closed Space under the aerodynamic fairing, and the transfer of heat energy to the zone of consumption by a heated working body enclosed in a closed system for the internal supply of the coolant. The efficiency of the installation is also enhanced by the use of heat and electricity accumulators that allow to store solar heat in the heat-consuming period (in summer) and use it in the heat-deficient period (in winter) due to the constructive execution of the light receiving trap providing maximum selection of solar energy entering the aperture area Mirrors, by installing an electric heater and an additional local ballast inductor-radiator of heat in the light receiving trap, and by using a mirror lavsan film with devices that regulate its tension, which minimizes diffraction of light at its microroughnesses and associated blurring and Defocusing of the light spot on the surface of the heat pipe and the input aperture of the light receiving trap.
This comparison indicates an excess of the state of the art claimed by the claimed invention and the solution with its aid of the assigned task.
The invention is explained with an example of its implementation. The drawings show:
 |
 |
 | |
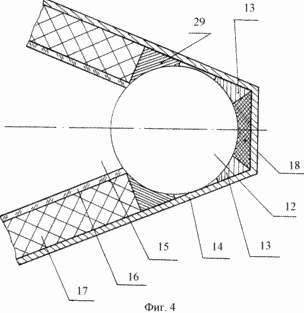 |
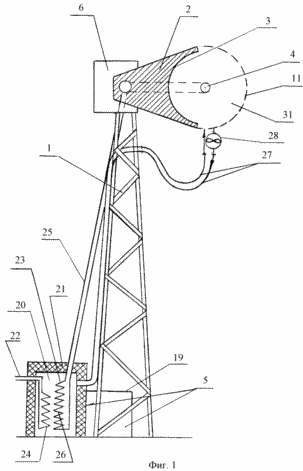
FIG. 1 shows a general view of an installation; FIG. |
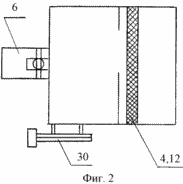
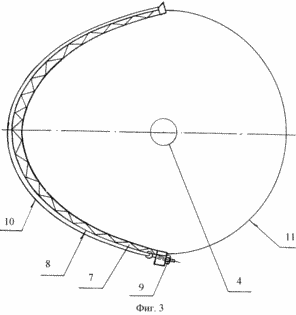
The solar energy plant contains a helio-concentrator 2 mounted on the frame 1 with a reflector 3 having a cylindrical parabolic shape of the enveloping surface in the focus of which an energy block 4 connected to the energy consumption zone 5 and a support-rotary platform 6 are arranged. The frame 1 is made in the form of a tower. The envelope surface of the reflector is formed by a grill frame 7, over which a reflective mirror film 8 made of lavsan, installed by means of lamellas and tension screws 9, and which is protected from the outside by the glass-cloth coating 10, is stretched from the curved outer side, and an aerodynamic fairing 11 is mounted on the opposite side of the grid frame, Made in the form of a cap of polycarbonate panels covering the power unit 4. The power unit comprises a heat pipe 12 with a block of emitter collectors 13 installed in the chamber 14 provided with a light receiving mirror trap 15 of tunnel type. The light receiving mirror trap is provided with wedge-shaped mirror walls 16 covered from outside by thermal insulation 17. Inside the bottom of the chamber of the emitter-collector unit there is a ballast inductor-radiator of heat 18. Outside the helio-concentrator there is an energy consumption zone 5, which includes an accumulator of electric energy 19, Consisting of a heat collector made in the form of a heat accumulator 20 placed in a heat-insulated chamber 21 and a secondary energy consumption circuit 22. The heat accumulator is provided with a two-circuit coolant system 23 and 24.
The first circuit 23 forms an internal coolant supply system consisting of a channel 25 filled with a working heat carrier and connecting the heat pipe 12 to a heat radiator 26 located in a heat storage and configured as a coil and the second circuit 24 is filled with a domestic heat carrier. Both circuits are located taking into account the possibility of air transfer of heat from one circuit to another. The air volume limited by the reflector and the aerodynamic fairing and the energy consumption zone are united by a convective forced air exchange system 27 equipped with a fan 28 mounted at the outlet of the aerodynamic fairing with the possibility of forcing heated air into the energy consumption zone. The light receiving trap 15, the heat pipe 12, the passage of the working heat carrier 25 and the convective heat exchange system 27 are covered by thermal insulation (not shown). An electric heater 29 is installed in the light receiving mirror trap 15, which is arranged to operate in a joint thermodynamic cycle with a ballast heat inducer-radiator 18.
HELIOTERGETICHESKAYA INSTALLATION WORKS AS FOLLOWING
Due to the fact that the frame 1 of the support-rotary platform 6 of the solar power plant is designed horizontally on a corner-by-corner ![]() And the azimuth angle
And the azimuth angle ![]() A single axis of rotation of the reflector, collinearly directed during installation of the installation on the Polar star, the process of controlling the installation for orienting it to the Sun is considerably simplified: for the formation of the azimuthal and angle turns of the reflector, 3 the command enters the turn mechanism (not shown) from the tracking devices 30 and the automatic guidance system in the sun. Находящийся в фокусе зеркала рефлектора 3 энергетический блок 4 установлен таким образом, чтобы световое пятно создавало на его облучаемой поверхности (на поверхности тепловой трубы и эмиттеров-коллекторов) плотность энергии солнечного излучения на единицу площади поверхности энергетического блока, необходимую для перевода рабочего тела тепловой трубы в парообразное состояние. Для уплотнения светового потока до величины, обеспечивающей необходимую температуру на светоприемной зеркальной ловушке 15 для преобразования термоэмиссионной энергии в электрический ток, зеркала 16 ловушки установлены таким образом, что образуют клиновидный тоннель, "загоняющий" солнечные лучи "в угол", заканчивающийся тепловой трубой и блоком эмиттеров-коллекторов 13, на которых концентрируется поток световой энергии. Плотность этого потока составляет около 15 Вт/см 2 . Выработанная блоком эмиттеров-коллекторов электроэнергия поступает частично потребителю, а частично на аккумулятор 19. Основная часть тепловой энергии поступает в зону энергопотребления 5 с рабочим теплоносителем, находящимся в канале 25 и змеевике 26, входящим во внутренний контур 23 теплоносителя. Кроме того, воздух, находящийся внутри воздушного объема 31, ограниченного аэродинамическим обтекателем 11 и рефлектором 3, нагревается вследствие контакта с тепловой трубой 12 и направляется по конвективной системе теплообмена 27 в зону энергопотребления 5. Поступившая от теплоносителя по каналу 25 и по конвективной системе теплообмена 27 тепловая энергия частично поглощается аккумулятором тепла 20, частично передается воздушным путем на внешний контур 24 бытового теплоносителя.
A single axis of rotation of the reflector, collinearly directed during installation of the installation on the Polar star, the process of controlling the installation for orienting it to the Sun is considerably simplified: for the formation of the azimuthal and angle turns of the reflector, 3 the command enters the turn mechanism (not shown) from the tracking devices 30 and the automatic guidance system in the sun. Находящийся в фокусе зеркала рефлектора 3 энергетический блок 4 установлен таким образом, чтобы световое пятно создавало на его облучаемой поверхности (на поверхности тепловой трубы и эмиттеров-коллекторов) плотность энергии солнечного излучения на единицу площади поверхности энергетического блока, необходимую для перевода рабочего тела тепловой трубы в парообразное состояние. Для уплотнения светового потока до величины, обеспечивающей необходимую температуру на светоприемной зеркальной ловушке 15 для преобразования термоэмиссионной энергии в электрический ток, зеркала 16 ловушки установлены таким образом, что образуют клиновидный тоннель, "загоняющий" солнечные лучи "в угол", заканчивающийся тепловой трубой и блоком эмиттеров-коллекторов 13, на которых концентрируется поток световой энергии. Плотность этого потока составляет около 15 Вт/см 2 . Выработанная блоком эмиттеров-коллекторов электроэнергия поступает частично потребителю, а частично на аккумулятор 19. Основная часть тепловой энергии поступает в зону энергопотребления 5 с рабочим теплоносителем, находящимся в канале 25 и змеевике 26, входящим во внутренний контур 23 теплоносителя. Кроме того, воздух, находящийся внутри воздушного объема 31, ограниченного аэродинамическим обтекателем 11 и рефлектором 3, нагревается вследствие контакта с тепловой трубой 12 и направляется по конвективной системе теплообмена 27 в зону энергопотребления 5. Поступившая от теплоносителя по каналу 25 и по конвективной системе теплообмена 27 тепловая энергия частично поглощается аккумулятором тепла 20, частично передается воздушным путем на внешний контур 24 бытового теплоносителя.
Интенсификации этого процесса содействует вентилятор 28, установленный на конвективной системе теплообмена 27. Охлажденный теплоноситель возвращается по каналу 25 в тепловую трубу, а воздух - по конвективной системе теплообмена 27 в воздушный объем 31.
При отсутствии солнца бесперебойная работа блока эмиттеров-коллекторов обеспечивается балластным индуктором-излучателем тепла 18. Для обеспечения многосуточной бесперебойной работы устройства высокотемпературный подогрев блока эмиттеров-коллекторов осуществляется электронагревателем 29, работающим в совместном термодинамическом цикле с балластным индуктором-излучателем тепла 18.
CLAIM
1. Гелиоэнергетическая установка, содержащая смонтированный на раме гелиоконцентратор с рефлектором, имеющим цилиндропараболическую форму огибающей поверхности, в фокусе которого размещен энергетический блок, связанный с зоной энергопотребления, и опорно-поворотную платформу, отличающаяся тем, что энергетический блок и цилиндропараболический рефлектор герметично укрыты аэродинамическим обтекателем, при этом энергетический блок снабжен заполненной рабочим телом теплоносителя тепловой трубой со смонтированной в ней светоприемной зеркальной ловушкой тоннельного типа и блоком вырабатывающих электроэнергию эмиттеров-коллекторов, а в зоне энергопотребления смонтированы теплоизлучатель, аккумулятор тепла и аккумулятор электроэнергии, связанный с блоком эмиттеров-коллекторов, причем тепловая труба соединена с теплоизлучателем замкнутым каналом транспортировки рабочего тела, образующим внутреннюю систему подачи теплоносителя.
2. Гелиоэнергетическая установка по п.1, отличающаяся тем, что она дополнительно снабжена конвективной системой принудительного воздухообмена, выполненной в виде замкнутого тракта, соединяющего воздушный объем, ограниченный рефлектором и аэродинамическим обтекателем, с аккумулятором тепла.
3. Гелиоэнергетическая установка по п.1, отличающаяся тем, что теплоизлучатель выполнен в виде змеевика.
4. Гелиоэнергетическая установка по п.1, отличающаяся тем, что светоприемная зеркальная ловушка тоннельного типа выполнена с клиновидно расположенными зеркальными стенками, укрытыми снаружи теплоизоляцией.
5. Гелиоэнергетическая установка по п.1, отличающаяся тем, что в светоприемную зеркальную ловушку дополнительно встроен балластный индуктор-излучатель тепла.
6. Гелиоэнергетическая установка по п.2, отличающаяся тем, что конвективная система принудительного воздухообмена снабжена вентилятором, смонтированным на выходе аэродинамического обтекателя с возможностью нагнетания нагретого воздуха в зону энергопотребления.
7. Гелиоэнергетическая установка по п.1 или 5, отличающаяся тем, что в светоприемную зеркальную ловушку встроен электронагреватель, установленный с возможностью работы в совместном термодинамическом цикле с балластным индуктором-излучателем.
8. Гелиоэнергетическая установка по п.1, отличающаяся тем, что аккумулятор тепла снабжен двухконтурной системой теплоносителя с возможностью воздушной передачи тепла от внутренней системы подачи теплоносителя к внешнему бытовому контуру теплоносителя зоны энергопотребления.
9. Гелиоэнергетическая установка по п.1, отличающаяся тем, что огибающая поверхность рефлектора образована решетчатой рамой, поверх которой с выгнутой наружной стороны натянута светоотражающая зеркальная пленка, установленная при помощи ламелей и натяжных винтов и защищенная снаружи стеклотканевым покрытием.
10. Гелиоэнергетическая установка по п.1, отличающаяся тем, что светоприемная ловушка, тепловая труба, внутренняя система подачи теплоносителя и конвективная система принудительного воздухообмена укрыты теплоизоляцией.
11. Гелиоэнергетическая установка по п.1, отличающаяся тем, что зеркальная пленка выполнена из лавсана.
12. Гелиоэнергетическая установка по п.1, отличающаяся тем, что обтекатель выполнен из поликарбонатных панелей.
13. Гелиоэнергетическая установка по п.1, отличающаяся тем, что рама опорно-поворотной платформы выполнена отгоризонтированной на совмещенной по углу места и азимутальному углу единой оси вращения рефлектора, коллинеально направленной при монтаже установки на Полярную звезду.
print version
Published on February 14, 2007




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.