| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2231681
![]()
Wind turbine for wind turbines
Name of the inventor: Tsybakin Y. (RU); Borovikov SN (RU); Tolmachev VN (RU); Savchuk AD (RU)
The name of the patentee: Military Technical University
Address for correspondence: 191123, St. Petersburg, ul. Zakharievskaya, 22, VITU, for invention and patent of the bureau
Starting date of the patent: 2003.02.25
The invention relates to a clean wind energy and can be used to generate electricity or performing mechanical work. The technical result is to increase the efficiency of the wind turbine and its environmental safety. Wind turbine contains a structural frame with bearing assemblies supporting the vertical shaft, kinematically coupled with the mechanical energy consumer, provided with a collapsible cover; rigidly mounted on the hollow shaft of the wind wheel drives two horizontal blades, the air flow adjusting device limitations. The hollow guiding device covering the wind wheel is mounted on the shaft (rotatably and feathering) respectively on upper and lower bearings. The vertical walls of the hollow guide vanes form a convergent (input) and the diffuser (outlet) channels for the flow of passing air. In confused channels installed inlet guide vanes and the diffuser in the duct - outlet guide vanes. On confuser channel input installed protective netting, fortified by its perimeter (at the entrance area of convergent channel hollow guide vanes).
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to a clean wind energy, in particular to a wind turbine having a vertical axis of rotation, and can be used for electricity generation or the performance of mechanical work, for example, to generate power in places where no electrical power and constant winds prevail.
Known wind turbine [1], comprising structural frame to support the vertical bearing shaft on which is rotatably mounted a hollow guide vane sidewalls confuser-diffuser forming the channel and disposed within the hollow guide apparatus rigidly mounted on the shaft of the wind wheel blades.
The disadvantages of analog are:
- A large aerodynamic drag propeller;
- The effect of low feathering hollow guide vanes with a concave wall;
- The inability to automatically control the power of a wind turbine and its overload protection in the wind, hurricanes, etc...
The prototype of the proposed invention is a wind turbine [2], comprising a structural frame to support bearing assemblies of the vertical shaft which is kinematically linked to a consumer of mechanical energy, is rigidly mounted on the shaft hollow wind wheel consisting of two horizontal discs with blades, a hollow convex-concave guiding apparatus mounted on a shaft rotatably and feathering comprising an inner and a profiled baffle and covering the wind-wheel generator confuser-diffuser channel with vertical walls, the air flow adjusting device limitations.
Disadvantages of the prototype are:
- Occurring upstream and downstream propeller air turbulence that greatly reduce the efficiency of energy conversion of incoming air flow in the propeller shaft torque;
- Possible injury (and death) of birds that fall between the wind wheel and the hollow guide vanes.
These drawbacks are aiming to improve the efficiency of wind energy conversion and, consequently, increase the power of a wind turbine, but also prevent injury and death of birds.
This object is achieved outlined below windmill comprising a structural frame to support bearing assemblies of the vertical shaft which is kinematically linked to a consumer of mechanical energy, is rigidly mounted on the shaft hollow wind wheel of the two horizontal discs with blades, a hollow convex-concave guide vane mounted rotatably and feathering and comprising an inner profiled baffle covering wind wheel and forming convergent-diffuser channel with vertical walls, the regulating device limits the flow of air, further in confused and diffuser channels of the hollow convex-concave guide vanes mounted guides (aerodynamic) blades and inlet confuser channel set mesh, reinforced along its perimeter.
Installing (assembling) in confused and diffuser ducts hollow convex-concave guiding unit guides (aerodynamic) blades needed to reduce air turbulence occurring upstream and downstream propeller, significantly reducing the energy conversion efficiency of the inlet air flow in the propeller shaft torque.
Installation (erection) at the entrance confuser channel grid, fortified by its perimeter, it is necessary to avoid possible injury (and death) of birds that fall between the wind wheel and the hollow guide vanes.
Running wind turbine in combination with the above features (features of the claims) for a new wind turbine and thus meets the criterion of "novelty".
The above set of distinctive features is not known at this level of technology and does not follow from the well-known rules of construction of wind turbines and their auxiliary equipment, which proves compliance with the criterion of "inventive step".
Constructive realization of a wind turbine with a specified set of essential features not present any structural and technical and technological difficulties, which implies compliance with the criterion of "industrial applicability".
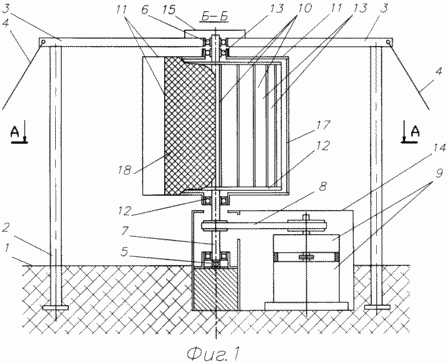
1 is a schematic view of a wind turbine in front with a cut on the BB.
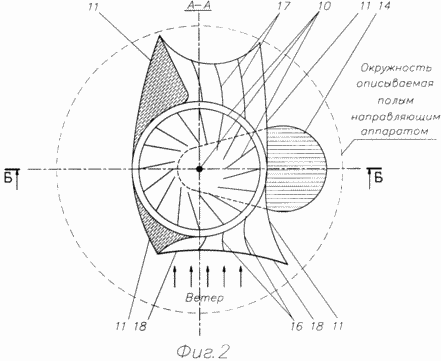
2 is a schematic sectional view taken along A-A wind turbine (1, top view).
Wind turbine comprises (see FIG. 1 and 2) a structural frame disposed on the base 1 (the concrete slab, ground and so on). The structural frame comprises two uprights, upper crossbar 3, 4 and stretch support bearing assemblies, respectively, the lower 5 disposed on the base 1, and 6 upper - in the center of the crossbar 3. The supporting bearing units 5 and 6 is a vertical shaft 7, 8 kinematically connected belt, chain or other transmission to the consumer of the mechanical energy 9, for example, an electric generator and gear. 7 is installed on the shaft 10 wind wheel consisting of a rigidly mounted on the shaft 7 of the upper and lower horizontal disc, around the periphery and between which is fixedly mounted blades and uniformly. Hollow guide apparatus 11, covering the wind wheel 10, mounted on the shaft 7 (and the rotatable feathering), respectively, the lower 12 and upper bearings 13. The vertical walls of the hollow guide vanes 11 form a convergent (input) and the diffuser (outlet) channels for the flow of passing air. In confused channels installed inlet guide vanes 16, and difuzornom channel - outlet guide vanes 17. At the entrance to the channel is set confuser net (safety) 18, fortified by its perimeter (at the entrance area of convergent channel hollow guide vanes 11). Dimensions of grid cells 18 can be compared with the linear gap 10 between the wind wheel and the hollow guide vanes 11. The grid should preferably be made of thin high strength material, such as steel wire coated with corrosion resistant coating. The mesh should have low aerodynamic drag passing airflow therethrough.
Wind turbine operates as follows. The flow of moving air raids on the hollow guide vanes 11, due to its concave-convex execution and use feathering effect automatically rotates the device 11 confused channels (with laden therein input vanes 16, a protective mesh 18) upstream and in this position consistently held up as long as the wind does not change its direction. the incoming air stream is compressed in confused channels without turbulence, thanks to the passage of the blade through the entrance, this is accompanied by an increase in air flow velocity and direction of the blades of the wind wheel Wind wheel 10. 10 receives the torque through which the shaft 7 and a kinematic linkage 8 is transmitted to the consumer of the mechanical energy 9 (electric generator with gearbox). From propeller airflow 10 enters the diffuser output channel defined vanes 17 between which it extends and twists without additional energy losses and velocity (flow rate thus falls uniformly) and exits from the apparatus 11. At a strong wind (or with strong gusts of wind ) "works" the adjusting device the airflow restriction (the same as in the prototype, in Figures 1 and 2 are not shown) which rotates the hollow guide vanes in the direction of rotation of the propeller 10, the air stream entering the confusor and channel respectively on the wind wheel 10, and decreases its rotation speed drops. With strong constant winds can occur stable equilibrium position of the vehicle 11 at an angle to the direction of the wind, when the forces of the automatic centrifugal friction regulator will be balanced by an aerodynamic force feathering apparatus 11.
When servicing the wind turbine and its repair, to ensure immobility 10 propeller unit 11 to deploy enough of its convex wall against the wind direction and fix it in this position in any way (for example, with additional extensions).
Power wind turbine power generator can be from 5 to 100 kW, depending on the size (dimensions) of a wind turbine. Installing the propeller wind turbine is preferred at a minimum height of 10-12 m.
Feasibility advantage of the invention lies in the fact that the installed (mounted) in confused and diffuser channels of the hollow convex-concave guide apparatus guides (aerodynamic) blades can reduce air turbulence arising at the input and output of the wind wheel. This eliminates the cost of energy to the vortex formation and significantly increases the efficiency of energy conversion of the incoming air flow in the propeller shaft torque. A plant (installation) on the inlet channel confuser (fortified by its perimeter) protective mesh avoids possible injury (and death) of birds that may get in between the wind wheel and the hollow guide vanes.
INFORMATION SOURCES
1. The Russian Federation patent №2039308, cl. F 03 D 3/02, 09.07.95, at Bul. №19.
2. Patent of Russian Federation №2166665, cl. F 03 D 3/02, 10.05.2001, at Bul. №13 - prototype.
CLAIM
Wind turbine comprising a structural frame to support bearing assemblies of the vertical shaft which is kinematically linked to a consumer of mechanical energy, is rigidly mounted on the shaft hollow wind wheel of the two horizontal discs with blades, a hollow convex-concave guide vane mounted rotatably and feathering and comprising an inner profiled baffle covering the wind wheel and forming convergent-diffuser channel with vertical walls, adjusting air flow restriction device, wherein in confused and diffuser channels of the hollow convex-concave guide vanes mounted guides (aerodynamic) blades and confuser channel input set mesh, reinforced by its perimeter.
print version
Publication date 31.01.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.