| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2294452
![]()
Wind turbines with a rotation around the vertical axis
Name of the inventor: Vysotsky Rusinov (RU); Ilyasov Gennadiy (RU); Kovalev Ivan
The name of the patentee: State Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education Saratov State Technical University (CSTs)
Address for correspondence: 410054, Saratov, Polytechnique, 77, Saratov State Technical University, Department of ITIS
Starting date of the patent: 2005.08.09
The invention relates to wind energy. The technical result is to increase the effectiveness, efficiency, reliability and power of a wind turbine. Wind motor with a rotation around the vertical axis comprises a rotor rotatable by the wind around its vertical axis relative to the horizon, and the rotary shaft connected to the rotor with a possibility to bring it into a rotational movement that rotor and adapted for transmitting the energy obtained from the wind by this a rotor which comprises a cylindrical body, hollow inside vertical elements mounted on its lateral surface in a vertical plane so that the wind was able to set in motion the cylindrical body, a and rotary transmission shaft is associated with a cylindrical body, comprising at least one or more cylindrical elements mounted above one another and provided with vertical elements located on the lateral surface of the cylindrical members in the vertical plane so as to form an ordered series wherein the vertical elements of each successive cylindrical elements form a subsequent row of vertical elements placed directly above the vertical elements of the previous row, each cylindrical member of a cylindrical rotor body formed in a hollow interior of the drum with vertical elements fitted to the side surface and are constructed as blades, designed as a part of the cylindrical surfaces arranged bulge during rotation of the rotor, wherein the motor is provided with guiding air Feed apparatus, the stator having at least one or more sections arranged one above the other, in each of which one cylindrical rotor element is arranged and each of which comprises a circular rigid upper and lower bases, between which the vane to form an ordered series , the blades of each successive section of the stator form a subsequent row of blades arranged on the previous close vanes previous stator section, moreover, each of the blades is designed as a part of the cylindrical surface of curvature larger radius than the radius of curvature of the blades, the blades are set bulge during rotation of the rotor, and the number of blades of each stator section to twice the number of rotor blades each cylindrical element arrangement pitch and the last half the arrangement pitch of the blades, which are arranged one after the rotor blade.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to wind power engineering, namely to wind turbines with a rotation around the vertical axis.
Known wind turbine (see. Patent number 2,065,992, publ. 1996.08.27, IPC F 03 D 3/00), comprising a vertical shaft and a wind wheel (rotor) blades, fixed at an angle to the radius of the wind turbine. The shaft is kinematically connected to an electric generator, a wind wheel blades is designed as a crown with a U-shaped groove, and mounting angle of the blades 600 are formed between the blades and pockets. Propeller blades are flat and the incoming flow of air as it strikes them as well, going to the blades, the air flow in the opposite half of the rotor again strikes the blades thereby inhibits the rotation of the rotor. All this leads to a decrease in engine power.
Known wind turbine with rotation around the vertical axis (see. № Patent 2,165,034, publ. 1999.06.10, IPC F 03 D 3/00) comprises a rotor rotatable by the wind around its vertical axis relative to the horizon, and the rotary shaft, associated with the rotor with the possibility of bringing it into a rotational movement that rotor and adapted for transmitting the energy obtained from the wind by this rotor which comprises a cylindrical body, hollow inside, the side walls are formed by the vertical elements in the form of flat blades mounted so as to wind I was able to enter into the hollow inside of the cylindrical body and bring it into a rotational movement, but also a rotary transmission shaft to which the housing is connected, wherein the cylindrical body comprises at least one or more cylindrical elements mounted on each other and rigidly interconnected is, each of the cylindrical bodies comprises a lower circular and rigid portion and a top circular and rigid part, between which are fixed vertical elements in the form of cylindrical blades disposed upright so as to form an ordered series of blades, with the blades of each successive tubular element form a subsequent number of blades, located directly above the previous close.
This design of the wind turbine is simple for installation, easy maintenance, by increasing the volume of the engine vertically on the same basis increased its capacity, but the device does not allow to create a directional whirling air flow, resulting in a reverse torque at the output of the air flow the hollow cylindrical during its passage through the rotor housing gap between the same blades, which leads to a significant reduction in the power of the wind turbine.
The object of the present invention is to increase engine power by eliminating reverse torque due to the creation of conditions for directional swirl airflow.
The problem is solved as follows in windmills with rotation around the vertical axis, comprising a rotor capable of rotating under the action of the wind on its vertical axis relative to the horizon, and the rotary shaft connected to the rotor with a possibility to bring it into a rotational motion that the rotor and adapted to energy transfer, resulting from the wind by this rotor which comprises a cylindrical body, hollow inside, vertical elements fitted on its lateral surface in a vertical plane so that the wind was able to set in motion the cylindrical body, a and rotary transmission shaft, with which is connected a cylindrical body comprising at least one or more cylindrical elements mounted above one another and provided with vertical elements located on the lateral surface of the cylindrical members in the vertical plane so as to form an ordered series wherein the vertical elements of each subsequent cylinder member formed after a series of vertical elements placed directly above the vertical elements of the previous row, each cylindrical member of a cylindrical rotor body formed in a hollow interior of the drum with vertical elements fitted to the side surface of the drum and are constructed as blades, designed as a part of a cylindrical surface arranged bulge during rotor speed, the engine being provided with a guide airflow apparatus, the stator having at least one or more sections arranged one above the other, each of which is placed a cylindrical rotor element and each comprising a circular rigid upper and lower bases , between which blades, forming ordered rows, the blades of each successive stator sections form a subsequent row of blades arranged on the previous close vanes previous stator section, moreover, each of the blades is designed as a part of a cylindrical surface mounted bulge during rotation of the rotor , the blades have a radius of curvature, more than five times the radius of the rotor blades, and the number of each stator vane section exceeds the number of blades positioned therein each cylindrical rotor element at least twice.
The proposed wind turbine design has the advantages of the prototype, and it is possible to increase the volume of the engine vertically and thus increase the capacity of the device. The disadvantage of the prototype - the occurrence of reverse torque and, consequently, reducing engine power - the proposed design of the engine is not at the expense of creating a provisional "spin" of the air flow, which allows to make use of the engine guide vanes of the proposed design. Execution of the stator blades and rotor blades in the cylindrical surface as part of their orderly arrangement of structural eliminates energy loss airflow as it passes into the inner space of the rotor, and that affects the increase of engine power as a whole.
The invention is illustrated by drawings.
 |
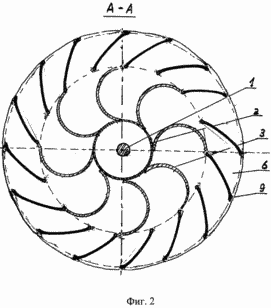 |
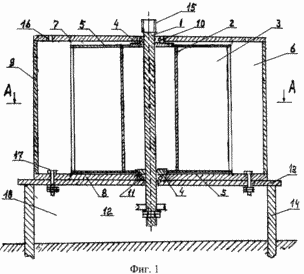
1 schematically shows a vertical section of a single cylindrical member of the rotor housing, disposed in the stator section. 2 is a section along A-A of Figure 1
The proposed wind turbine includes a rotor body of cylindrical elements, one of which is represented in section in Figure 1. A cylindrical rotor member mounted on the drive shaft 1 of a cylindrical drum 2 on the side surfaces of which are reinforced vertical elements 3 in the form of blades, which are part of the cylindrical surface is convex towards the rotor during rotation. The cylindrical drum 2 rotor attached to the shaft 1 by means of flanges (upper and lower) mounted on the upper and lower ends of the cylindrical drum 2, which together with the blades 3, reinforced stringers 5, located in the stator section, comprising guide vanes 6, the radii of curvature more than five times the radius of the rotor blades, each of which represents a portion of a cylindrical surface, the convexity directed along the rotation of the rotor. The vanes 6 are mounted between the base 7 and the upper 8 and lower reinforced connecting struts 9. The drive shaft 1 is mounted in an upper position at the support bearing 10 mounted on the upper base 7 of the stator, and a lower position in the shaft 1 mounted supporting thrust bearing 11 mounted in the lower base 8 of the stator. To remove the torque rotor shaft 1 fixed pulley 12, located under the base plate 13 of the engine mounted on supports 14.
When increasing the engine size in the case of vertical drive shaft 1 precast provided coupling 15. By connecting the stator section subsequent to its lower base and the upper base in the previous section stator provided holes for fastening the stator 16. The bottom section is attached at its lower base to the base plate engine 13 by bolts 17. it is possible that the upper base of the previous section of the stator and the lower stator base subsequent sections are integrally formed.
WORK wind turbines are as follows
In the presence of wind at a speed equal to or higher than the calculated one, the rotor is driven by the difference of moments of aerodynamic forces acting on the concave and the convex side of the blades 3 of the rotor. The torque of the rotor increases in the presence of pre-swirl of air flow in the stator due to the influence of the air flow 6 of the stator blades, playing the role of the guide apparatus, and is transmitted actuated energy consumer units via the shaft 1 and mounted thereon another pulley 12 or other gear. Rotating the rotor shaft 1 in bearings 10 and 11, substituting the frictional force on the rolling forces, which increases the mechanical efficiency of the wind turbine. To increase the power of the proposed wind turbine is provided for connecting the second possibility of the same or other engine using another coupling 15 at the top of the shaft 1 and the bolts for the cover 7 in which the stator has openings 16.
The whole design of the wind turbine rests on supports 14 that transmit the entire load of gravity and overturning moment on the foundation and the internal load perceived by the stator and rotor frames and must be designed for maximum strength with the power of the wind in the area with a safety factor of not less than 3.
The proposed solution of the wind turbine as compared to the prior art has the following advantages:
- A wind turbine rotor is provided with a stator, which increases the air flow area is used, it carries out a preliminary twist and removes the pressure on the rotor blades, rotating against the direction of the wind, which increases the torque of the rotor and thus engine power;
- Rotor stator frames and especially allow to execute the construction of the proposed technical solutions of the wind engine necessary rigidity and strength;
- Possibility of increasing the power of the engine by connecting it to another or the same engine structure.
The economic rationale of the proposed wind turbine in the possibility of utilization of cheap and clean wind power, the use of which in the economy frees up other forms of energy, currently in operation, simplicity of design and its steady-state, ie, it does not need to turn into the wind, what would need to use some of the energy, construction and stationary allows to erect high-power engine, the magnitude of which is directly dependent on the return of the wind motor rotor.
The prospect of wind turbine development: if such an engine to put into the river, then turn the rotary hydraulic motor (GDR), working without the dam, which is important for small mountain rivers.
CLAIM
Wind motor with a rotation about a vertical axis, comprising a rotor capable of rotating under the action of the wind on its vertical axis with respect to the horizontal, and a rotating shaft associated with the rotor comprising a body of cylindrical shape, hollow inside, comprising at least one or more cylindrical elements mounted above one another and provided with vertical elements mounted on the side surface of the cylindrical member to define said uporyadochnogo row, wherein the vertical elements of each successive cylindrical elements form a subsequent row of vertical elements placed directly above the vertical elements of the previous row, characterized in that each a cylindrical rotor body cylindrical element made as a hollow in the drum with vertical elements mounted on its lateral surface and are constructed as vanes which are structurally part of the cylindrical surface is convex and spaced along the rotor, wherein the motor is provided with air flow guiding apparatom- a stator having at least one or more sections arranged one above the other, each of which is placed a cylindrical rotor element and each comprising a circular rigid base - upper and lower between these bases installed blades to form uporyadochnogo series, the blades of each successive stator sections form a subsequent row of blades, moreover, each of the blades is designed as a part of a cylindrical surface mounted bulge during rotation of the rotor, the radii of blades of curvature is more than five times the radius of the rotor blades and the number of blades of each stator section exceeds number of blades positioned therein each cylindrical rotor element at least twice.
print version
Publication date 17.03.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.