| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2292485
![]()
WIND-MOTOR WITH AIR-CONSTRUCTION
The name of the inventor: Boris Petrovich Khozyainov (RU); Khozyainov Denis Borisovich (RU); Lobanova Milena Borisovna
The name of the patent holder: Khozyainov Boris Petrovich (RU); Khozyainov Denis Borisovich (RU); Lobanova Milena Borisovna
Address for correspondence: 650026, Kemerovo, ul. Spring, 28, KuzGTU, Patent Department
Date of commencement of the patent: 2005.08.12
The invention relates to the field of wind power, in particular to wind turbines with a vertical axis of rotation of a wind turbine, and can be used for obtaining mechanical and electrical energy. The technical result consists in increasing the coefficient of wind energy use and reducing the material consumption in the manufacture of a wind turbine. A new feature in the wind turbine is that the tip and the movable plane of each wind turbine blade, support rings and wind control screens are made of film materials with different physical and mechanical properties in the form of one or more hollow sealed volumes filled with a gas mixture with different internal pressure that are connected between And form a volume of the desired structure that is additionally covered by the outer film along the boundaries of the structure, with newly formed gaps between the outer film and the previously formed volumes and are hermetically sealed and filled with a gas mixture of different internal pressures.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The claimed invention relates to the field of wind power, in particular to wind turbines, and can be used for obtaining mechanical and electrical energy.
The main task, the solution of which is directed to the claimed device, is to increase the efficiency of the wind turbine and reduce the material consumption in its manufacture.
A wind turbine is known, comprising a rotating wind turbine in the form of a vertical shaft with "collars" fixed to it, two or more horizontal structural-rod support rings covered with aerodynamic covers connected to the "collars" of the vertical shaft by means of cable inclined stretch marks, blades located between the support Rings, and located outside the wind turbine along the circumference of wind-guided screens freely rotating around the vertical axes. [Certificate of utility model No. 8740 U1 (EN) IPC F 03 D 3/06. Structural-cable wind turbine / Khozyainov BP, Khozyainov DB, Khozyainova G.Ya. No. 98103343/20; Declared. 24.02.98; Opubl. 16.12.98, Bul. No. 12].
The disadvantage of this wind turbine is that the structural-rod support rings and wind control screens have a large weight, which reduces the efficiency of the wind turbine.
A wind turbine is also known, consisting of a wind turbine with a vertical axis of rotation, where each blade of the wind turbine contains a tip made in the form of an inlet part of the aerodynamic profile with a curved axis of symmetry along the circumference of rotation of its center of gravity and a freely rotating moving plane hinged on the vertical axis by means of rods , Having a length corresponding to the distance from the axis of rotation of the movable plane to the ends of the tip [Patent of the Russian Federation for invention No. 235823 C1 (RU), IPC F 03 D 3/04 Wind turbine with blades "Bell" or "Ajax" / BP Hosts, Khozyainov DB, Khozyainova G.Ya. No. 98113538/06; Declared. 07/07/98; Opubl. 27.08.99, Bul. № 24 (prototype)].
The disadvantage of this wind turbine is that the wind turbine blade has a large weight and does not have sufficient stiffness.
The aim of the invention is to increase the efficiency of the windmill by reducing the weight of its structures.
This goal is achieved in that in a wind turbine comprising a rotating wind turbine in the form of a vertical shaft with "collars" fixed to it, two or more horizontal structural-rod support rings closed by aerodynamic covers connected to the "collars" of the vertical shaft by means of cable inclined stretch marks , Blades with tips made in the form of an inlet part of the aerodynamic profile with a curved axis of symmetry along the circumference of rotation of its center of gravity that are located between the support rings and placed on the outside of the wind turbine around the vertical free winding screens around the vertical axes, each wind turbine blade comprising a freely rotating movable A plane hinged on a vertical axis by means of rods, according to the invention, the tip and movable plane of each wind turbine blade, support rings and wind control screens are made of film materials with various physical and mechanical properties in the form of one or more hollow sealed volumes filled with a gas mixture with Different internal pressure, which are connected to each other and form the volume of the required structure, which is additionally covered by the outer film along the boundaries of the structure, the newly formed gaps between the outer film and the previously formed volumes are hermetically sealed and filled with a gas mixture with different internal pressures.
Each supporting ring has several hard-hanging profile belts with areas, to which the blades are attached, with the hanging rigid profile belts fitted with hinges for fastening the support ring to the "collars" of the vertical shaft with the help of cables.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
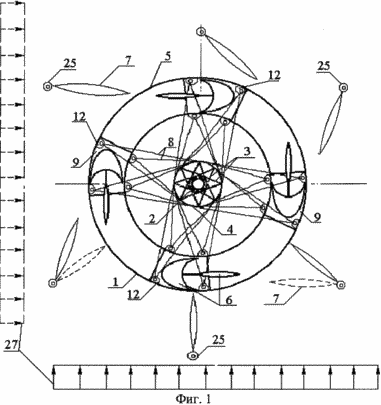
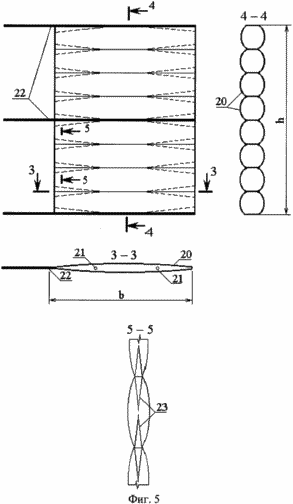
1 shows a wind turbine in a plan.
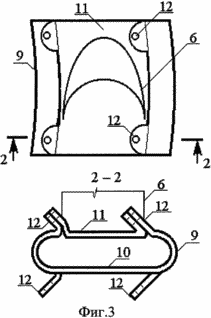
2 shows the attachment of the "collar" to the vertical shaft of the wind turbine. Plan and side view.
3 shows a hooking hard profile belt. Plan, cut.
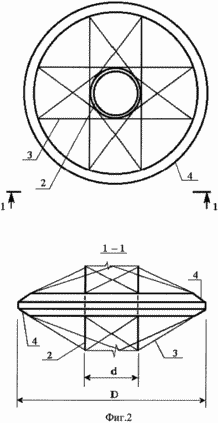
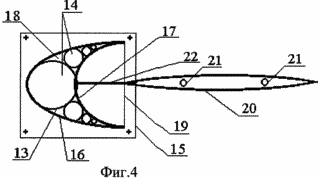
4 shows the profile of the blade.
FIG. 5 shows a design of a movable blade plane in which each end of the horizontal cylindrical element is folded into two vertical folds that form a narrowed profile along the vertical edges.
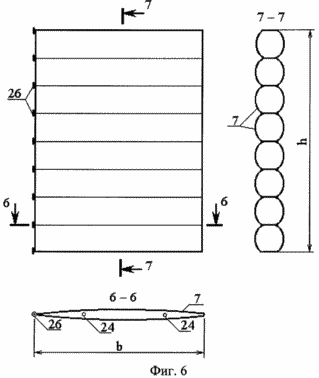
6 shows a construction of a wind control screen.
All the drawings show wind turbine designs made of a material with low stiffness (for example, capron 56026 with polyisobutylene coating).
The dashed line shows the position of the wind control screens when the direction of the wind changes by 90 °.
The wind turbine contains a wind turbine 1 with a vertical axis of rotation in the form of a vertical shaft 2 with 3 "collars" 4 fixed to it with metal rods 4, horizontal support rings 5 and blades 6. The support rings 5 are made of film materials with various physical and mechanical properties (for example , Kapron 56026 coated with polyisobutylene or aluminum foil) in the form of one or more hermetic hollow toroidal rings filled with a gaseous mixture with excess pressure inside. On the supporting rings 5 are fixed blades 6. Outside the wind turbine, around the circumference there are wind-guiding screens freely revolving around the vertical axes 7. The supporting rings 5 are fixed to the "collars" 4 by means of cable inclined stretches 8 and clasping rigid profile belts 9 that correspond to the section of the support ring 5 and Are made of a rigid light plate, for example an aluminum sheet. Bracing rigid profile belts 9 consist of a lower part 10 and an upper part 11 with a platform for fastening the blade. Belt 6 of wind turbine 1 can be made of film materials 13 with various physical and mechanical properties (for example, kapron 56026 coated with polyisobutylene or aluminum foil) and consists of several sealed load-bearing volumes 14, filled with a gas mixture with different excess pressure. Sealed load-bearing volumes 14 are arranged vertically, fixed to the areas of the upper portion 11 of the gripping rigid profile belts 9 by means of the end rigid plates 15. The sealed load-bearing volumes 14 are interconnected and form the profile of the tip of the blade 6 and are additionally coated with a surface film 16 along the boundaries of the blade profile in Form of a half-ellipse with a lower stiffness than the surface film 17 intended for making a semicircle, the material of which is highly rigid. The surface film 16 connected to the volumes 14 provides the desired profile of the convex portion of the tip of the blade, and the surface film fragment 17, and connected to the sealed carrier volumes 14, provides the desired profile of the inner concave surface of the tip of the blade. The formed spaces 18 between the sealed load-bearing volumes 14 and the surface film 16 and 17 are hermetically sealed and filled with a gas mixture with different internal pressures providing a predetermined blade profile. And to provide the desired shape of the blade along its length, diaphragms 19 are arranged in the form of membranes or rigid plates that do not intersect any of the hermetically sealed carrier volumes 14 and, by configuration, repeat the profile of the blade. The blade 6 is provided with a movable plane 20 made in the form of a set of horizontal cylinders. These horizontal cylinders can be made of materials with different physical and mechanical properties (for example, kapron 56026 coated with polyisobutylene or aluminum foil), filled with a gaseous mixture with excessive internal pressure providing spatial stiffness of the moving plane 20, since they are combined into a single volume at Assisting the holes 21 in the shell of the cylinders. They can also represent interconnected individual cylindrical volumes. The movable plane 20 of the blade 6 is attached to it by means of arms 22 fixed to the rigid plates 15 by means of hinges or to the diaphragms 19 in the form of rigid plates. To make the aerodynamic profile of the movable plane 20 of the blade 6 folds 23 are made, which ensure a narrowing of the profile to the vertical faces. The wind control screens 7, consisting of several hollow horizontal cylinders, narrowed along the vertical faces, are similar to the movable plane 20 of the blade 6, and can be made of materials with different physical and mechanical properties. The horizontal cylinders of the windscreen screens 7 can be combined into a single volume by means of holes in the shell of the cylinders 24. The wind control screens 7 are attached to the vertical post 25 by means of hinges 26 and can freely rotate in a predetermined sector under the influence of the airflow 27.
Wind turbine works as follows. When the wind appears, the airflow 27 is directed to the wind turbine 1 through the wind control screens 7, which, with a small mass, easily rotate in the given sector and occupy a radial position on the windward side of the wind turbine 1 in the zone of unfavorable wind on the blade 6. In the favorable air flow zone 27, The blades 6 within the wind turbine 1 the wind control screens are arranged parallel to the movement of the airflow 27 and at an angle thereto in the zone of favorable effect of the airflow 27 on the blade 6 falling outside the wind turbine 1. On the leeward side of the windmill, the wind control screens 7 occupy a position within the free turn sector , Contributing to a free air mass exit. The airflow 27, reinforced by wind control screens, on the blades 6 of the wind turbine 1, causes it to rotate. Since the mass of the entire wind turbine 1 is small, the launch of the wind turbine and its operation occurs at low natural wind speeds. This extends the time range of the wind turbine operation and increases its efficiency.
The claimed technical solution will allow to reduce the consumption of materials, to facilitate the design of the wind turbine, to increase the efficiency of the windmill and to reduce the laboriousness of its construction.
CLAIM
1. Wind turbine with air-bearing structures, containing a rotating wind turbine in the form of a vertical shaft with "collars" fixed on it, two or more horizontal structural-rod support rings covered with aerodynamic covers, connected to vertical shaft collars by means of cable inclined stretches, blades With tips made in the form of an entrance part of the aerodynamic profile with a curved axis of symmetry along the circumference of rotation of its center of gravity that are located between the support rings and located outside the wind turbine along the circumference of the wind-guiding screens freely rotating around the vertical axes, each blade of the wind turbine comprising a freely rotating moving plane, Hinged on the vertical axis by means of rods, characterized in that the tip and the movable plane of each wind turbine blade, supporting rings and wind control screens are made of film materials with various physical and mechanical properties in the form of one or several hollow sealed volumes filled with a gas mixture with different Internal pressure that are interconnected and form the volume of the desired structure that is additionally covered by the outer film along the boundaries of the structure, the newly formed gaps between the outer film and the previously formed volumes and are hermetically sealed and filled with a gas mixture with different internal pressures.
2. Wind turbine according to claim 1, characterized in that each support ring has several rigid profile belts surrounding it with areas to which the blades are attached, while the gripping rigid profile belts are provided with hinges for fastening the support ring to the "collars" of the vertical shaft by means of Guy.
print version
Date of publication 02.02.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.