| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2273766
![]()
CONICAL WIND MOTOR FOR WIND
The name of the inventor: Gdanskiy Nikolai Ivanovich (RU); Maltsevsky Vladislav Vasilievich
The name of the patent holder: Moscow State University of Engineering Ecology
Address for correspondence: 105066, Moscow, ul. Staraya Basmannaya, 21/4, to the Vice-rector for scientific work A.V. Katalymov
Date of commencement of the patent: 2004.11.10
The invention relates to wind energy and is intended for use in areas with low wind speeds. The technical result consists in increasing the reliability of the structure by providing an automatic orientation of the blades relative to the wind flow and protecting the wind turbine from overloads during storm winds. The conical windmill comprises a rotating frame in the fixed housing, on which the rotary shaft and the shafts of the blades are rotatably mounted, the rotary shaft and the shafts of the blades being connected by transmissions with a constant ratio of angular velocities of 2: 1. The wind vane is rigidly fixed on the pivot shaft, the shafts of the blades are mounted obliquely on the rotating frame, the transmission from the shafts of the blades to the pivot shaft is made dentate through parasitic wheels, half of the gears placed on the pivot shaft are equipped with hubs, mounted thereon rotatably by 180 ° and Have a longitudinal slot in the hub, the swivel shaft being hollow with a profiled slot and slots in the lower part, a rod with a finger entering the profiled slot and a slot of the sprocket hub is mounted inside it, and a slotted bushing with a stopper , Which enters the splines of the rotary shaft, and in the fixed housing there is installed an actuator with a movable actuator, with which the end of the rod is connected with relative rotation.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to wind energy and is intended for use in areas with low wind speeds. This design allows increasing the overall reliability of the wind turbine.
A windmill is known in which a frame with vertically arranged blades is mounted on a central shaft which can rotate about their axes and are connected by gears to a driving gear rigidly connected to a weather vane loaded in the engagement direction, the ratio of the gear train from the weather vane to the blades being 1 : 2.
The main disadvantages of the well-known wind power unit are: the use of gears of rather complex construction and the discrete nature of the mechanism's operation, which protects the unit from storm winds. The discrete nature of the triggering of the protective mechanism leads to the fact that the stopping of the unit and the orientation of its blades in the wind should be performed when the maximum possible wind speed and, correspondingly, the maximum rotations of the frame with blades are reached.
The closest in terms of the totality of characteristics is the wind power plant - Patent of the Russian Federation No. 2030777, cl. F 03 D 3/02, 7/06, 1995, comprising in the fixed housing a rotating frame on which the pivot shaft and the blade shafts are rotatably mounted, the pivot shaft and the blade shafts being connected by transmissions with a constant ratio of angular velocities of 2: 1. The orientation of the wind of the swivel shaft with the block of sprockets is carried out through an additional gear mechanism using additional devices that take into account the direction of the wind.
The main disadvantages of this design are:
1) the need for an additional device that provides orientation of the installation to the wind,
2) the lack of a mechanism to protect it from storm winds.
The objective of the invention is to increase the reliability of the structure by providing an automatic orientation of the blades relative to the wind flow and protecting the windmill from overloads in breeze winds.
The task is achieved in that in a conical windmill comprising a rotating frame in a stationary housing on which a rotary shaft and shafts of blades are rotatably mounted, the rotary shaft and the shafts of the blades being connected by transmissions with a constant ratio of angular velocities of 2: 1, according to the invention, The shaft is rigidly fixed to the wind vane, the shafts of the blades are mounted obliquely on the rotating frame, the transmission from the shafts of the blades to the pivot shaft is made dentate through parasitic wheels, half of the gears placed on the pivot shaft are equipped with hubs, mounted thereon rotatably by 180 ° and have a longitudinal A slot in the hub, the swivel shaft being hollow with a profiled slot and slots in the lower part, a rod with a finger entering the profiled slot and a slot of the sprocket sprocket is mounted inside it, and a slotted bushing with a stop is mounted on the reverse end of the rod, In the slots of the rotational shaft, wherein in the fixed housing there is installed a drive of translational motion with a movable actuating member with which the end of the rod is connected with relative rotation.
 |
 |
 |
 | ||
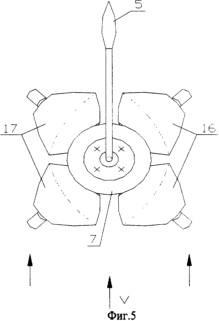 |
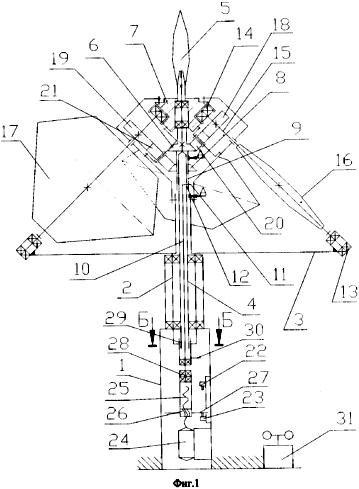
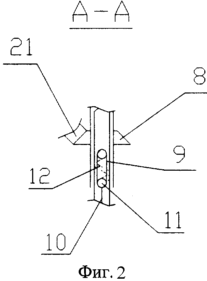
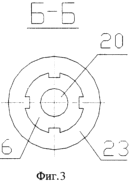
FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view of the structure, FIG. 2 is a view AA, FIG. 3 is a sectional view of the BB, FIG. 4 is a top view of the windmill from the working position of the windmill, FIG. 5 is a top view of the windmill At the stopped position of the windmill. In the fixed housing 1, the shaft 2 of the windmill engine 3 is rotatably mounted. Inside the shaft 2, the shaft of the weather vane 4 is mounted in bearings. The weather vane 5 is fixed to the shaft of the weather vane 4 and the fixed gear 6 is rotatably mounted and the upper housing 7 is rotatably mounted on the shaft of the weather vane 4 , With the ability to rotate by 180 ° - a turning gear 8 that has on the hub a longitudinal slot 9. Inside the shaft of the weather vane 4 is placed a rod 10 equipped with a finger 11, which enters the screw slit 12 of the shaft of the weather vane 4. On the frame 3 in the bearings 13 and 14 are installed On the shafts 15 of the blades 16 and 17. On the shafts 15 and fixed gear wheels 18 and 19 are fixed in the fastenings with the parasitic wheels 20 and 21. The parasitic wheels 20 engage with the fixed wheel 6 rigidly mounted on the shaft of the weather vane 4, and the parasitic wheels The wheels 21 engage with the rotary wheel 8 mounted on the shaft of the weather vane 4. The end switches 22, 23 and the geared motor 24 are mounted in the housing 1, the output shaft having a screw 25 with a nut 26 which, due to the projections 27 entering In the slot of the housing, the rotation around the axis is blocked. The nut housing 26 is connected to the rod 10 via the bearings 28. A splined sleeve is mounted on the rod 10, the splines 29 of which enter the splines of the weather vane shaft 4. and the locking element 30 is rigidly fixed to the spline hub 30. A wind speed sensor 31 is mounted on the housing 1. |
|
The operation of the wind turbine is illustrated by the example of a four-bladed design.
In working position with wind speed ![]() , Not exceeding the critical
, Not exceeding the critical ![]() Cr (
Cr ( ![]()
![]()
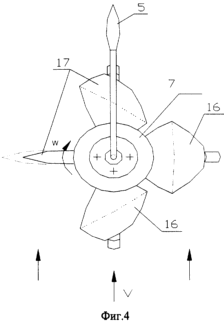
![]() Kp), the windmill frame 3 (Fig. 4) rotates due to the difference of the front resistance of the blades to the incoming wind flow counterclockwise at a certain angular velocity
Kp), the windmill frame 3 (Fig. 4) rotates due to the difference of the front resistance of the blades to the incoming wind flow counterclockwise at a certain angular velocity ![]() . The stem 10 is in its lowest position. Its finger 11, through the screw slot 12 of the rotational shaft 4 and the longitudinal slot 9 in the hub, keeps the rotary gear 8 in a position where the blades 16 and 17 of the windmill rotate relative to the housing at an angular velocity
. The stem 10 is in its lowest position. Its finger 11, through the screw slot 12 of the rotational shaft 4 and the longitudinal slot 9 in the hub, keeps the rotary gear 8 in a position where the blades 16 and 17 of the windmill rotate relative to the housing at an angular velocity ![]() / 2, taking the most advantageous position in relation to the wind flow. The orientation of the sprockets 6 and 8 mounted on the rotary shaft 4 with respect to the wind flow is provided by the weather vane 5.
/ 2, taking the most advantageous position in relation to the wind flow. The orientation of the sprockets 6 and 8 mounted on the rotary shaft 4 with respect to the wind flow is provided by the weather vane 5.
When the wind speed is exceeded ![]() Critical value
Critical value ![]() Cr (
Cr ( ![]() >
> ![]() Cr ), the signal from the wind speed sensor 31 switches on the geared motor 24 by moving the nut 10 upwardly inside the rotational shaft 4 with the nut 26 until the feed circuit of the geared motor 24 is opened by the limit switch 22. Two actions are performed:
Cr ), the signal from the wind speed sensor 31 switches on the geared motor 24 by moving the nut 10 upwardly inside the rotational shaft 4 with the nut 26 until the feed circuit of the geared motor 24 is opened by the limit switch 22. Two actions are performed:
1) the pin 11 of the rod 10 through the screw slit 12 of the rotational shaft 4 and the longitudinal slot 9 in the hub turns the rotary wheel 8 180 ° by rotating the blades 17 90 ° along the gears through the gear train (in FIG. 5, the dashed lines show the position of the blades 17 At the working position of the windmill),
2) the shaft 2 of the turntable 4 of the wind turbine is fixed relative to the rotational shaft 4 by means of a stopper 27 resting against the lock formed in the wall of the rotational shaft 4.
In this case, the blades of the windmill occupy constant symmetrical positions with respect to the direction of the wind flow, which provides a significant reduction in the aerodynamic drag of the entire structure. The slopes of their middle lines (dashed lines) to the wind flow are ± 22.5 °.
When the speed decreases below the critical value, the signal from the wind speed sensor 31 reverses the geared motor 24 by lowering the stem 10 downward with the nut 26 until the feed circuit of the geared motor 24 is released by the limit switch 23. In this case:
1) the connection of the shaft 2 and the rotating frame 3 of the windmill with the rotary shaft 4 opens,
2) the pin 11 of the rod 10 through the screw slit 12 of the rotational shaft 4 and the longitudinal slot 9 in the hub reverses the rotation wheel 8 by 180 °, turning through the gear transmission of the blade 17 by 90 ° against the movement (in FIG. 5, the dashed lines show the position of the blades 17 at Working position of the windmill), the blades 17 return to the working state, after which the windmill starts normal operation.
CLAIM
A conical windmill comprising a rotating frame in the fixed housing on which the rotary shaft and the shafts of the blades are rotatably mounted, the rotary shaft and the shafts of the blades being connected by transmissions with a constant ratio of angular velocities of 2: 1, characterized in that the winding shaft is rigidly fixed to the weathervane, The shafts of the blades are mounted obliquely on the rotating frame, the transmission from the shafts of the blades to the pivot shaft is made dentate through parasitic wheels, half of the gears placed on the pivot shaft are equipped with hubs, mounted thereon rotatably by 180 ° and have a longitudinal slot in the hub, This rotary shaft is made hollow with a profiled slot and slots in the lower part, inside it is installed a rod with a finger entering the profiled slot and a slot of the sprocket sprocket, and at the reverse end of the rod, a slotted bushing with a stopper is inserted in the splines of the rotary shaft, Wherein in the fixed housing there is installed an actuator of translational movement with a movable actuating member with which the end of the rod is connected with relative rotation.
print version
Publication date 31.01.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.