| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2292484
![]()
Wind turbine for wind turbine
The name of the inventor: Boris Petrovich Khozyainov (RU); Khozyainov Denis Borisovich (RU); Lobanova Milena Borisovna
The name of the patent holder: Khozyainov Boris Petrovich (RU); Khozyainov Denis Borisovich (RU); Lobanova Milena Borisovna
Address for correspondence: 650026, Kemerovo, ul. Spring, 28, Kuzbass State Technical University, Patent Department
Date of commencement of the patent: 2005.06.15
The invention relates to the field of wind power, in particular to wind turbines with a vertical axis of rotation of a wind turbine, and can be used for obtaining mechanical and electrical energy. The technical result consists in increasing the coefficient of wind energy use by wind turbine blades with a vertical axis of rotation due to changes in geometric parameters and aerodynamic coefficients of the blades. New in the wind turbine is that the tip of the wind turbine blade is equipped with a mechanism for a fixed change in the distance between its free ends. In addition, the tip of the blade is provided with stiffening diaphragms made in the form of two sectors rigidly fixed to the tip parts, one of the sectors wrapping the other with its edge with the possibility of sliding and pivoting around the hinge securing the two parts of the tip.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The claimed invention relates to the field of wind power, in particular to wind turbines with a vertical axis of rotation of the wind turbine, and can be used for obtaining mechanical and electrical energy.
A wind turbine is known, consisting of a wind turbine with a vertical axis of rotation, where each blade of the wind turbine contains a tip made in the form of an inlet part of the aerodynamic profile with a curved axis of symmetry along the circumference of rotation of its center of gravity and a freely rotating moving plane hinged on the vertical axis by means of rods, Having a length corresponding to the distance from the axis of rotation of the movable plane to the ends of the tip, the tip comprising two freely rotating parts connected by a hinge with a vertical axis of rotation located at the extreme entrance point of the tip where the extreme positions of the free rotation sector of each of the two parts are given Axis of symmetry of the tip and the position of the parts at which the contour of the input part of the formed aerodynamic profile is formed (see RU 2135823 C1, class F 03 D 3/04, 27.08.1999), taken as the closest analogue of the invention (prototype).
The disadvantage of this wind turbine is that the blade of the wind turbine can not be controlled under conditions of varying natural wind speed.
The technical result consists in increasing the efficiency of the wind turbine operation under conditions often changing in strength and in the direction of the wind flow due to remote control of the geometric and aerodynamic parameters of the blades perceiving the air flow.
This technical result is achieved due to the fact that in a wind turbine consisting of a wind turbine with a vertical axis of rotation, where each wind turbine blade contains a tip made in the form of an inlet part of an aerodynamic profile with a curved axis of symmetry along the circumference of rotation of its center of gravity and a freely rotating moving plane, Hinged on the vertical axis by means of rods having a length corresponding to the distance from the axis of rotation of the movable plane to the ends of the tip, the tip comprising two freely rotating parts interconnected by a hinge with a vertical axis of rotation disposed at the extreme entry point of the tip where the extreme The positions of the free rotation section of each of the two parts are defined by the axis of symmetry of the tip and the part position at which the outline of the input part of the formed aerodynamic profile is formed, according to the invention, the tip of the blade is provided with a mechanism for fixing the distance between the free ends of the tip. In this case, the tip of the blade is provided with diaphragms of stiffness made in the form of two sectors rigidly fixed on the tip parts, one of the sectors wrapping the other with its edge with the possibility of sliding and pivoting around the hinge securing the two parts of the tip.
 |
 |
 |
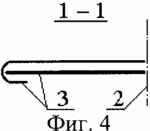 |
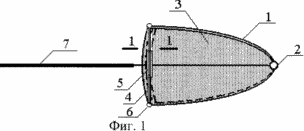
FIG. 1 shows a profile of a blade with elements for adjusting its geometric parameters when folded, acting predominantly at high wind speeds.
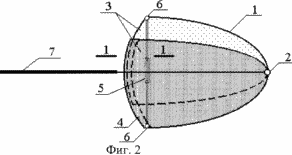
2 shows a profile of a blade with elements for adjusting its geometric parameters in a partially opened form, operating predominantly at average wind speeds.
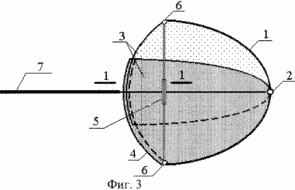
3 shows a profile of a blade with elements for adjusting its geometric parameters in an expanded form, operating at low wind speeds.
4 is a cross section 1-1 showing the circumference of one sector of the diaphragms to another.
A wind turbine with a vertical axis of rotation of a wind turbine equipped with blades that contain a tip 1 consisting of two parts connected by a vertical hinge 2 and a stiffening diaphragm 3. Each diaphragm consists of two sectors. One of the sectors of the diaphragm contains on the edge of the girth 4, in which the other sector of the diaphragm moves. The blade is provided with a mechanism 5 changing the distance between the free ends of the tip of the blade which is controlled remotely or in direct contact with it and fixed to the free ends of the tip parts by means of hinges 6. As such a mechanism, a lanyard provided with a radio controlled motor rotating the lanyard nut Or other such mechanism. In addition, the blade is provided with a stabilizing plane 7.
WINDROWER WORKS AS FOLLOWING
At low wind speeds, the airflow pressure on the blade is weak. Therefore, the free ends of the blade tip 1 are extended to the largest distance and thereby increase the blade area blown by the air flow. As a result of the increase in the area of the blade, the force acting on the blade changes, and accordingly the torque that rotates the wind turbine. As a result, the windmill starts to work at low wind speeds. With increasing wind speed, the wind turbine starts to rotate faster and a larger blade area with the open parts of the tip, having a large sail, starts to slow down the rotation. Therefore, it is more expedient to reduce the free ends of the tip by reducing the area of the blade. When reducing the free ends of the tip, the aerodynamic coefficients of the blade also change. The proposed design of the blade will allow to regulate its aerodynamic characteristics, to increase the efficiency of the windmill operation under conditions of varying wind speed.
CLAIM
1. A wind turbine consisting of a wind turbine with a vertical axis of rotation, wherein each wind turbine blade comprises a nozzle formed as an inlet to the aerodynamic profile with a curved axis of symmetry along the circumference of rotation of its center of gravity and a freely rotating movable plane hinged on a vertical axis by means of rods Having a length corresponding to the distance from the axis of rotation of the movable plane to the ends of the tip, the tip being comprised of two freely rotating parts interconnected by a hinge with a vertical axis of rotation disposed at the extreme entry point of the tip where the extreme positions of the free turn sector of each of the two parts Are defined by the axis of symmetry of the tip and the position of the parts at which the outline of the input part of the formed aerodynamic profile is formed, characterized in that the tip of the blade is provided with a mechanism for fixing the distance between the free ends of the tip.
2. Wind turbine according to claim 1, characterized in that the tip of the blade is provided with stiffening diaphragms made in the form of two sectors fixed rigidly on the tip parts, one of the sectors wrapping the other with its edge with the possibility of sliding and pivoting around the hinge securing the two Parts of the tip.
print version
Date of publication 02.02.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is monitored.