| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2193688
![]()
Wind turbines for wind turbines
Name of the inventor: VG Eleskin .; Lapochkin YV .; Skulevich AN .; Starodumov MI
The name of the patentee: Eleskin Vitaly; Lapochkin Yuri; Skulevich Alexander; Mikhail Starodumov
Address for correspondence: 103009, Moscow, p / 184, for the PPF "JUS" pat.pov. S.M.Kochemazovu, reg. number 748
Starting date of the patent: 2001.09.19
The invention relates to power engineering, in particular to wind turbines, and may be used to create a wind turbine with a rotation axis perpendicular to the wind direction. The technical result consists in enabling the blades rotate to a position with the greatest aerodynamic blade with an optimum angle of attack, reducing the load on the blade rotation mechanism and improving the stability of impeller rotation speed provided by the fact that a wind turbine comprising an impeller with a vertical axis rotation, which are mounted for rotation about a vertical axis blades having individual rotation mechanism configured as a wind vane, kinematically coupled with the pivot blade according to the invention the upper end of each blade configured to variations in the blade plane symmetrically about a vertical axis by a distance not a V / 5.27, wherein B - maximum blade width.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to wind power, and in particular to Orthogonal wind turbine with blades having a vertical axis of rotation.
Known wind turbine comprising mounted on a vertical shaft rotor with upper and lower needles between which at their ends are placed rotary balancer blade shafts which via discharge sleeves associated chain drive (transmission ratio 1: 2) with the common vane (SU 1483081 A1, F 03 D 3/02, 30.05.1989). Performing rotary blades optimally orient them in the process, which ensures optimum aerodynamics of the blades when moving upstream against the wind. In this case it is possible to adjust the load on the engine blades. However, the overall mechanism of rotation of the blades, which is a chain drive connecting each vane blade is complicated, which reduces the reliability of the device. In addition, the chain drive may not be tough enough, which causes an increased level of self-oscillation and reduced vibration resistance throughout the elastic structure, which in turn is the cause of sudden failures and self-protection and low efficiency of a wind turbine from the strong winds.
Known wind power plant with the axis of rotation intersects the direction of the wind, comprising a rotor with blades, mounted at an angle of 42 ÷ 55 degrees to the axis of rotation of the rotor (RU 2099589 C1, F 03 D 3/00, 20.12.1997). This unit is provided with the possibility of simultaneous deflection of all the blades on their lower bearings under centrifugal forces. This solution provides an increase in the moment of inertia of the rotor blades by increasing the rotation speed. This provides protection from electric overload.
The closest in technical substance and the result achieved to the described invention is a wind turbine comprising a rotor with a vertical axis of rotation, which are mounted for rotation about a vertical axis blades having individual rotation mechanism configured as a wind vane, kinematically connected to the axis of rotation of the blade ( RU 2119094 C1, F 03 D 7/06, 20.09.1998). Purchasing Each rotary blade separate turning mechanism allows to increase the power of the wind turbine, increases the reliability of the device with an overall simplification of the structure and reduction of metal. However, work on the rotation of the blade from the position with the greatest air resistance when the blades coincides with the plane of the impeller radius was accomplished solely by the rotation mechanism and weathervanes. As a result, blade turning mechanism in the loaded mode operates as a weather vane blades increases resistance, which reduces the resource and reliability.
The present invention is the development and creation of wind turbine having improved performance in the wind.
As a result of solving this problem it is possible to obtain a technical result consisting in the fact that it is possible to rotate the blade to the position with the greatest aerodynamic blades with the optimal angle of attack by the centrifugal force, biasing the top of the blades relative to the axis of symmetry at the time of matching blades plane with the direction of the radius impeller reduces the load on the blade rotation mechanism, but also increases the stability of impeller rotation speed.
These technical results are achieved in that the wind turbine comprising an impeller with a vertical axis of rotation, which are mounted for rotation about a vertical axis blades having individual rotation mechanism configured as a wind vane, kinematically coupled with the pivot blade, the upper end of each blade adapted to variations in the blade plane symmetrically about a vertical axis by a distance not more than B / 5.27, wherein B - maximum blade width.
A distinctive feature of the present invention is that the upper end of each blade configured to variations in the blade plane symmetrically relative to the vertical axis. This reduces the area of the blade that interacts with the flow of wind on the windward side and the leeward blade increases and becomes a function of wind vane, which in turn considerably relieves the vane itself. It was established experimentally that the deviation of the upper end of the blade in the cavity of the blades relative to the vertical axis should not exceed B / 5.27, because otherwise substantially increased resistance to air flow, and due to asymmetry in the deflection of the upper end of the blade wind turbine efficiency is sharply reduced, ie, . newly acquired properties weathervanes sail will endeavor to keep the sail along the flow of the wind, and the wind vane will be unable to resist the flow of air and control the sail.
The vanes may be shaped as a rectangle or an oval, or any shape having a vertical symmetry axis.
Advantageously each vane kinematically connected to the blade pivot via unloading mechanism, which can be formed as a safety clutch.
 |
 |
 |
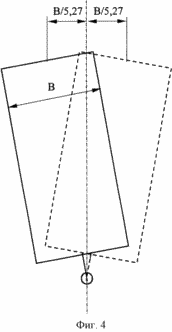 |
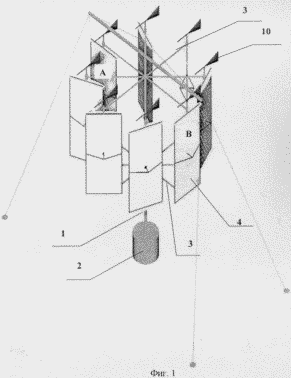
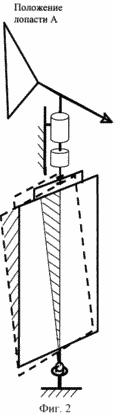
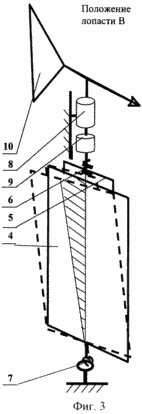
1 is a perspective view of wind turbine, Figure 2 schematically illustrates a blade in position most of the time (position A in Figure 1) drag the wind flow, Figure 3 schematically shows the position of the blade at the moment the smallest (position B in FIG. 1) drag the wind flow, and a balancing blade assembly, and Figure 4 shows in plan the blade deflection in its plane about a vertical axis.
It comprises a wind turbine mounted on a vertical support shaft 1 with the impeller 2 comprising the upper and lower spokes 3, which are placed at the ends of the vane 4 having the upper and lower supports. The blades are made around the vertical rotary axis extending through the blade support.
Construction of the blades may be different Bat. The upper ends of the blades 4 are arranged to reciprocate in the blade planes. Obviously, in this case four blades themselves perform reciprocating oscillating movement in their planes with respect to the vertical axis. Reciprocating the upper ends of the blades 4 are made via nodes schematically shown in Figure 2, which is provided with each blade 4.
You can offer a great variety of such structural units. Each node can represent, for example, the guide runner 5 and 6. Each runner 5 is rigidly connected to the frame and its blades it is in the same plane, as shown in Figure 3. The guide covers 6 runner 5 and the runner can make it back and forth movement. Thus, every runner and guide kinematic form a prismatic pair.
To ensure the reciprocating rocking motion of the lower blade support 4 must have three degrees of freedom of angular and can be performed, for example, in the form of ball bearings 7.
Turning mechanism comprises a wind turbine blade 8 made, for example, a gear with a transmission ratio 1 ÷ 2 and unloading mechanism 9 blades 4 made, for example, a safety clutch. As discussed above, each blade has its own autonomous mechanism 8 turns. Essentially turning mechanism controls the angle of attack of the blade.
The mechanism of rotation of the blade vane 10 contains, cinematically connected to the axis of rotation of the blade.
Advantageously, the kinematic relationship weather vane with a blade pivot had a ratio of 1: 2, thus providing a single blade turn on two turns a weather vane. Vane 10 always occupy the angular position at which the aerodynamic drag of wind vane wind flow is minimal. Due to the kinematic connection with the vane as a result of rotation of the impeller, each blade is rotated about a vertical axis, this is automatically set angle of attack, i.e. blade so oriented in the direction of the wind that provided the best wind turbine aerodynamics. Gear ratio 1: 2 allows the blades to perform only half a turn of a full rotation of the impeller, ie, full duty cycle the blade makes for half of its turnover.
Wind turbine works as follows
Fitting assembly is performed, connect the generator (not shown) via a transmission (not shown) to the shaft of the impeller 1.
installation work begins with the appearance of the wind flow, informing the impeller total torque greater than the friction torque in the bearings and the drag torque in the generator.
Under the action of wind, each vane 10, turning his blade sets 4 to the required angle of attack. The blade 4 of the wind flow affects the spokes 3 and generates a torque on the impeller causing it to rotate.
As a result of rotation of the impeller blades on the centrifugal force. At the moment when the blade plane coincides with the radius of the impeller (position A in Figure 1) has the largest blade aerodynamic resistance. Consequently, the upper end of the blade in the blade begins to plane deviates about its vertical axis at a distance equal to not more than B / 5.27, in the direction of the centrifugal force by rotating the blade relative to the support 7, as shown in Figure 3. It should be noted that at this point the blade about the vertical pivot axis is located symmetrically. blade rotation axis remains the same as it passes through the lower bearing 7, which has not changed its position. Due to the asymmetry arises space equal to twice the area of the shaded triangle, with respect to the axis of rotation of the blade on the blade there is a torque tending to rotate the blade to a position with the least air resistance. towards the air flow when the vane and vane arranged parallel to itself when moving blade mounted in the blade position, in which the minimum resistance to air flow. Thus, the rotation of the impeller blade rotates under the influence of the moment arising due to the asymmetry of the blade pivot axis relative to the area, reducing its wind resistance.
At the same time caused the blade rotation is transferred to a weather vane, which rotates in the same direction as that of the blade, exposing its plane of the wind flow, with the result that at the moment the weather vane shaft is formed, counteracting and balancing point of the blade rotation. At the same time the wind vane turn, must not be less than the time of rotation of the blade. This condition is ensured by the choice of the corresponding area of the wind vane size. With gusts of wind or gale-force winds triggered unloading mechanism and the blade covers, turning the position close to the vane by reducing the angle of attack, and the weather vane and occupies the position with the minimum angle of attack. As a result, the blade edge is rotated into the wind, which does not allow wind turbines to increase the number of revolutions of the impeller, stabilizing the impeller speed. Further successively blade passes the position with the smallest aerodynamic resistance (position B in Figure 1) by moving towards the air flow vane and blade are arranged in parallel with the minimum resistance to air flow and again approaches the position A with the greatest air resistance. By this time, the impeller has made a complete revolution. However, because the gear ratio of the rotation mechanism of the blade 1: 2, the blade turned only 180 degrees. In the next moment of coincidence with the plane of the blade radius of the impeller by centrifugal force the upper end of the blade moves in the direction of the centrifugal force by deflecting the blade, as shown in Figure 3, ie repeats the process described above.
Thus, in one turn of the impeller blade makes rocking deviation once, ie, Oscillation frequency reciprocating blade deviations from the vertical axis in the plane of the blade is equal to the frequency of rotation of the impeller.
Since all blades are identical, it is obvious that all the blades are deflected as the impeller rotates alternately as described above. At the same time in a single impeller turn each blade is rejected once.
CLAIM
1. The wind turbine comprising a rotor with a vertical axis of rotation, which are rotatably mounted around a vertical axis blades having individual rotation mechanism configured as a wind vane, kinematically connected to the blade pivot axis, characterized in that the upper end of each blade is arranged possibility of variation in the plane of the blade is symmetrical about a vertical axis at a distance of not more than B / 5.27, wherein B - maximum blade width.
2. The wind turbine of claim. 1, characterized in that each vane is kinematically connected to the blade pivot via unloading mechanism.
3. The wind turbine of claim. 2, characterized in that the discharge mechanism is designed as a safety clutch.
print version
Publication date 31.01.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.