| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2295059
![]()
WIND ENERGY CONVERSION SYSTEM WITH AUTOMATIC PROTECTION
Name of the inventor: NAVARRO Josep Ramis (ES)
The name of the patentee: NAVARRO Josep Ramis (ES)
Address for correspondence: 103735, Moscow, ul. Ilinka, 5/2 "Sojuzpatent" pat.pov. O.F.Ivanovoy
Starting date of the patent: 2001.12.06
The invention relates to the field of wind energy and can be used in wind energy conversion systems with automatic protection. The technical result is to increase the reliability of the system operation efficiency, but also increases the coefficient of performance (COP). energy conversion system of the wind with automatic protection comprises a vertical positioning shaft on which is mounted a core with several equidistant sleeves, inside which extends a shaft, both ends of which are bevel gears connected to a bevel gear with half the number of teeth which constitute part of the vertical positioning a shaft, on the other hand with the opposite ends of the sleeves bevel gears connected with exactly the same bevel gears located on the vertical shaft mounted in bearings, and is provided a ball joint or a pivot joint for connecting the upper part of the vertical shaft with the inclined upper cantilevered portions ascending shafts serving to support and guide the folding blades, driven by the wind.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a wind energy conversion system with automatic protection. The invention is obvious innovation in the field of energy production based on natural energy without pollution and provides an ideal operation of the drive, eliminating the risks associated with damage to or failure of machinery. This is achieved by an integrated protective devices, the advantage of which is that in the event of high winds, thunderstorms and storms automatic means drive mechanisms based sensors and other automation elements include a safety device, which in turn by a drive motor or otherwise alters the direction of rotation rotating the entire unit, causing coagulation and folding blades or elements having a triangular sail shape, causing wind turbine stops. Features and design elements that make up the installation, significantly different from those of any of the currently known wind turbines. This fact, as well, and novelty and practical value of the invention provide a reasonable basis for the provision of the right holder, according to his application, the exclusive rights to manufacture and sell the described installation in Spain by virtue of this registration of patents for inventions.
technique described above provides for the existence of different wind turbines equipped with, as a rule, in the form of rotating blades mill wheel. There are also models with blades resulting in movement of a horizontal shaft in the form of blades different in number and shape, and a plate-based mechanisms, resulting in movement of the vertical axis in the form of spiral vanes, turbine, or any other sleeves. All existing systems have a number of disadvantages associated with the frequent failure of and damage due to lack of protective devices.
The invention is to provide a wind energy conversion system in which the above drawbacks would be absent.
The problem is solved in that the energy conversion system of the wind with automatic protection according to the invention comprises a vertical positioning shaft on which is rotatably mounted a core with several equidistant sleeves, inside which, forming part of the central rotating block shaft extends, on both of which the ends are bevel gears which are connected with a bevel gear with half the number of teeth which constitute part of the vertical positioning of the shaft on the other hand, on opposite ends of the sleeves bevel gears connected with exactly the same bevel gears located on the vertical shaft mounted in bearings , and in the upper part of the vertical shafts is provided a ball joint or a hinge for connection with the upper inclined portions rising cantilevered shafts serving as a support and guide for the folding blade, driven by the wind.
Preferably, the claimed system of the wind energy conversion comprises a bearing and a cruciform yoke arranged on the inclined upper arm portion ascending shafts connected with bushings at both ends traverse are pulleys, which by a flexible and resilient connection are connected to the bottom corners of the triangular blades separated into two part on both sides support their ascending shaft, said blades are affected by the wind, are configured coagulation sails and are mounted on the ascending shaft by means of equidistant elastic ropes along the entire height, allowing the blades to fold into the shape of sails on the ascending shaft in the event that due sensors or other electronic or mechanical means a change in direction of rotation of the block.
Equally preferably, the vertical positioning shaft extends uplink through mechanisms center of the unit, and in its upper part, the shaft ends round guide disc, which peripherally on the bottom plane or bottom mounted by means of ball joints the upper end of the ascending shaft supporting the blade in the form of sails driven by the wind, they provide a uniform movement in the guide disc are mechanisms by which the entire mechanism when changing unit rotation clotting occurs blades shaped triangular sail, causing the blades cease to operate and blocked.
The claimed system enables the wind power conversion to overcome these drawbacks, since its construction is based on the entire block is rotated around the central shaft, fitted at the top plane of rotation of peripherally distributed ascending shafts on which are fixed on both sides of double triangular blade. Triangular blade fold on their poles like sails. It occurs when the block starts to rotate in the opposite direction when stormy gusts, during a storm or other adverse circumstances, the reverse movement is provided automatically by means of sensors and other components, thus avoiding damage to or failure of a wind energy conversion system mechanisms.
This energy conversion system of wind with automatic protection has a vertical central shaft, on which the axis is mounted rotating unit mechanisms, which in turn in several peripheral points attached triangular blade, consisting each of two halves attached to the rising stem or support that in the upper part are movable around the central shaft in the correct direction, while the reverse is rotatable itself upward rod on which are fixed double triangular blade so that the blades are twisted around a rod in the form of sails, allowing thus avoiding a sharp gust of wind exposure. Thus each rod upward or support on which the blades are fixed, in its lower part has a drive through a bevel gear transmitting rotation of the core of the central unit with the rotor equipped with the transmission, converts the movement into energy.
Triangular shaped blade sails, in its lower part, the cables have to ensure their securing to small pulleys at both ends of a traverse connected with the free bearing supports upward. Mounted on these springs or other resilient members provide tensile folding blades and their subsequent deployment. Passing through the pulleys, ropes held against possible displacement by special guides.
All conical toothed gear wheel are identical, i.e. have the same number of teeth, while the central bevel gear coaxial with the lower vertical shaft has teeth exactly two times smaller than the bevel gear wheels on vertical shafts by the edges of the transmission hub.
Vertical shafts, representing the lower part of the console supports folding blade with bevel gears and corresponding swivels coaxially connected to cross-members supporting the bottom folding blade. The whole unit is connected via bearings to the upper parts of the supports cantilever double triangular blades. Upper closure arm portions supports by means of ball joints are fixed to the upper disk of the central shaft, in which they are inserted through small vertical shaft. In gusty wind conditions or adverse weather unit provides drive rotation direction of draw, while the lower rotating central core fixed by bearings on a fixed support fixed to the ground.
For a better understanding of the above general characteristics of the device attached drawings illustrating, in schematic form, one of the possible cases of operation of the wind energy conversion system with automatic protection. It is necessary to note, that the drawings have exclusively informative role. Depicted on these figures should be viewed as a generalization. No restrictive features to claim they do not have.
DESCRIPTION OF THE FIGURES Below, in accordance with the accompanying drawings:
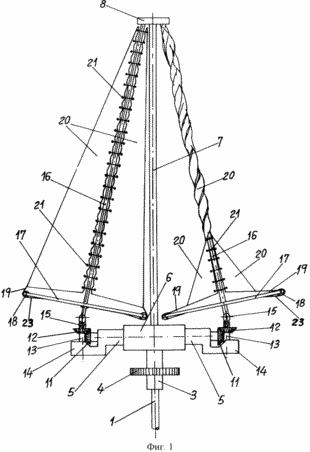
1 - total elevation view of a wind energy conversion system.
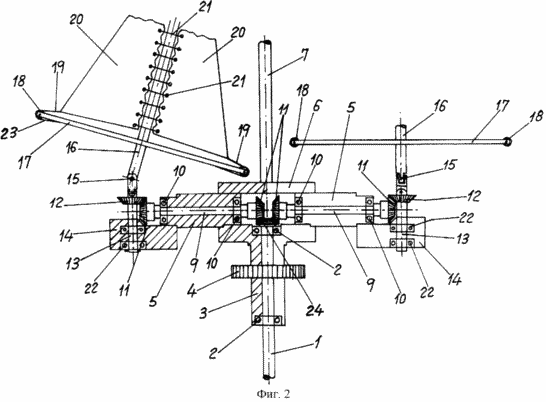
2 - a fragment of the vertical projection.
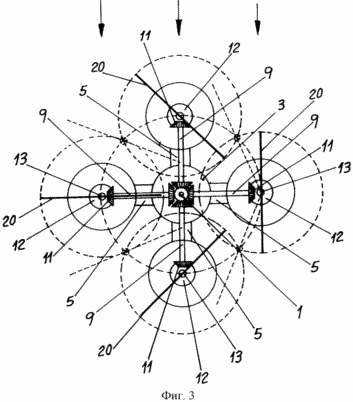
Figure 3 - schematic representation of a wind power generator in a conventional horizontal projection
poi his work.
1 shows an arrangement of double triangular shaped blade sails. Each of the blades mounted on the ascending shafts or bearings. These ascending shafts at their upper ends are fixed on the disk, which ends with the central stationary shaft. The lower part of the ascending shafts, which are attached to double triangular blade traverses contain a small pulleys at the ends. They are attached by an elastic rope bottom corners of the deployed blades. In its lower part, shafts or ascending triangular blade support end bevel gears, through which power generated by the rotation is converted into useful energy.
2 shows a radial section of a pair of bevel gears, such as in the rotary core, the transfer of motion to the bevel gear with fewer teeth twice through which energy is generated. The unit has several blades arranged at an equal distance from each other. The blades overlap during rotation without interfering with each other, which allows for the best performance.
Figure 3 shows an arrangement of four triangular blades and their rotation under the influence of wind. A continuous line shows the double triangular blade dotted line - the same blades in intermediate positions during rotational movement.
It should be stated that the figures available digital links given below correspond to the various elements of the system in the description of their characteristics and functions, and are used to quickly determine the location of a particular item. Reference numeral 1 denotes the lower part of the positioning vertical shaft mounted in bearings 2 disposed in the rotating core 3 and 4 provided with a gear or other transmission means for converting rotation energy into power. The core 3 is located at the base of the block and comprises a plurality of plugs 5 which can be any amount that best - four. Bushings mounted on a base 6 5 which supports upward vertical shaft 7 ending disc 8. The disc is rotational movement guide vanes or coagulation shaped sails, when rotated in the opposite direction.
Inside each sleeve 5 shaft 9 is mounted in bearings 10. Both ends of the shaft are located bevel gears 11 coupled with exactly the same bevel gears 12 disposed perpendicular to the first so that the central bevel gear 24, with half the amount of teeth is coaxially coupled with the upper part of vertical shaft 1, whereas the toothed wheel 12 being in connection with the ends of the sleeves 5 mounted on vertical shafts 13 mounted in blocks 14 by means of bearings 22. The upper portion of gear wheels 12 located on the vertical shafts 13 have pivotal connections in the form of ball joints 15 providing a certain inclination of the rising portion of the upper cantilevered shaft 16. this shaft has a cruciform yoke 17, the ends of which provided for fixing the pulleys 18 by springs 23 or other elastic or flexible double blade members 19 20 arranged on both sides of the shaft 16 rising ropes 21 providing tension double blades 20 shaped folding sails.
Upper arm portions 16 of the shaft rising double triangular blades 20 at their ends and by means of corresponding ball joints are secured and positioned by a small vertical shaft in the upper disc 8, which ends with an upward vertical shaft 7. The disc serves as a guide for the movement of the blades 20 under the influence of wind and includes a mechanism which in the case of rotation in the opposite direction to the rotation of the vertical shaft 1 at 180 ° in gusty winds or other adverse weather phenomena causes the blade to fold double 20 in the shape of sails, to avoid the failure of or damage to the system. The blades are shown in a folded state on the right in Figure 1 of the accompanying drawings.
On each of the components of the wind energy conversion system with automatic protection can be considered in some detail described. It only remains to add that the system parts can be made of different materials, can be different sizes and shapes and allow the amendment of the practice suggests structural changes, if such changes do not break the main structural elements, which are the subject of the claimed invention.
CLAIM
1. The wind energy conversion system with automatic protection, characterized in that it comprises a vertical positioning shaft (1) on which is rotatably mounted the core (3) with several equidistant plugs (5), inside which, forming part of the central rotating unit passes the shaft (9) at both ends which are bevel gears (11) which are connected with a bevel gear (24) with half the number of teeth which constitute part of the vertical positioning of the shaft (7), on the other hand, on opposite ends of the sleeves (5) the bevel gears (11) are connected with exactly the same bevel gears (12) located on the vertical shaft (13) mounted in bearings (22), and in the upper part of the vertical shaft (13) includes a ball joint ( 15) or swivel for connection to the inclined upper parts of the ascending cantilevered shaft (16) serving as a support and guide for the folding blade (20) driven by the wind.
2. The wind energy conversion system according to claim 1, characterized in that it comprises a cruciform and bearing yoke (17) arranged on the inclined upper parts of console ascending shaft (16) connected to the bushings (5), at both ends crosspiece (17) there are pulleys (18), which by means of a flexible and resilient connection are connected to the bottom corners of the triangular blades (20) divided into two parts on either side of the support of the rising shaft (16), said blade (20), which affects the wind, are configured coagulation sails and are mounted on the ascending shaft (16) by means of equidistant elastic ropes (21) over the entire height, allowing the blades (20) fold into the shape of sails on the upstream shaft (16) in the event that due to the sensors or other electronic or mechanical means changes the direction of rotation of the block.
3. The wind energy conversion system according to claim 1, characterized in that the vertical positioning shaft (7) passes through an uplink center block arrangements, and in its upper part a shaft (7) ends with a circular guide plate (8) which peripherally on the bottom plane or bottom mounted by means of ball joints the upper end of the ascending shaft (16) supporting the blade (20) in the form of sails driven by the wind, providing them with uniform movement, a guide disc (8) are mechanisms by which a change total rotation block mechanisms clotting occurs blades (20) having a triangular sail shape, whereby the blade (20) is blocked and cease to function.
print version
Publication date 17.03.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.