| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2276743
![]()
WINDOWS
The name of the inventor: Tretyakov Vitaliy Evgenevich
The name of the patent holder: Tretyakov Vitaly Evgenievich
Address for correspondence: 443045, Samara, ul. Aurora, 122, ap. 333, pat. L.I. Sinitsyna
Date of commencement of the patent: 2005.03.10
The wind power plant belongs to the field of wind energy, in particular to wind turbines with guide devices that convert the energy of the air flow, and can be used for obtaining both mechanical and electrical energy. The technical result consists in expanding the operating speed range of the oncoming flow, maximum utilization of its energy, reducing the losses of the working path and increasing the effectiveness of the wind farm. The wind power plant comprises a fixed carrier body which is the main guiding device in the form of a spatial blade grid with a central outlet channel in which an impeller is arranged on a vertical shaft coaxially with a central axis in accordance with the invention, with the upper housing member being freely rotatable with respect to Central axis, a single unit from the air intake, nozzle and stabilizer; The spatial lobed grid is formed from two surfaces of revolution and constructed in the form of a circular array of spatial blades between them that form working channels; The air intake completely covers the working channels of the rear zone of the guide apparatus and is connected to the outlet nozzle with the possibility of free rotation relative to the central axis.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Wind turbine refers to wind power, in particular to wind turbines with guiding devices that convert the energy of air flow, and can be used to obtain both mechanical and electrical energy.
A wind-driven device is known that includes devices for changing the direction of the air flow, which includes, among other things, a hull, an exhaust device and an air flow guide and is designed to convert airflow energy (RF patent No. 2093702, F 03 D 3/04 of 22.01. 96).
However, this installation does not allow maximum use of wind energy due to large losses in an extended vertical working path.
The wind power plant is known with a concentrator and stream accelerators, which, in particular, contains a streamlined body, a confuser, a nozzle and a turboplastic rotor and is designed to convert wind energy into electrical energy (as.N. 2078995, 6 F 03 D 9/00 of 26.05. 92).
But the large sail area of the confuser assumes an increase in the strength of the load-bearing elements and mechanisms and their mass, and this reduces the overall efficiency of the installation. Constructive complexity with a large number of movable pairs and friction pairs increases the unit cost of the installation and calls into question its advantages over the classical scheme of horizontal-axial installations.
The closest technical solution is a wind turbine comprising an annular body with a central channel and a fairing at its inlet that includes, among other things, guide vanes, an elastic outlet with a ring and a wind wheel mounted on a vertical shaft, and is intended to convert wind energy No. 1122882, F 03 D3 / 04 of 06.08.82).
But in this installation only the front part of the directing device is working, and on the rear, with respect to the direction of the air flow, a leeward zone of low pressures is created, half the size (and even more) of the diameter of the guiding device, which leads to the flow of the working medium into the region of low pressures On the transition from the guide device to the impeller. Those. Part of the air flow with its potential energy "runs to freedom", not reaching the impeller, thereby reducing the efficiency of the plant.
It is an object of the present invention to extend the operating speed range of the oncoming flow, to maximize its energy use, to reduce the losses of the working path and to increase the efficiency of the wind farm.
In order to solve the task, the wind power plant comprises a fixed carrier body, which is the main guiding device in the form of a spatial blade grid with a central outlet channel in which an impeller is arranged coaxially with the central axis on the vertical shaft, and on the upper housing element, Relative to the central axis, a single unit from the air intake, the nozzle and the stabilizer; The spatial lobed grid is formed from two surfaces of revolution and constructed in the form of a circular array of spatial blades between them that form working channels; The air intake completely covers the working channels of the rear zone of the guide apparatus and is connected to the outlet nozzle with the possibility of free rotation relative to the central axis.
 |
 |
|
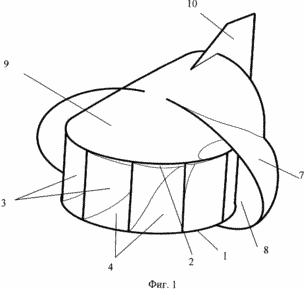
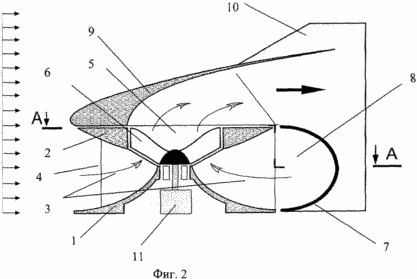
1 shows a general view of an installation; FIG. 2 shows a wind-section in a section; FIG. 3 is a top view with a cut AA. Figures 1, 2, 3 show a wind turbine, where 1 is the lower base, 2 is the upper body element, 3 is the spatial blades, 4 is the working channel of the guide, 5 is the central outlet channel of the shell, 6 is the impeller, 7 is the air intake , 8 - internal cavity of the air intake, 9 - nozzle, 10 - stabilizer, 11 - generating device, 12 - interface into zones, 13 - front zone, 14 - rear zone. |
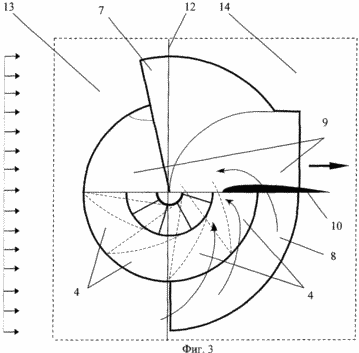 |
Mutual arrangement of units and parts of the wind farm: the lower base 1 and the upper element 2 are concentrically arranged relative to the central vertical axis and represent two surfaces of rotation. The lower base 1 and the upper element 2 are rigidly connected to each other by spatial blades 3 constructed as a circular array with respect to the central axis and spatial working channels 4 are formed between each pair of blades 3. A plurality of these elements forms a fixed carrier body being the main guide apparatus. It is made in the form of a space vane lattice with a central outlet channel 5 in which the impeller 6 is coaxially located. On the upper housing element 2, a single unit is installed, from an air intake 7, a nozzle 9 and a stabilizer 10, with respect to the central axis. The impeller 6 is connected to the generating device 11. The air intake 7 is made in the form of a space shell surrounding the working channels 4 of the rear zone 14 of the guide apparatus and, creating its boundary between the areas of increased and reduced pressure, forms an internal cavity 8. The conditional interface 12 between Front zone 13 and rear zone 14 passes through the inlet part of the air intake.
In this case, working channels 4 are formed from the condition of minimizing the extent of the working path in the guiding device and the vertical component of the working medium's motion path.
WINDOWS WORK AS FOLLOWING
The nozzle 9 and the air intake 7 are guided by the stabilizer 10 in the direction of the air flow, rotating around the guide device. The airflow captured by the guide device and the air intake 7 passes through the channels 4 of the guide apparatus located in the frontal zone 13 and through the internal cavity 8 formed by the air intake 7 and the channels 4 located in the rear zone 14 enter the central channel 5 and onto the working channel Wheel 6 located in it. Having transferred part of its energy to the wheel 6, the exhaust air stream (working medium) is discharged through the nozzle 9 to the outside. The impeller 6 transfers the received energy to the generating device 11. The cut of the nozzle 9 is in the rear zone 14 of the reduced pressure region, and the inlet part of the air intake 7 is in the front zone 13 of the braking pressure region from the oncoming flow.
Two opposing effects ("pull" and "push") give an additional positive impulse to the operation of the airflow and transfer the installation to the category "two in one".
To the above, we add that the spatial boundary formed by the surface of the mobile unit from the elements 7 and 9 protects the unit from harmful "suction" effects in the transition region from the guide device to the impeller 5 and thereby reduces energy losses in the working path Installation.
Movable block of elements 7, 9, 10 is made of light materials and with a low specific gravity has a low moment of inertia. Depending on the rated power of the installation and, accordingly, the mass of the mobile unit of the elements 7, 9, 10, it is possible to use together with the stabilizer 10 or, in its place, additional devices and mechanisms.
The installation on the upper housing element, a single unit from the air intake, the nozzle and the stabilizer, with the possibility of free rotation relative to the central axis, allows to obtain additional energy from the flow captured by the air intake, to include the channels of the rear zone in operation and to get rid of the harmful influence of the low pressure rear zone .
The formation of a three-dimensional lobed lattice of two surfaces of revolution and constructed in the form of a circular array of spatial blades between them makes it possible to form working channels with a minimum length of the working path in the guiding device and the vertical component of the trajectory of the working medium.
Coupled together with the outlet nozzle, with the possibility of free rotation relative to the central axis, the air intake completely encloses the working channels of the rear zone of the guide apparatus and allows the energy of jets not captured by working channels of the front zone to be guided through them to the impeller.
The use of the wind turbine of the proposed design significantly increases the efficiency of wind energy use, widens the range of working wind speeds and maximizes the full use of low-potential, pulsating and "yawing" airflow. Due to the simplicity of the design scheme with the minimum number of units, parts and kinematic pairs, an increase in the reliability and durability of the installation is achieved.
CLAIM
The wind power plant comprises a fixed carrier body which is the main guiding device in the form of a spatial blade grid with a central outlet channel in which an impeller is placed on the vertical shaft coaxially with the central axis, characterized in that it is freely mounted on the upper housing element with respect to the central body Axis, a single unit from the air intake, the nozzle and the stabilizer, while the spatial lobed grid is formed of two surfaces of rotation and constructed as a circular array of spatial blades between them that form working channels; The air intake completely covers the working channels of the rear zone of the guide apparatus and is connected to the outlet nozzle with the possibility of free rotation relative to the central axis.
print version
Date of publication 02.02.2007gg




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.