| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2050466
![]()
Wind turbine and hydro
Name of the inventor: Fedchishin Vitaly G.; Fedchishin Alexey V.
The name of the patentee: Fedchishin Vitaly G.; Fedchishin Alexey V.
Address for correspondence:
Starting date of the patent: 1992.04.27
Use: in the wind industry to create new types of stationary and transport of wind and hydro. The inventive wind turbine is provided with a conical central nonrotating pinion connected via the satellite link in the form of a two-part shaft planted on its end bevel gears, the shafts of which pairs (top and bottom) are fixed blade, and both sides of each of the satellite shafts connected releasable clutch movable sleeve through which a pusher, a tapered sleeve, the cam box and connected with a non-rotating central axis on which the top of the bracket is rigidly fixed to the contact groups associated with two springs freely placed on the central axis of the vane. When used as a wind turbine hydrogenerator he has hermetically sealed with a shortened cone sleeve to the central axis and closed on top of the gearbox casing airtight lid.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to wind energy and hydropower, and can be used to create new types of stationary and transport of wind and hydro.
Known orthogonal wind turbines with a vertical axis of rotation of the rotor [1] convert lift for fast-moving circle fixedly secured profiled (more than two) blades in pulling force characterizing torque.
Known and wind turbine [2], containing slanted rotary blade, kinematically connected with the central non-rotating gear transmission ratio of 2: 1.
However, such kinematic constraints and design solutions do not provide the cycloid trajectory of rotation of vertically arranged blades. This wind turbine [1] requires the initial and each subsequent calm after the forced acceleration of the rotor to the desired speed, and at higher speeds creates harmful to biological objects (primarily birds and bees) infrasonic vibrations and noise. The wind turbine [2] lower part of the blade works with a high efficiency.
The aim of the invention is to increase torque at lower rotor speeds, increased reliability in operation by the spontaneous reversal of the blades at the downstream Burevoi wind speeds and the possibility of using as an autonomous hydrogenerator.
This object is achieved in that the vanes additionally arranged in pairs (top and bottom) at the bracket ends and oriented planes towards conventional vertical lines lying on the generator from the rotation of their axes, while the kinematic linkage bevel gear of each double blade the central conical nonrotating pinion performed gear sum ratio i i i 1 · February 2: 1 ( ![]() on January 2
on January 2 ![]() 2) by means of a satellite two-part shaft planted on its end bevel gear (for example, when the six-bladed rotor sum i · 0.5 Feb. 4, while chetyrehlopastnym isum 0.8 x 2.5 2).
2) by means of a satellite two-part shaft planted on its end bevel gear (for example, when the six-bladed rotor sum i · 0.5 Feb. 4, while chetyrehlopastnym isum 0.8 x 2.5 2).
Separation of the satellite shafts with wind speeds Burevoi carried introduced a spring-loaded swivel flag with axial eccentric sleeve, pushers and detachable sleeves. Releasable coupling parts have a through slot and can engage only about 180, so the blade always retain the desired orientation.
Freely placed on top of the central axis of the non-rotating vane is held by two springs in a neutral position between the contact groups attached to rigidly associated with this axis bracket.
When using the wind turbine as a hydro generator it is sealed, the blades are shortened and reinforced, the upper part of the non-rotating axis is shortened to tapered sleeve that is placed inside the rotary gear and closes tight cover and disconnect the satellite shafts for preventive or emergency stop of the unit is carried out outside the operator panel by a control the voltage across the set instead of the cam solenoid plunger.
There are no known sources of patent and scientific and technical information, containing information on similar technical solutions, with features similar to the features distinguishing the claimed solution from prototype, and properties that match the properties of the claimed solution, so we can assume that it has significant differences, enable the practice of creating a new type of efficient wind energy converter or water flow.
 |
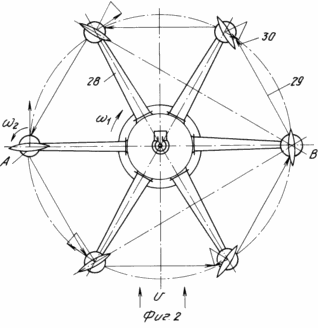 |
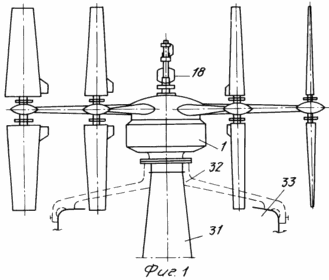
1 shows a side view of a wind turbine on the windward side; FIG. 2 shows a plan view and a distribution of torques depending on the location and orientation of the blades.
 |
 |
 |
 | ||
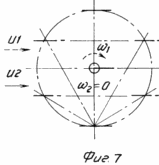 | ||
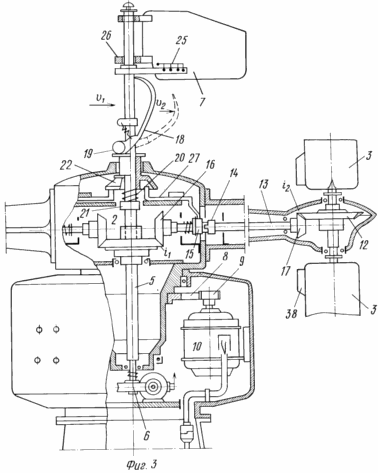
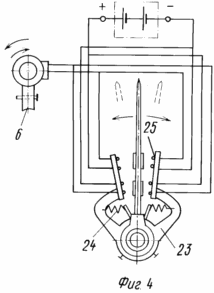
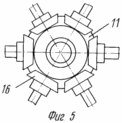
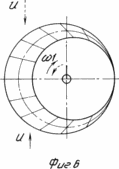
3 illustrates the internal and external kinematic connection; 4 electrical circuit unit self-aligning to the wind; Figure 5 a top view of the arrangement of bevel gears encircling around the central non-rotating gears in the six-bladed rotor; 6 is a diagram of change in torque (or driving force) generated by the rotor blade in one turn and a half-turn around its own axis in the opposite direction; 7 orientation of the blades on the flow at Burevoi wind speeds.
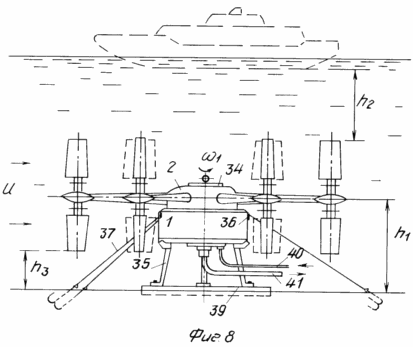
Figure 8 shows an embodiment of using a wind turbine (in the sealed design with reinforced blade design) as a stand-alone hydro generator.
Wind turbine comprises a housing 1, the gearbox 2, blade 3, the axis of which is kinematically connected by means of gears with a central non-rotating gear 4 with planted on it axis 5, block bottom worm gear 6, a top-mounted vane 7, drive cylindrical gear 8, which is in permanent or alternately engaged with the gears 9, 10 of energy transducers. Wind turbine further comprises a cone (instead of cylinder 4) the central non-rotating gear 11, kinematically associated with each of the driven bevel gear 12 via a satellite link, designed as a two-part shaft 13 comprising the junction of the split sleeve 14 with the movable sleeve 15, and at the ends tightly planted bevel gears 16 and 17. on the axis 5 has a spring-loaded rotary box 18 with cam 19, spring 20, locking ring 21, collet 22, the bracket 23 with the springs 24 and 25 contact groups, on top of the axle 5 freely located in two 7 vane bushings 26 connected to the spring sleeve 24. The bottom cone 22 arranged circumferentially pushers 27 included in the movable bushing 15 slots split sleeves 14. The three blades for wind load balancing pairwise located (top and bottom) at the ends of arms 28, which are connected each other in forming ropes 29, pulls turnbuckles 30. When using a wind turbine without a mast 31, it can be retrofitted with fixing platform 32 to 33 water towers, wind on the open rooftops or any other elevations.
The subsea performance in the upper part 2 is placed sealed gear cover 34, the housing 1 is provided below the supports 35, and side braces 36, in which a banner anchor cables 37 are connected.
Wind turbine works as follows
Initially, the blade 3 are set and locked with the orientation of the planes on the line (for example, passing through the point B, Figure 2). The bracket 23 is fixed on the axle locking screws 5 in the state in which the weather vane is perpendicular to the plane 7 the line AB.
Displacement of the locking ring 21 exhibiting tension springs 20 corresponding actuation flag 18 when the Burevoi (or other fixed) wind velocity, thus released from engagement all blades for wind pressure on the unbalanced flaps 38 are deployed downstream, without causing him a drag and preventing the wind turbine against breakage.
By reducing the wind speed up to 19 working eccentric values rising up flag 18 relieves pressure on the cone sleeve 22 and the pushers 27, which allows the movable sleeve 15 back to enter into engagement, bringing the wind turbine to its original state.
The hydrogenator (8) after its installation in the area of continuous flow fixing poles 35 and 39 based on the stretching anchor wires 37 via a cable 40 is energized to drive worm gear 6, by which exhibit the desired orientation of the blades 3 by analogy with that shown in 2.
Stop hydraulic generator can be carried out in two ways: by applying voltage cable 40 to the solenoid plunger, a turn worm gear blades 6 3 90 (the first method is more preferable).
Generated hydrogenerator electricity through the power cable 41 is supplied to the consumers. Since unlike stable enough air flow rate for the flow of water, in this case it does not require the use of special stabilizers, voltage and frequency.
CLAIM
1. Wind turbine comprising a housing within which the central gear set, a reinforced central part of the shaft, the lower end of which is connected with the worm gear to provide a braking shaft and the upper end of a vane, the vane, which are connected to the axis of the gears, and the drive gear, associated with the gear energy converters, characterized in that it is provided with the satellite links, each of which is designed as a two-part roller with bevel gears at its ends, some of which are associated with a central gear made conical, and the other with a gear axis diametrically disposed vanes releasable coupling with a movable sleeve and the plunger, conical sleeve and eccentric with a flag and a flag with the eccentric and cone sleeve mounted on the shaft between the vane and the central bevel gear and two roller sections are interconnected by a releasable coupling, which is connected with the plunger cone sleeve.
2. Wind turbine according to claim 1, characterized in that it is provided with contact groups bracket rigidly secured to the shaft and connected by means of two springs with the vane.
3. Wind turbine according to claims. 1 and 2, characterized in that it is provided with a platform on which the reinforced body.
4. Hydraulic generator comprising a housing which is installed inside the shaft, the lower end of which is connected to the worm gear shaft to provide a braking blades which are connected to the axis of the gears, and the drive gear associated with the gear energy converters, characterized in that it is provided with a central gear, strengthened in the central part of the shaft, the satellite links, each of which is designed as a two-part roller with bevel gears at its ends, some of which are connected to a central gear, made conical, and others with the gear fixed to the axis diametrically opposite blades of the split sleeve a movable sleeve and the electromagnetic plunger and tapered bushing, the conical bushing mounted in the housing above the center shaft bevel gear, the roller and the two sections are interconnected by a releasable coupling, wherein the solenoid plunger is associated with the cone sleeve and the gear is formed with a tight cover.
print version
Publication date 17.03.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.