| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2263816
![]()
Windmills
Name of the inventor: Vyarhejchyk EN (RU); Crank NN (RU); Stoyanov IS
The name of the patentee: Pyatigorsk State Pharmaceutical Academy
Address for correspondence: 357532, Stavropol, Pyatigorsk, etc. Kalinina, 11, Pyatigorsk State Pharmaceutical Academy.
Starting date of the patent: 2003.11.17
The invention relates to the field of wind energy. The technical result is to increase the coefficient of performance (COP) and power settings. The wind power plant comprises mounted in the support rotatably vertical shaft, rectangular blades, mounted at equal distance from the shaft rotatably about their axes parallel to the axis of the shaft, with the angular velocity twice lower angular velocity possible rotational and sideways, opposite the shaft rotation, the blades are formed as a symmetric profile width equal to twice the distance from the shaft edge to the blade axis of rotation, having a kinematic connection with the vane and the angle between the plane of the wind vane and blade plane at the time of its coincidence with the axis of the shaft is 90 °, wherein the upper bearing shaft is in the yoke, fixed horizontally on the upper ends of the three vertical supports, which are fixed in the ground at an equal distance from each other.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to wind energy and can be used as a cost-effective high-power wind power plant.
Known wind turbines vane type, and vertical axis wind turbine type-8 (Novosibirsk State Technical University, the company "NTEC", Novosibirsk. These wind turbines are bulky, have a rather low efficiency and is not economically feasible.
Near analogue of the invention is a wind turbine comprising mounted in the support rotatably vertical shaft, rectangular blades, mounted at equal distance from the shaft rotatably about their axes parallel to the shaft axis at an angular velocity twice lower angular velocity possible rotation of the shaft and in the direction opposite to the rotation shaft, wherein the blades are formed as a symmetric profile width equal to twice the distance from the edge of the shaft to the axis of rotation of the blades having a kinematic connection with the vane and the angle enclosed between the plane of the wind vane and blade plane at the time of a possible match with the axis of the shaft is 90 ° (see., e.g., RU 2164624 C1, cl. F 03 D 3/06. 27.03.2001, 3C).
This analog has enough power and high efficiency.
The purpose of this invention is to increase the efficiency and capacity of the wind power unit (WPU).
This object is achieved by a wind power installation (WPU), having a shaft with upper and lower legs where the upper bearing shaft is in the yoke, fixed horizontally on the upper ends of the three vertical supports, which are fixed in the ground at an equal distance from each other.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
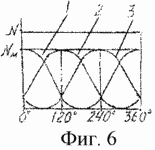 |
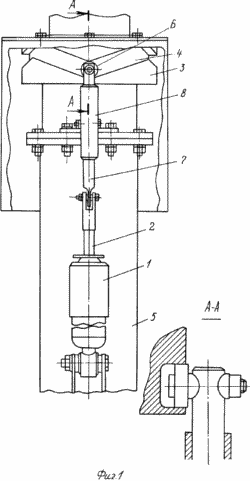
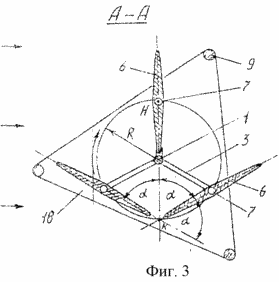
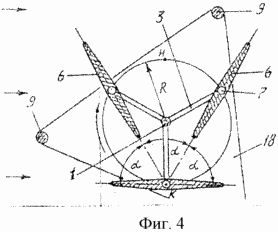
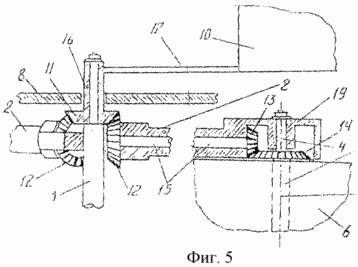
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS Figure 1 shows a general view of wind turbines; Figure 2 - wind turbine wind wheel, side view; Figure 3 - A-A sectional view; Figure 4 - A-A sectional view rotated by an angle of 60 °; Figure 5 - the kinematic connection of the blades with a weather vane; 6 - the schedule of power changes, transmitted blades on the shaft at one of its turnover.
Turbine consists of a vertically mounted on the upper and lower supports of a three-shaft attached to it two upper 1 and lower three planet carrier 3 at their ends by means of semi-axes 4 are rotatably mounted around their axes 5, 6 are three rectangular vanes symmetric profile (1 2). The upper and lower half-line 4 are fixed to the ends of the spar 7, which is fixed blade frame, steering light and durable material.
The blades 6 have a width d, is equal to twice the distance d 'from the edge to the shaft axis of rotation the blade 5, i.e. d = 2d '. The upper bearing shaft is located in one yoke 8 fixed horizontally on the upper ends of the three vertical supports 9 which are fixed in the ground at an equal distance relative to each other (Figures 3 and 4). Each blade 6 is kinematically coupled with the vane 10 through the bevel gears 11, 12, 13, 14 and the intermediate shaft 15. The gears 13 and 14 are arranged in a housing 19 secured to the end of the carrier 2. The pinion gear 11 is kinematically connected to all the blades 6 is formed together with the tubular shaft 16 is movably seated on the upper end portion of the shaft 1 (Figure 5) .Flyuger 10 is connected to the shaft 16 through the shaft 17. The driven gear 14 fixed to the upper semi-axis 4, and has a number of teeth two times more than the pinion 13, and gears 11 and 12 have the same number of teeth. Propeller blades, located on the building of 18 wind turbines, are exposed so that the angle enclosed between the planes of adjacent blades is of 60 °, ie, L = 60 and the angle enclosed between the plane of the blade and wind vane plane, at the time of a possible match with the axis of the shaft is 90 °. The gears 12 and 13 are fixed on the ends of the shaft 15 extending inside the carrier 2. The lower support shaft 1 located in a building 18, which houses an electric generator coupled to the shaft 1, and the necessary equipment.
Wind turbine operates as follows. In the presence of wind, as indicated by arrows (3 and 4), vane, turning in the wind, turning the operating position "in the wind" all blades. Under the pressure of the wind on the blades of the wind wheel with the shaft 1 will rotate. Will rotate about the axes 5 and vanes with an angular velocity twice lower than the shaft, and the opposite side of the shaft. This property gives the sail blades, whereby the blades at any point of the circumference with radius R and perceive the shaft is transmitted to the wind power except for the point "C" in which blades take a position parallel to the wind. To determine the power at the shaft, a schedule (6) changing the power transmitted to the blades of one shaft of its rotation.
At the beginning of a turn, one of the blades when the wind perpendicular point "H" (Figure 3), it receives and transmits all the energy on the shaft pin direct wind flow cross section area equal to the working surface of the blades, i.e. transmits at the maximum power shaft N m equal to
![]()
where C - power transmission blade - to the shaft, it is C = Sin 2 ![]() °, where
°, where ![]() ° - angle of rotation of the blades to the wind;
° - angle of rotation of the blades to the wind; ![]() - The volume of air in kg / m 3; F - the working area of the blade surface in m 2; v - wind speed in m / s; g = 9,81.
- The volume of air in kg / m 3; F - the working area of the blade surface in m 2; v - wind speed in m / s; g = 9,81.
When the blade is perpendicular to the wind C = 1. Other angles of rotation of the blade to the wind factor. C will decrease and when the shaft is rotated by 180 ° C = 0. C will change proportionally and the power transmitted to the blade shaft. Curve 1 (Figure 6) shows a change in power transmitted to the shaft of one blade per revolution. Curves 2 and 3 show the change in the power transmitted to the shaft the other two blades. The total power transmitted three blades on the shaft at one of its turnover increase compared to the power N m 1.5 times (6). Given the possible deflection power transmitted to the shaft all the blades, take the factor is not 1.5, and then 1.3 N constant power at the wind turbine shaft will be equal ![]()
Power loss at the rotation of the blades is not because while rotating propeller blades themselves are able to rotate about their axes in the right direction under the influence of the surrounding air environment. From a weather vane only requires a little effort when changing wind to keep the blades windage. Speed n shaft under load there will be equal
![]()
where R - distance from the shaft to the blade axis of rotation, ![]() = 3.14. In determining the efficiency of wind turbines take into account that the area of the largest cross-sectional propeller wind (mid-section) is equal to 1.5 square blades (see. Above), excluding the area of the longitudinal section of the shaft and driven, then the power of N in the wind flow with the cross-section is equal to
= 3.14. In determining the efficiency of wind turbines take into account that the area of the largest cross-sectional propeller wind (mid-section) is equal to 1.5 square blades (see. Above), excluding the area of the longitudinal section of the shaft and driven, then the power of N in the wind flow with the cross-section is equal to
![]()
hence power ratio N / N a - have efficiency, i.e. 1.3 / 1.5 = 0.866 ..., rounding the number based on the longitudinal section of the shaft area and drove find that the wind turbine efficiency is not less than 0.8.
An essential feature of the invention is that the turbine shaft has a double-sided support, wherein the support is in the upper cross member fixed to the upper ends of the three vertical columns, fixed to the ground.
The advantage of the proposed design is a high capacity and efficiency, and the power of the wind turbine.
CLAIM
Wind Turbine (WPU) containing mounted in the support rotatably vertical shaft, rectangular blades, mounted at equal distance from the shaft rotatably about their axes parallel to the axis of the shaft, with the angular velocity twice lower angular velocity possible rotation of the shaft, and in the direction opposite the shaft rotation, the blades are formed as a symmetric profile width equal to twice the distance from the edge of the shaft to the blade axis of rotation, having a kinematic connection with the vane and the angle enclosed between the plane of the wind vane and blade plane at the time of its coincidence with shaft axis is 90 °, characterized in that the upper bearing shaft is in the yoke, fixed horizontally on the upper ends of the three vertical supports, which are fixed in the ground at an equal distance from each other.
print version
Publication date 02.02.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.