| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2187017
![]()
SAIL-SHIELD WIND-MOTOR FOR THE WIND
The name of the inventor: Salman Sa'man Saubanovich
The name of the patent holder: Salmanov Salman Saubanovich
Address for correspondence: 350921, Krasnodar, pos. Belozerny, 7, ap. 9, S.S. Salbanov
Date of commencement of the patent: 2001.03.19
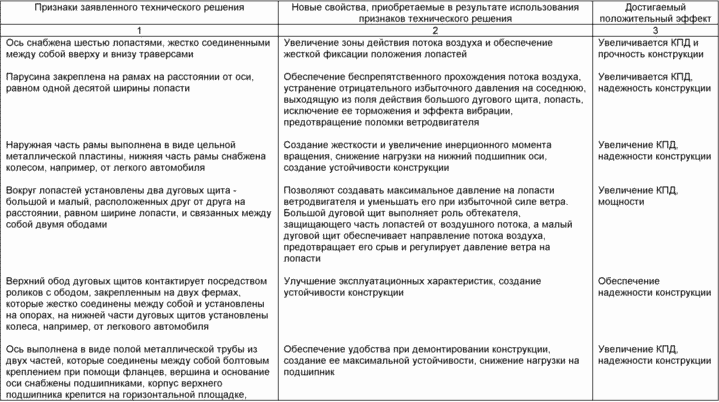
The invention relates to wind energy and can be used in high-power wind power units. The technical result of increasing the efficiency is ensured by the fact that in the sail-shield windmill containing the blades mounted on the vertical axis, made in the form of frames with a canvas stretched on them, according to the invention, the axle is provided with six blades rigidly connected to one another at the top and Below the traverses, the canvas is fixed to the frames at a distance from the axis equal to one-tenth of the width of the blade, the outer part of the frame is made in the form of a solid metal plate, the lower part of the frame is provided with a wheel, for example, from a passenger car, around the blades there are two arc shields - large and small Located at a distance equal to the width of the blade and interconnected by two rims, the upper rim of the arc shields being contacted by rollers with a rim fixed on two trusses which are rigidly connected to each other and mounted on supports on the lower part of the arc shields Wheels are installed, for example, from a car.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to wind energy and can be used in high-power wind power units.
Known wind turbine (application for invention 97102951/06, F 03 D 1/00, published on November 20, 1999), containing a wheel-rotor in the form of a mill water wheel.
The disadvantage of such a windmill is the low efficiency (efficiency), due to incomplete openness of the power elements (blades) and the availability of conditions for creating an internal negative gift on them in the cylinder.
The sail windmill is known (the author of the USSR over 1178931 A, F 03 D 3/00, published on September 15, 1995), containing frames mounted on a vertical axis with stretched backing grids and sail blades on the frames, which are equipped with rectangular windows With valves, accepted by us as a prototype.
The disadvantage of this wind turbine is the low efficiency, which is due to the small number of blades, which significantly affects the rotor's wind intake, because At a certain moment of rotation of the rotor, the width of the effect of wind on the blade will be narrowed, but also by the presence of a vibrational effect (see Fig. 4a).
The object of the invention is to improve the efficiency.
The task is achieved by the fact that in a sail-shield windmill containing the blades mounted on the vertical axis and made in frames with a canvas stretched on them, the axle is provided with six blades rigidly interconnected at the top and below by traverses, the canvas is fixed to the frames at a distance from Axis, equal to one-tenth the width of the blade, the outer part of the frame is made in the form of a solid metal plate, the lower part of the frame is equipped with a wheel, used, for example, from a car; two arc shields are installed around the blades - large and small, Equal to the width of the blade and connected by two rims, the upper rim of the arc shields being contacted by means of rollers with a rim fixed on two trusses which are rigidly connected to each other and mounted on supports, on the lower part of the arc shields there are wheels used, For example from a passenger car, the axle is made in the form of a hollow metal pipe of two parts which are bolted together by means of flanges, the top and the base of the axle are provided with bearings, the upper bearing housing being fixed to a horizontal platform, the ends of which secure the two farms in the middle part , The rollers are attached to the outer perimeter of the rim fixed on the trusses, the wheels of the arc shields interact with a trench executed eccentrically about the axis. Analysis of the distinctive features that create a positive effect is presented in the table.
The proposed sail-shield windmill is illustrated by the drawings shown in FIGS. 1-4.
 |
 |
 |
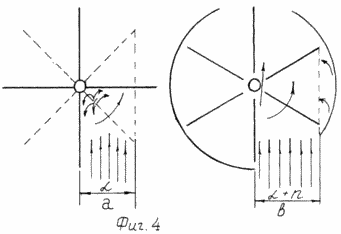 |
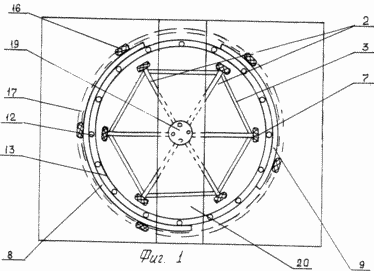
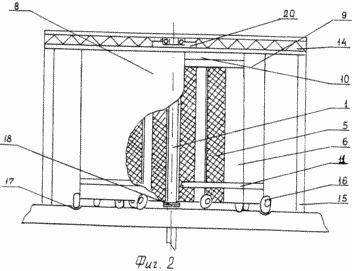
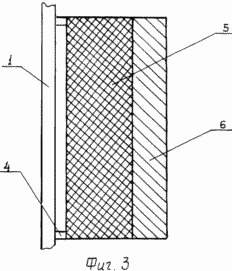
1 shows a sidewall-shield windmill, top view; FIG. 2 is a side view of the same; FIG. 3 shows a blade, a front view; FIG. 4 schematically shows the effect of the air flow on the blade: a - wind turbine - prototype, c - the proposed wind turbine.
The sail-shield windmill contains six blades 2 mounted on the vertical axis 1, rigidly connected to each other above and below the traverses 3. The blades 2 consist of frames 4 stretched on them by a canvas 5 at a distance from the axis 1 equal to one tenth of the width of the blade 2 and the metal Plate 6. The lower parts of the frames 4 are provided with wheels 7. Around the blades 2 are installed two arc shields - a large 8 and a small 9, located from each other at a distance equal to the width of the blade 2. Between each other, the arc shields 8 and 9 are connected by rims 10 and 11. The upper rim 10 of the arc shields 8 and 9 is contacted by means of rollers 12 with a rim 13 which is fixed on two trusses 14 rigidly connected to each other and mounted on the supports 15. The rollers 12 are fastened along the outer circumference of the rim 13. On the lower part of the arc shields 8 and 9 Wheels 16 are installed which cooperate with a groove 17 which is eccentric with respect to the axis 1. The axis 1 is made in the form of a hollow metal tube of two parts which are connected together by bolt fastening with the help of flanges 18. The apex and the base of the axis 1 are provided with bearings 19, Of the upper bearing 19 is fixed to a horizontal platform 20, the ends of which secure the two trusses 14 in the middle part.
The sail-shield wind turbine is operated as follows
When the working wind speed appears, the operator installs the arc shields 8 and 9 by moving them through the wheels 16 along the chute 17 and the rollers 12 installed between the rims 10 and 13 to the position of maximum air flow by the blades 2.
The wind affects the entire working part of the blade 2, the canvas 5 is stretched, creating a torque, and the solid metal plate 6 increases the inertial moment of rotation of the blades 2.
The distance between the axis 1 and the canvas 5 of the blade 2 ensures an unimpeded flow of air, eliminates the negative overpressure to the adjacent blade leaving the large arc shield 8, and thereby eliminates its braking and the vibration effect (Fig. 4b).
In this case, the large arc shield 8 serves as a fairing protecting part of the blades 2 from the effect of the air flow, and the small arc shield 9 prevents the air flow from stalling, provides its direction and regulates the pressure on the blade 2.
If the wind force exceeds the required pressure on the blades 2 of the windmill, the arc shields 8 and 9 are displaced towards the open blades 2 for blasting, thereby reducing the pressure on them; A small arc shield 9 does not prevent the flow of air from blasting out of the field of action of the large arc shield 8.
The proposed technical solution makes it possible to design wind turbines that reach a height of 10-12 m and a sail area of more than 50 m 2 , which makes it possible to use it in wind power units of high power.
To prevent negative environmental factors, it is proposed to install a canopy on farms 14.
 |
 |
CLAIM
1. A sail-shield wind turbine, comprising blades mounted on the vertical axis, made in the form of frames with a canvas stretched on them, characterized in that the axis is provided with six blades rigidly interconnected at the top and below by traverses; the canvas is fixed to the frames at a distance from the axis , Equal to one-tenth of the width of the blade, the outer part of the frame is made in the form of a solid metal plate, the lower part of the frame is provided with a wheel, for example, from a passenger car; around the blades there are two arc shields - large and small, located at a distance equal to the width of the blade , And interconnected by two rims, the upper rim of the arc shields being contacted by means of rollers with a rim fixed on two trusses which are rigidly connected to one another and mounted on supports; on the lower part of the arc shields, wheels are mounted, for example, from a passenger car.
2. The wind turbine according to claim 1, characterized in that the axis is made in the form of a hollow metal pipe of two parts which are connected together by bolt fastening by means of flanges, the top and the base of the shaft are equipped with bearings, the upper bearing housing is fixed to a horizontal platform, the ends of which Fasten two farms in the middle.
3. The wind turbine according to claim 1, characterized in that the rollers are attached to the outer perimeter of the rim fixed on the trusses.
4. The wind turbine according to claim 1, characterized in that the wheels of the arc shields cooperate with a groove made eccentrically about the axis.
print version
Publication date 31.01.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.