| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2281412
![]()
DEVICE FOR ENERGY TRANSFORMATION OF ENVIRONMENTAL FLOW
The name of the inventor: Dubovsky Leonid Yakovlevich (RU); Mikhalap Valery Ivanovich
The name of the patent holder: Dubovsky Leonid Yakovlevich (RU); Mikhalap Valery Ivanovich
Address for correspondence: 197227, St. Petersburg, PO Box 405, S.A. I screamed
Date of commencement of the patent: 2004.12.20
The invention relates to means for converting the energy of a flow of a medium, for example wind, water, and can be used, for example, in wind power, in particular in wind turbines for the use of wind energy. The technical result consists in increasing the efficiency of the plant by providing the possibility of joint, coordinated and synchronized operation of several rotary blades, which leads to more efficient use of energy of the medium flow. The device comprises a power support with a shaft, a planetary mechanism with a housing containing a pair of coaxial bevel gears mounted on the semiaxes and having two toothed crowns, a pair of coaxial bevel gears having one gear ring, a central conical wheel. The large serrated crowns of the first pair of conical wheels are equal to the serrated crown of the central conical wheel and are meshed with it, and the small serrated crowns of the first pair of conical wheels are equal to the gear rims of the second pair of conical wheels and are meshed with them. Each pair of conical wheels has a coaxial driven shaft with a flange, with a rotating blade perpendicular to the driven shaft on each flange. Each flange is further provided with a second pivoting blade perpendicular to the first blade, oriented in the opposite direction to the first blade.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to means for converting the energy of a flow of a medium, for example wind, water, and can be used, for example, in wind power, in particular in wind turbines for the use of wind energy.
To assess the novelty and inventive level of the claimed solution, consider a number of known technical means of a similar purpose.
A wind-receiving device is known in the form of a wind wheel with rotary blades equipped with overload protection devices installed on radial rods, a mechanism for orienting the wind receiving device, a turning mechanism for blades containing a planetary mechanism with elements of the Maltese mechanism, and blade rotation gears kinematically rigidly connected with planetary planetary satellites Mechanism by means of gear pairs and flexible mechanical transmissions, see application for the grant of a patent of the Russian Federation for invention No. 94021138, F 03 D 5/00.
This device provides a high coefficient of wind energy utilization by optimizing the position of the blades relative to the wind flow and high sensitivity to wind, reliable operation in different climatic zones, has compact and technologically advanced mechanisms.
A mechanism is known for converting rotary motion into a complex, comprising a body, an input and four output shafts, four conical wheels, a carrier, a retarded central cone wheel, which is characterized in that the carrier is designed as a cross having an axis of rotation perpendicular to the plane of the crosspiece and passing through The center of the crosspiece, on which two pairs of coaxial bevel gears are located, each conical wheel of one of the two pairs has two toothed crowns, and each conical wheel of the other pair has one gear ring, the equally small toothed crowns of the first pair of conical wheels with which it is engaged , The spider is fixed to the input shaft passing through the axis of rotation of the crosspiece, the toothed crown of the braked central cone wheel coincides in size with the large toothed rims of the first two conical wheels and is meshed with them, each of the four bevel gears has an output shaft, the body consists of a glass , Fixed on the input shaft passing through the axis of rotation of the cup and the fixed wall on which the retarded central conical wheel is fixed, see RF patent No. 2190790, F16H2 / 46, the patent holder of which is the applicant of the present invention.
The kinematic capabilities of this mechanism are significantly higher than in similar devices. The possibility of implementing various three-dimensional cyclic trajectories of the motion of the functional elements of a mechanical system significantly expands the functional purpose of this mechanism and the field of its application.
An aircraft is known including a body, an engine and two lifting devices arranged symmetrically about the longitudinal axis of the housing in the horizontal direction, which is characterized in that each of the lifting devices includes two pairs of drive wings, each made in the form of a sector with an arc, The first of which is horizontal, perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the body, and the second is vertical, perpendicular to this horizontal axis, while on each of these rotation axes there is one pair of drive axes Wings with the possibility of their synchronous rotation in opposite directions, a horizontal shaft on which both pairs of wings are fixed, located in the space between the planes of the wings, passing through the point of intersection of the horizontal and vertical axes of rotation perpendicular to these axes and fixed to the side of the body with rotation at the front view On the housing for the right hoisting device counterclockwise and for the left hoisting device - clockwise synchronized with a ratio of 1: 1 with opposite rotation of each pair of wings, in the initial position the drive wings of one pair are located in vertical planes on opposite sides of the horizontal Axis of rotation of this pair, and the wings of the other pair are located in horizontal planes on one side of the vertical axis of rotation of this pair, and in the initial position, the direction of rotation of the vertically spaced wings of both lifting devices closest to the body has a vertical component directed upwards and coincides with the direction of rotation The top of the horizontally arranged wings of the corresponding lifting device when viewed from above on the body, see RF patent No. 2128131, B 64 C 29/00, the patent holder of which is the applicant of the present invention.
The lifting power of the above-described design of the aircraft significantly exceeds the lifting power of known structures with the same areas of working surfaces of the lifting devices, which allows to significantly increase the weight return of the aircraft with a reduction in transverse dimensions. In addition, due to the parallelism of the planes of flapping wings to the flow of air during horizontal flight, the drag of the proposed design is much less than that of the design described in the prototype, which will allow achieving high flight speeds.
A wind power plant is known, containing a power support, a flowning mechanism with a tail element, a power consumer kinematically connected to a rotor blade having a central body, two pairs of mutually perpendicular shafts connected to the blades installed therein, the kinematic connection of the consumer to the rotor being in the form of a planetary A reducer disposed around a central body provided with two pairs of mutually perpendicular movable bevel gears mounted on the shafts and one fixed conical gear located perpendicularly to the remaining gears, wherein the first pair of opposed gears engages a fixed gear with a gear ratio of 1: 1 , And the second pair of gears has a reduced tooth height and is engaged with the first pair. This installation is characterized in that it further comprises a platform located on the power support, wherein the power consumer, the rotor and the planetary gear are placed on this platform, the rotor is provided with two additional shafts, the first of which is horizontally mounted rotatably, connected to the central body and kinematically Is connected to the power consumer, and the second additional shaft is fixedly mounted coaxially with the first and is connected to the central body, the fixed gear being fixed to the end of the second shaft, see asc. USSR No. 1719714, F 03 D 5/00.
A wind turbine is known that contains rotary blades, a planetary gearbox whose central bevel gear is placed on a hollow vertical support and a vertical shaft mounted in the support, the first end of which is connected to an energy machine, and the second one fixes the main axles perpendicular to the shaft connected to the rotary blades And conical gears interacting with the central gear with a gear ratio of 1: 1, the wind installation being provided with two additional semi-axles fixed to the second end of the shaft, located in the plane of the main semi-axes and perpendicular to them, as well as additional rotary blades and additional conical gears interacting With the gears of the main semi-axes, the blades of the main semi-axes being located in the vertical plane and directed in opposite directions, and the blades of the additional semi-axes are arranged in a horizontal plane and oriented in the same direction, see as. USSR No. 1652643, F 03 D 5/00.
For the greatest number of similar features and the result achieved with their use, this technical solution is chosen as a prototype of the first independent object of the claimed invention.
The disadvantages of the prototype is the insufficient efficiency of energy conversion of the medium flow.
The aim of the invention is to increase the efficiency of converting the energy of the medium flow.
According to the invention, a device for converting the energy of the fluid flow comprising a power support to the shaft, two pairs of coaxial semiaxes fixed perpendicular to each other at the upper end of the shaft, four rotor blades arranged perpendicular to the semiaxes, a planetary mechanism with a housing comprising two pairs of coaxial bevel gears On the semiaxes, the central conical wheel fixed to the power support coaxially to the shaft is characterized in that the first pair of coaxial bevel gear wheels has two toothed crowns, and the second pair of coaxial bevel gear wheels has one gear ring, the larger gears of the first pair of conical wheels being equal The gear ring of the central conical wheel and are meshed with it, and the small gear wreaths of the first pair of bevel gear wheels are equal to the gear teeth of the second pair of bevel gear wheels and are meshed with them, each pair of conical wheels having a coaxial driven shaft with a flange on which is fixed The pivoting blade is perpendicular to the driven shaft, in addition, on each flange, a second pivoting blade is also installed perpendicular to the first blade, oriented in the opposite direction to the first blade.
This is a set of essential features of the invention, ensuring the achievement of our goal in all cases to which the requested scope of legal protection applies.
In addition, the invention has a number of optional features that characterize its particular cases, specific forms of its material embodiment, namely:
- rotary blades are made with a shape that excludes the possibility of their interaction with each other in any position of the shaft;
- the rotary blades are made in the form of a sector with an arc less than a quarter of the arc of the forming circle;
- rotary blades are made in the form of rectangles with a rounded top.
The claimed technical solution is new, since it is characterized by the presence of a set of features that are not present in prior art technical solutions.
The immediate technical result that can be obtained by implementing the claimed feature sets is to increase the efficiency of converting the energy of the medium flow due to the fact that in any position of the device the flow of the medium simultaneously interacts with all the rotary blades which, to varying degrees, depending on their specific position With respect to the direction of the flow of the medium, but at the same time, according to one another, the energy of the flow of the medium is converted into a rotation of the shaft, creating moments of one direction on the shaft.
This allows us to recognize the claimed technical solution with the appropriate criterion "inventive step".
 |
 |
 |
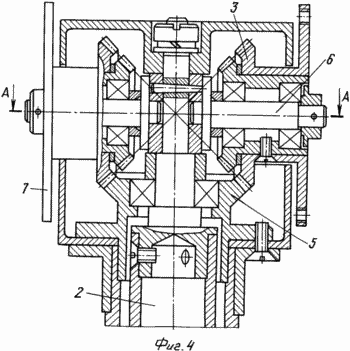 |
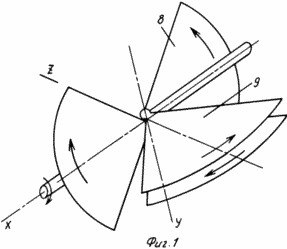
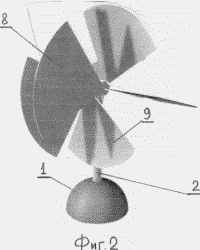
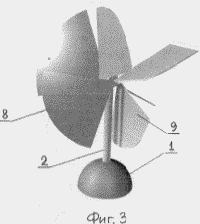
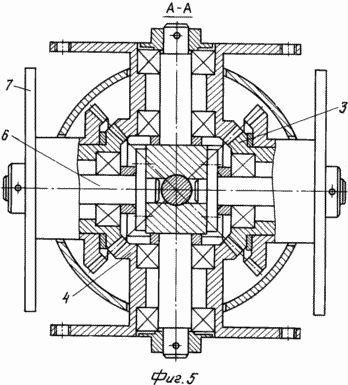
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS Fig. 1 is a schematic illustration of the operation of the device by the example of the motion of four rotary planes, Fig. 2 is a perspective view of a device with eight rotatable blades, Fig. 3 is the same at another shaft position, Fig. .4 is a sectional view of the planetary mechanism, FIG. 5 is a sectional view of AA in FIG. 4. FIG. The device comprises a power support 1 with a shaft 2, for example, vertically oriented, a planetary mechanism with a housing comprising a pair of coaxial bevel gears 3 mounted on semiaxes and having two toothed crowns, a pair of coaxial bevel gears 4 having one gear ring, a central conical Wheel 5. The large serrated crowns of the first pair of conical wheels 3 are equal to the gear ring of the central conical wheel 5 and are meshed with it, and the small serrated crowns of the first pair of bevel gears 3 are equal to the gear teeth of the second pair of bevel gears 4 and are meshed with them. Each pair of conical wheels 3, 4 has a coaxial driven shaft 6 with a flange 7. The driven shafts 6 pass through the walls of the body of the planetary mechanism rotatably. On each flange 7, the first pivoting blade 8 is fixed perpendicular to the driven shaft. Each flange 7 is further provided with a second pivoting blade 9 perpendicular to the first blade, oriented in the opposite direction to the first blade 8. |
|
 | ||
Rotary blades 8 and 9 must be formed with a shape that excludes the possibility of their interaction with each other in any position of the vertical shaft 2. They can be made in the form of a sector with an arc less than a quarter of the arc of the generating circle, or in the form of rectangles with a rounded apex.
DEVICE WORKS AS FOLLOWING
Under the influence of wind, the blades of the device, fixed on the output shafts of the planetary mechanism and executed in compliance with their specific shapes and sizes, will rotate and describe complex cyclic spatial trajectories. In this case, each of the eight blades in any of its positions creates a relatively vertical shaft, while the directions of the moments from all the blades coincide. The planetary mechanism synchronizes and converts the rotation of all the coaxial output shafts into a rotation of the vertical shaft.
The possibility of industrial application of the claimed technical solution is beyond doubt, since it can be realized using known technologies and technical means. At present, the existing mock-up of the claimed device has been manufactured and tested, which has proved its operability, the possibility of manufacturing in an industrial manner and sufficient efficiency of converting the energy of the medium flow into rotational motion of the shaft.
The invention provides for increasing the efficiency of the plant as a whole by allowing the joint synchronized and synchronized operation of several rotary blades, which leads to more efficient use of energy of the medium flow, for example wind. The claimed device has wide functional capabilities and can be used in wind turbine designs, hydraulic turbo-drives, etc. Converters of energy. In addition, the device can operate in a reversible mode, i. E. Transform the energy of rotation of the shaft into a directed flow of the medium, and can be used in the constructions of fans, propulsors of water vehicles, and so on. Converters of energy.
CLAIM
1. A device for converting the energy of a fluid flow comprising a power support with a shaft, two pairs of coaxial semi-axes fixed perpendicular to each other at the upper end of the shaft, four rotor blades perpendicular to the semiaxes, a planetary mechanism with a housing comprising two pairs of coaxial bevel gears On the semiaxes, the central conical wheel fixed to the power support coaxially with the shaft, characterized in that the first pair of coaxial bevel gear wheels has two toothed crowns, and the second pair of coaxial bevel gear wheels has one gear ring, the larger gears of the first pair of bevel gears Are equal to the serrated crown of the central conical wheel and are in meshing with it, and the small serrated crowns of the first pair of conical wheels are equal to the gear rims of the second pair of conical wheels and are meshed with them, each pair of conical wheels having a coaxial driven shaft with a flange on which The pivoting blade is fixed perpendicular to the driven shaft, in addition, on each flange, a second pivoting blade is also installed perpendicular to the first blade, oriented in the opposite direction relative to the first blade.
2. The device according to claim 1, characterized in that the rotary blades are formed with a shape that excludes the possibility of their interaction with each other in any position of the shaft.
3. Apparatus according to claim 2, characterized in that the rotary blades are in the form of a sector with an arc less than a quarter of the arc of the forming circle.
4. The device according to claim 2, characterized in that the rotary blades are made in the form of rectangles with a rounded apex.
print version
Date of publication 02.02.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.