| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2211947
![]()
Wind turbine for wind turbine
The name of the inventor: Chudikov NN; Head G.A.
The name of the patent holder: Pyatigorsk State Pharmaceutical Academy
Address for correspondence: 357533, Stavropol Territory, Pyatigorsk, Kalinin Ave., 11, PyatGFA, Pat. Department
Date of commencement of the patent: 2001.12.17
The invention relates to the field of wind power, in particular to wind turbines with a vertical shaft. The technical result, consisting in increasing the power and efficiency of the wind turbine, is provided by the fact that in a windmill consisting of a vertically arranged shaft and two rectangular blades capable of rotating about their axes parallel to the axis of the shaft with an angular velocity half the angular velocity Of the rotation of the shaft, and in the direction opposite to the rotation of the shaft, according to the invention, each blade has two identical flaps on the sides that can be rotationally rotated about axes parallel to the axis of rotation of the blade, preferably at an angle of + 30 ° relative to the plane of the blade under the action of a kinematically connected flaps through the connecting rods Eccentric attached to the carrier coaxially with the axis of rotation of the blade with an eccentricity directed along the carrier.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of wind power, in particular to wind turbines with a vertical shaft.
Wind turbines with a vertical shaft are known: EP 0003590 dated 01.09.1978, German patent 3534997 A-1 dated 01.10.1985, these wind turbines have bulky construction and small efficiency.
Wind turbine is also known according to RF patent 2164624 from 27.03.01. Such a wind turbine, having significant efficiency and being economically expedient, has insufficiently high efficiency.
The object of the present invention is to increase the power and efficiency of the wind turbine.
This goal is achieved by the fact that each blade of the windmill has two identical flaps on the sides that are able to rotate about the axes parallel to the axis of rotation of the blade at an angle of preferably + 30 ° relative to the plane of the blade under the action of an eccentric camshaft connected to the flaps via the connecting rods fixed to the carrier coaxially Axis of the blade with an eccentricity directed along the carrier and at both ends of the blade and flaps perpendicular to the axis of the blade plates are fixed, the total width of the blade together with the flaps greater than twice the distance from the edge of the shaft to the axis of rotation of the blade and is preferably the width of the five flaps.
 |
 |
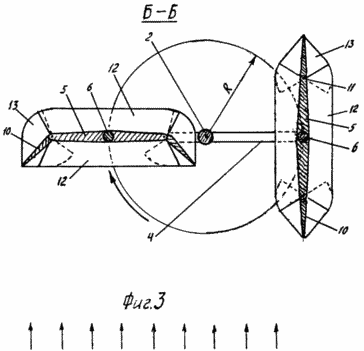 |
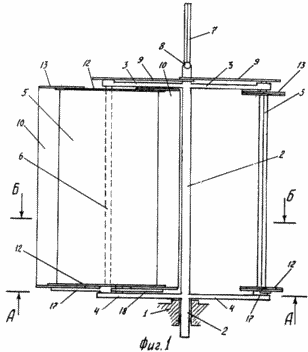
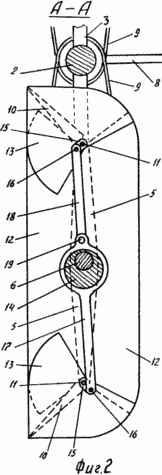
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The essence of the invention is illustrated in the drawing, in which FIG. 1 shows a wind turbine, a front view; 2 is a section AA; FIG. 3 shows a section B-B. FIG. This two-bladed windmill consists of a shaft 2, vertically disposed in the support 1, with carriers 3 and 4 fixed to it, at the ends of which two rectangular blades 5 are mounted, capable of rotating about their axes 6 (FIG. 1) parallel to the axis of the shaft, Half the angular velocity of rotation of the shaft, and in the direction opposite to the rotation of the shaft. The blades are kinematically connected to the wind vane 7 through the drawbar 8 and the chain gear 9. On each side of the blade there are two identical flaps 10 that can simultaneously rotate about their axes 11 parallel to the axis of rotation of the blade on both sides of the blade, Angle ± 30 o . At both ends (top and bottom) of the blade and flaps, plates 12 and 13 are fixed in a position perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the blade. The eccentrics 14 are fixed to the axes of the blades axially on the axes of the blades, with an eccentricity directed along the drivers, and the axes of the blades pass through the eccentrics. On the flaps, and fixed levers 15, which are connected by axes 16 with connecting rods 17 and 18, sitting on eccentrics (Fig. 2). The connecting rod 18 is suspended and connected to the connecting rod 17 by the axis 19. This connection of the flaps with the eccentric is possible on both sides (bottom and top) of the blade. The total width of the blade together with the flaps is more than twice the distance from the edge of the shaft to the axis of rotation of the blade and is preferably equal to the width of the five flaps. |
Wind turbine works as follows. In the presence of wind, as shown by arrows (Figure 3), the weather vane 7 is rotated through the blade chain 9 into the working position to the wind (Figures 1 and 3). Under the influence of wind on the blade, the windmill will rotate. At the beginning of the turn, when the blade is perpendicular to the wind, it assumes a cup-shaped shape formed by the plates 12 and 13 and deflected against the wind by flaps due to the eccentric and connecting rods. With further rotation of the windmill, the depth of the blade bowl decreases, and when the windmill is rotated by 180 °, the flap planes coincide with the plane of the blade, taking a streamlined shape (FIG. 3). With each turn of the windmill, the blades rotate to the wind with the other side, so the flaps are always deflected towards the wind. Thus, taking a cup-like shape, the blade perceives itself and transmits to the shaft not only the force of a direct wind blow, but also the additional pressure it creates inside the bowl on its walls. And in other positions, the flap with flaps, possessing sail, is capable of catching most of the wind energy and transferring to the shaft more power. Thus, this wind turbine catches most of the wind energy, which increases its power and efficiency. When three such blades are used, the power and efficiency of such a wind turbine is further increased.
An essential feature of the present invention is that the blades have flaps kinematically connected via connecting rods with eccentrics attached to the carriers, and plates are fixed at the ends of the blades and flaps.
The advantage of the proposed design is a significant increase in power and efficiency of the wind turbine.
CLAIM
1. A wind turbine consisting of a vertically disposed shaft and two rectangular blades capable of rotating about their axes parallel to the axis of the shaft, with an angular velocity half the angular velocity of rotation of the shaft, and in the direction opposite to the rotation of the shaft, characterized in that each The blade has two identical flaps on the sides that are able to rotate about the axes parallel to the rotation axis of the blade at an angle of preferably + 30 ° relative to the plane of the blade under the action of an eccentric cam follower connected to the flaps via the connecting rods attached to the carrier coaxially with the axis of rotation of the blade with eccentricity directed Along the carrier.
2. A wind turbine according to claim 1, characterized in that at both ends of the blade and flaps, the plates are fixed in a position perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the blade, the total width of the blade together with the flaps greater than twice the distance from the edge of the shaft to the axis of rotation of the blade and is preferably the width of the five flaps .
print version
Publication date 31.01.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.