| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2105190
![]()
VETROCOLESO
The name of the inventor: Petrov Yu.S.
The name of the patent holder: North Caucasus State Technological University
Address for correspondence:
Date of commencement of the patent: 1996.01.09
Usage: both in stationary and moving systems using wind energy. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION: A wind wheel comprising blades and a fixed axis is additionally provided with movable axes fixed to a fixed axis and latches fixedly mounted on each blade and a movable axis with the possibility of turning the blade through an angle (0-90) o with respect to this axis, Diametrically located blades are fixed in opposite directions.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to wind power, in particular to the wind wheel design, and can be used in the development of wind turbines or wind turbines.
A wind wheel is known [1], containing a vertical column with traverses, fixed vertical profiled blades fixed to them and a fixing device.
The disadvantage of this wind wheel is that its design does not allow changing the wheel parameters to increase the efficiency continuously in the process of its rotation, but does not allow choosing and realizing the optimal mode of the power plant in accordance with constantly changing external factors (wind speed, direction, ).
The closest to the claimed wind wheel is the construction of the VBL-3 wind wheel, which contains three blades of sheet steel, reinforced in the hub with ball bearings. The position of the blades can be adjusted by turning about the longitudinal axis from 7 to 2 o . When adjusting, the blades are rigidly fixed in one or another position. Regulation is carried out with the purpose of creating optimal working conditions for the wind wheel, increasing its efficiency.
The disadvantage of such a technical solution is that the regulation is carried out within narrow limits; It corresponds to a single regime of installation, a certain complex of aerodynamic factors. When these factors change, the parameters of regulation enter into contradiction with them and do not ensure the optimal operation of the power plant.
The task of the technical solution is to increase the efficiency of the wind wheel due to the fullest use of wind energy, and to improve the operational properties of the wind farm and the reliability of its operation.
The technical result consists in creating an additional degree of freedom, due to the possibility of turning the blade relative to its own axis during wheel rotation.
This technical result is achieved by the fact that the known wind wheel including the blades and the fixed axis is additionally provided with movable axes fixed on the fixed axis and fixators rigidly mounted on each blade and movable axis with the possibility of turning the blade at an angle (0-90) o relative to This axis, and on the diametrically located with respect to the fixed axis of the latch the locks are directed in opposite directions.
Due to this arrangement of the latches, rotation of the blades is possible in opposite directions, on one half of the axis - clockwise, and on the other - against. The axes can be two or more, which is determined, in particular, by the size of the blades. With any direction of the wind, the wheel rotates in the same direction, determined by the direction of the latches.
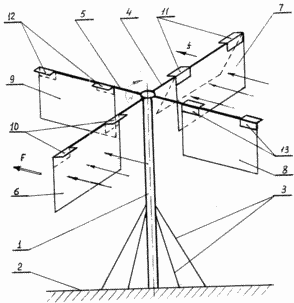 |
Such a design allows to increase efficiency, to use wind energy most fully, to increase the safety and reliability of the wind farm. The essence of the installation is explained by a drawing on which a wind turbine is schematically depicted which consists of a fixed axis 1 fixed at the base 2 by means of cables 3. At the top of the fixed axis 1, movable axles 4, 5 are rotatably mounted around it, on which the blades 6 , 7, 8, 9 with rigidly fixed fasteners 10, 11, 12, 13. Blades 6, 7, 8, 9 are fixed in such a way that they can rotate about their axis by an angle of up to 90 ° . |
THE WIND WHEEL WORKS AS FOLLOWING
When wind is directed along arrow F (see drawing), it blows parallel to axis 5, and no forces act on blades 12, 13 that could create a torque. The rotational moment is created by the forces of wind acting on the blades 6, 7, and the force F acts on the blade 6, tending to turn the axis 4 clockwise, and the force f (indicated in the drawing by the arrow) will act on the blade 7, tending to turn the axis 4 counter-clockwise Arrows. Resistance to the wind will have the entire surface of the blade 6, tk. It is located perpendicular to the wind and can not turn towards the direction of air movement. Is prevented from turning to this side by means of locks 10 rigidly fixed to the movable axis 4.
Blade 7, initially and located perpendicular to the wind, will turn under its action relative to its own axis by an angle of 90 ° , because The locks 11 are directed in the direction of the wind and do not exert any resistance to the rotation of the blade. Turning the blade in the direction of the wind will reduce its resistance to the moving flow of air. Blade 7 will rotate to such an angle that the torque generated by its weight is balanced by the torque generated by the moving air flow. Blades are made of light material, for example, canvas, filter cloth, etc.
When the blade 7 is deflected by an angle close to 90.degree . , It will have a very small resistance (at 90.degree . It will go to zero) to the rotation of the axis 4. The rotational torque produced by the blade 6 will be much greater than the counter-torque created by the blade, Rotation of the whole system by a certain angle, and when the whole system rotates by an angle of 90 ° , the position of the blade 6 takes the blade 8 and the position of the blade 7 is the blade 9. Next, the blades 8 and 9 repeat the action of the blades 6, 7.
In the event that the wind changes direction to the opposite (in relation to the example considered above), then the wind resistance and, consequently, the torque will create a blade 7, the latches 11 of which do not allow it to turn counterclockwise. Blade 6 will deflect to a certain angle and create a slight counteracting moment.
The blade system will continue to rotate the moving axes 4, 5 in the same direction (clockwise). Thus, with the wind direction reversed, the reverse system will continue to rotate without changing direction.
This factor of maintaining the direction of rotation of the wind wheel, regardless of the direction of the wind, is very important, because Creates conditions for the maximum selection of wind energy regardless of the change in its direction.
When the blades rotate, each of them turns alternately (at an interval of 180 ° ), working in the entire area of the blade, and each turns alternately braking, but on an insignificant part of the blade area, thereby creating a torque.
The proposed design of the wind wheel is significantly different from the known windlasses in that the blades have an additional degree of freedom, i. E. They can turn around their own axis during the rotation of the wheel.
The range of generated power can be very wide depending on the area of the blades and the wind speed. The power plant can be designed for a different set power.
The proposed design can find application both in stationary installations, and in mobile and moving, for example, in boats driven by a wind wheel (instead of a sail).
Using the proposed design will allow, in comparison with the prototype, to increase the efficiency of the wind wheel, the operational properties of the wind farm; Safety and reliability of its operation.
CLAIM
A wind wheel comprising vanes and a fixed axis, characterized in that it is additionally provided with movable axes fixed on a fixed axis and fixatives rigidly mounted on each blade and a movable axis with the possibility of rotating the blade at an angle of 0 to 90 ° with respect to this axis, and diametrically Located blades fixators are directed in opposite directions.
print version
Publication date 17.02.2007gg




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.