| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2136958
![]()
wind power generating apparatus
With pneumatic power transmission and WAY PNEUMATIC POWER TRANSMISSION DEVICES In VETROPRIEMNYH
Name of the inventor: Malishkin Victor M.; Sergey Kalashnikov
The name of the patentee: Malishkin Victor M.; Sergey Kalashnikov
Address for correspondence: 392000, Tambov, ul.M.Gorkogo 16 kv.7, Kalashnikov Sergey Petrovich
Starting date of the patent: 1998.05.14
The invention relates to wind energy, namely wind power gearless motors for wind power and generate electricity. The technical result consists in providing evenly distributed transmission of the wind flow of the reaction from the propeller blades to a power generator, eliminating the torque conversion and transmission devices, reducing device weight and installation, is achieved by the fact that wind power device with a pneumatic power transmission, comprising a horizontal axis of rotation, an air turbine , generator, control, and wind wheel system according to the invention comprises a central bearing, the energy concentrator as an input tapered conical diffuser, annular rotating rim propeller coupled with blades operated valves connecting the internal cavity of the rim and / or the atmosphere of the blades, the blades of wind wheel have an arcuate shape with a trough in the direction opposite to the direction of rotation. In the method of the pneumatic power transmission, consisting in pumping the air turbine through the air flow generated in the hollow propeller blades during rotation according to the invention the air stream is captured on the periphery of the rotating wind wheel and passes through the wind wheel in the direction from the periphery to the center of rotation at a pressure greater than atmospheric.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Wind power generating apparatus with a pneumatic power transmission relates to wind energy, namely wind power to the gearless motors for wind power and generate electricity.
It is known wind power device with a pneumatic power transmission, comprising a horizontal axis of rotation, an air turbine, generator, control system and wind-wheel, taken as a prototype. (See. Ya Shefter "The inventor of the wind turbines and wind turbines", M., publisher of the Ministry of Agriculture of the USSR, 1957, p. 53-54, Fig. 43).
The disadvantages of the described device are lower efficiency of the device, the presence of external loads acting on the structure of the blades due to the vacuum in the working cavity of the wind wheel, a large consumption of materials, massiveness.
A method is known pneumatic power transmission devices vetropriemnyh comprising pumping air through a turbine air flow generated in the hollow propeller blades during rotation adopted as prototype (see. SU 55996, cl. F 03 D 1/00, 30.11.39).
The technical result consists in providing evenly distributed transmission of the wind flow of the reaction from the blades of the wind wheel to the electric generator, eliminating the torque conversion and transmission device, reducing the weight of wind energy devices, simplifying the mounting structure of wind power devices, the use of wind energy to bring the propeller to the operating position, reducing the cost of electricity It is achieved in that the wind power generating device with pneumatic power transmission, comprising a horizontal axis of rotation, an air turbine, an electric generator, control, and wind wheel system according to the invention comprises a central bearing, energy kontsetrator as input a tapered conical diffuser, annular rotating rim propeller coupled with blades controlled valves connecting the inner rim of the cavity and / or to the atmosphere of the blades, wherein the propeller blades have an arcuate shape with a trough in the direction opposite to the direction of rotation. In the method of pneumatic power transmission, consisting in pumping the air turbine through the air flow generated in the hollow propeller blades during rotation according to the invention the air stream is captured on the periphery of the rotating wind wheel and passes through the wind wheel in the direction from the periphery to the center of rotation at a pressure greater than atmospheric.
The invention is illustrated by drawings, in which:
 |
 |
 |
 |
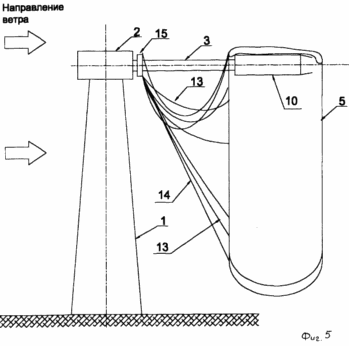 |
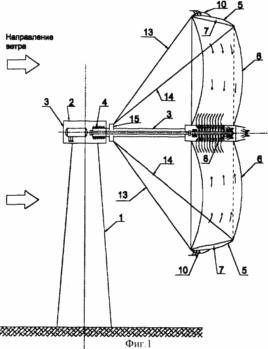
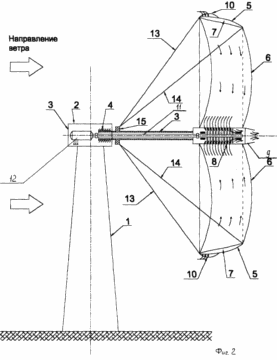
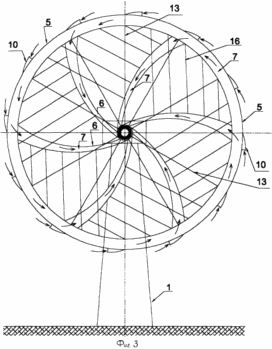
FIG. 1 - wind power generating device in the operating position; FIG. 2 - the transmission power of the pneumatic circuit (longitudinal section); FIG. 3 - pneumatic power transmitting circuit (cross section); FIG. 4 - mounting diagram of the device of the blades front and rear extensions; FIG. 5 - wind power generating apparatus in the inoperative position. The proposed wind power generating device with pneumatic power transmission tower comprises a base 1 (FIG. 1) with a rotary assembly for orienting the propeller 2 on the horizontal axis 3 in the direction of the wind. Hollow horizontal axis 3 rotates on the central bearing 4 placed in the rotary unit 2 (FIG. 2). Wind wheel made of rigid, semi-rigid or flexible airtight material, for example of a fabric diffuser contains amplifier 5 as an annular rim encompassing the blade 6 (Fig. 1). Annular rim 5 and blades 6 are communicating longitudinal cavity 7, which are connected to the receiving aerial 8 turbine nozzle 9 (Fig. 3). On the outer perimeter of the annular rim 5 are controlled air valves 10 through which the internal cavity of the rim 5 connected to the atmosphere. 6 propeller blades (on a side of the wind flow) have an arcuate shape with a trough in the direction opposite to the rotation direction and rotation of the propeller at providing charge air movement along the longitudinal cavities 7 in the periphery of the blades 6 to the air turbine 9. The turbine 9 is placed on a horizontal axis 3 and connected to a shaft 11 extending along the axis of the inner cavity 3, with an electric generator 12 which can operate as a power generator mode and a motor mode. Generator 12 is disposed in the rotary unit 2 (FIG. 2). |
For fixing and holding the propeller in the operating position, it comprises a radially extending front and rear cables 13, the cables 13, 14. The front cables are suspended from one end of the front edge of the rim 5, and the other end on the flange 15 the horizontal axis 3. The rear cables 14 are suspended from one end to the rear the edge of the rim 5, and the other end on the flange 15 the horizontal axis 3. The lengths of the front and rear cables 13 and 14 determine angle of attack of the rim 5 to the incoming wind flow, which is determined depending on the required amount of the diffuser conicity amplifier.
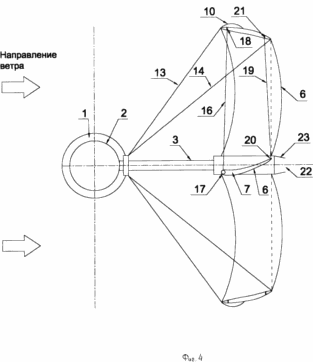
Front extensions 16 are attached at one end to an intermediate point of the front edges 17 of blades 6, and the other end to the front stiffener rim 18 5 in the opposite direction of the wind flow of the reaction (Fig. 4). The rear extensions 19 are attached at one end to intermediate points of the trailing edges 20 of the blades 6 and the other end to the rear stiffener 21 of the rim 5 in the direction opposite to the wind flow reaction. The lengths of the front and rear extensions 16 and 19 define the angle of attack of the blades 6, which is set depending on the wind speed, the radius of the considered cross-section of the blade 6 and the desired angular velocity of the wind wheel.
Along the perimeter of the outlet nozzle 22 (FIG. 2) air turbine 9 placed swiveling regulating valve 23, which allow you to change the output of the nozzle cross-sectional area 22 and to adjust the amount of air passing through the air turbine 9. Management regulating valves made of automatic control system (not shown in the diagram ).
The wind wheel inoperative position under its own weight and sags formed on the axle 3 and the cables 13, 14 and extensions 16 and 19 in the state shown in FIG. 5.
Wind power generating apparatus for driving a working position in the electric motor 12 is switched mode and rotates the air turbine 9. The turbine 9 while rotating the closed valves 10 injects air from the atmosphere into the internal cavity 7 of the blades 6 and the annular rim 5. Under the influence of excess pressure air inflation occurs and the formation of propeller with aerodynamic shape blades 6, necessary and sufficient for its unwinding under the influence of the incoming wind flow. As the angular velocity of the wind wheel by centrifugal force continues its deployment in the body of revolution shape, its stiffness increases. After reaching the calculated angular propeller speed at which blade 6 and an annular rim 5 propeller acquire the desired shape, the automatic control system stops the forced rotation of the turbine 9, the valves 10 are opened on the outer contour of the rim 5. Wind wheel, rotatable wind flow through the valves 10 grips the outside air and pumps it into the internal cavity 7 of the rim 5. From the inner cavity 7 of the rim 5 of forced air flow by longitudinal channels in the blades 6 is fed to the inlet 9 of the turbine nozzle, passes through the turbine 9 causes it to rotate through the rear nozzle and exits to the atmosphere. The turbine 9, the rotatable air flow drives the generator 12 that produces electricity.
When changing wind flow direction for the two swivel orientation axis 3 of rotation of the wind propeller rotates toward the right direction in electromotive Command control system (not shown in the diagram).
When changing the wind speed within the operating speed range can be controlled by several parameters windwheel: changing the shape and / or size of the diffuser amplifier (rim 5) change the angles of attack of blades 6, by varying the amount of air flowing through the cavity 7 and the turbine 9.
Changing the shape and dimensions of the diffuser of the amplifier by varying the length of radial front and rear cables 13 and 14. For example, increasing the length of the rear cables 14 at a constant length of the front allow wires 13 to move under the action of wind point rear edge of the rim 5 points relative to the front edge and reduce the angle of attack rim to the air flow. Increasing the angle of attack of the rim 5 and therefore the wind flow concentration produced an increase the length of the front wires 13 and / or decreasing the length of the rear cables 14.
The angles of attack of blades 6 regulated by changing lengths of the front and rear extensions 16 and 19. For example, reducing the length of the front stretch 16 leads to a shift of the leading edge 17 toward the blade 6 to the rotational axis and relative to the trailing edge 20 and, consequently, reduce the angle of attack relative to the oncoming flow air. Reducing the length of the rear extensions 19 results in displacement of the trailing edges 20 of the blades 6 in the direction of the rotational axis and relative to the front edge 17 and, consequently, an increase in the angle of attack the blade 6 relative air flow.
With an increase in wind flow velocity is an increase in speed and the amount of air pumped through the turbine 9 and a corresponding increase in the air turbine speed elekrogeneratora 9 and 12, which could affect the quality of the generated electricity. Therefore, to maintain the frequency of rotation of the turbine in a predetermined range 9 automatic control system closes the valve 21 by reducing the sectional area of the outlet nozzle, and reducing the amount of air passing through the turbine 9, and the air speed of the turbine decreases accordingly 9 and 12. When the power generator reducing the wind velocity air valve 21 open, increasing the area of the outlet nozzle section, the amount of air passing through the turbine and 9, respectively, is increased speed air turbine power generator 9 and 12.
With a sharp increase in wind speed up to values exceeding design (working) automatic control system closes the valves 10 on the annular rim 5 comprises an electric 12 mode electric motor powered by a backup source and fully opens the regulating valve 21 in the outlet nozzle air nozzle air turbine 9. Rotating air turbine 9 produces in the internal cavities of the blades 6 and 7 the annular rim 5 vacuum (below atmospheric pressure), under the effect of a higher atmospheric pressure geometrical dimensions of the blades 5 and rim 6 are reduced and hence the drag decreases the wind flow. When propeller elements some flexibility is its folding to a safe position.
CLAIM
1. Wind power device with pneumatic power transmission, comprising a horizontal axis of rotation, an air turbine, an electric generator, and a wind-wheel control system, characterized in that the device comprises a central bearing hub energy input in the form of a tapered conical diffuser, annular rim rotating propeller connected to the vanes controlled valves connecting the inner rim of the cavity and / or to the atmosphere of the blades, wherein the propeller blades have an arcuate shape with a trough in the direction opposite to the direction of rotation.
2. A method in a pneumatic power transmission devices vetropriemnyh comprising pumping air through a turbine air flow generated in the hollow propeller blades during rotation, characterized in that the air stream is captured on the periphery of the rotating wind wheel and at a pressure greater than atmospheric, passing through in the direction of the wind wheel from the periphery to the center of rotation.
print version
Publication date 18.01.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.