| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2070660
![]()
THERMAL POWER GENERATION
The name of the inventor: Mosolov Vladimir Gerasimovich
The name of the patent owner: Mosolov Vladimir Gerasimovich
Address for correspondence:
Date of commencement of the patent: 1994.07.25
Usage: used in wind power. The essence of the invention: a heat-vortex power plant contains a pipe with a vortex generator, a wind wheel mounted on a vertical shaft, and an electric generator. The power plant is equipped with an additional vortex generator, a deflector, and an air heating system with pipes. Wind turbines are installed in the pipe, and the wings of the wind turbines are located in the zone of the vortex air flow.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the electrical and electric power industry, in particular to the design of wind power plants.
In the known wind-driven installations mounted in the pipe, an upward air flow (vp) is used and, as a rule, these installations are based on traditional cylindrical generators.
Two technical solutions have been adopted for the prototype: a solar-wind power plant built by German specialists in Spain (article "Wind Turbines in a Pipe," author of Korney Arseniev, published in the journal Technique of Youth No. 9, 1982, p.34) And the vortex electrical installation (the book Wind Energy, author D. de Renzo, translated from English, edited by Dr. Y. Shefter, M. Energoizdat 1982, 32) [2]
The reference to the two prototypes is due to the fact that the proposed technical solution, both ideologically and constructively, is contrasted precisely with these prototypes.
The disadvantages of both prototypes are:
Low efficiency, i.e. At significant costs, the solar-wind power station has a comparatively small output power (100 kW) [1]
The big difference between night and day speeds. (At night 4 m / s, day 12 m / s) [1]
The possibility of working only in regions with a large number of sunny days [1]
Use of the ascending st. Excludes the use of wind wheels equipped with wings, and therefore does not provide an opportunity to obtain an optimal angle of interaction between the so-called. And the wings of the wind wheels [1] and [2]
The use of mainly high-speed cylindrical generators leads to the need to use transient devices (reducers) in which about 25% of the output power of the electrical installation is lost [1] and [2]
In the formation of the vortex vp. A smaller part of the input vertical cuts of the vortex generator (somewhere 1/3) is used, which reduces its power [2]
Ascending velocity vs. By a factor of several (5-8 times) less than the vortex flow rate. [1] and [2]
When solar energy is used, a significant temperature difference between the bottom and the top of the pipe (the main thrust creation parameter) is not achieved [1]
Dependence of the power and constancy of the vortex sf Of the speed of the outer wind [2]
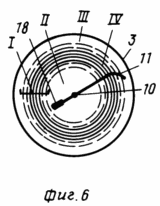
The essence of the proposed invention is that when applied to wind wheels, a non-rising HP is used. And the vortex s.c. Directly in the pipe. Vortex vp Formed by the main vortex generator, is located at some distance from the central axis (the shaft) and from the inner surface of the tube (the approximate location of the EH zones in the pipe is shown in Figure 6). At the same time, the velocity of the vortex vortex. (Zone I) increases several times in comparison with the speed of the high water column. At the entrance to the tube and reaches a maximum in the core of the vortex s.p. (Zone IV). Velocity speed In the central part of the tube (zone II) is close to zero, and near its inner surface (zone III) is approximately equal to the velocity of the high-speed column. At the entrance to the pipe. For different diameters, the position of the vortex is. Etc. in the pipe will be different. With an increase in the diameter of the tube, the velocity of the vortex is. Etc. increases. How many times will the speed of the vortex vp increase? In comparison with the ascending c.p. The inner zone (zone II) will increase so many times, i.e. The total area of the ascending settlement decreases. Consequently, the resulting power of the wind power plant, both in the ascending and the swirling vp. Will be the same; The law of conservation of energy is not violated. When using vortex s.p. Which rises in a spiral at a certain angle, the wings of the wind wheels are installed directly in the pipe in the zone of the vortex s.p. (Zone I) at the optimum angle to it. In the inner part of the pipe (zone II, where the speed of the HP is close to zero), there is a shaft with fastening elements and fastening elements for wind wheels or counterweights for single-winged wind wheels. In addition, because of the small lever use of the ascending in. Etc. in the inner zone would be ineffective. V.p. Outer zone (zone III) and is not used, therefore there is no need to grind the inner surface of the pipe when taking into account friction losses.
Comparison of the proposed technical solution with prototypes makes it possible to establish compliance with the criterion "NOVELTY".
The development of a powerful wind turbine is solved in two ways (hence the reference to two prototypes):
A) Creation of the necessary constant speed (thrust) of the ascending st. In a pipe, where the approach to solving this problem differs from the first prototype [1]
B) the transformation of the resulting ascending b.p. In the vortex s.p. And using it directly in the pipe to rotate the rotor of the generator, while in the second prototype [2], an ascending branch is used. Created by a vortex s.p.
When implementing the first stage, creating the necessary speed (thrust) of the ascending one in. Etc. in the pipe, taking into account the geographical position of Russia and many other regions, we suggest not a canopy from a transparent film, under which air is heated by solar energy [1] and a "tent", the air under which is heated by means of batteries (grates) or directly (Direct) supply of warm air through the hopper into the pipe. To this end, excess (waste) heat from metallurgical, coke-chemical and other plants, mines (at a depth of about 3000 m the air temperature can reach 60 ° ), CHP, heated water from nuclear power plants, etc. should be used for this purpose. You can also use natural heat, for example, heat from geothermal sources. The "tent", whose diameter will depend on the required mass of air supplied to the pipe, is raised from the upper edge of the slots of the main vortex generator with a drop to 2 meters along the perimeter, i.е. Has a conical shape. The two-meter clearance is intended for intake of outside air. The "tent" (bunker), the pipe, the surface of the earth under the "tent", the supply pipes must be insulated, that is, the draft depends mainly on the height of the pipe and the temperature difference between its bottom and the top.
In winter, especially when using a version with direct supply of warm air into the pipe (for heating the air under the tent in winter, more heat will be required), the air temperature difference between its bottom and the top will increase dramatically, i.e. The thrust will increase. In addition, to increase the thrust, a deflector and an auxiliary vortex generator are applied in the upper part of the tube. The wind, flowing over the deflector, creates under it some discharge, which partially increases the thrust. The auxiliary vortex generator supports vortex motion And, due to the vacuum created under it, increases traction.
In the second stage, the ascending branch of the v. With the help of the main vortex generator is converted into a vortex generator. In this case, all input slots of the main vortex generator are used, which ensures the greatest flow of air into the pipe (when the vortex generator is operating from the outer vp, the inlet slots open only from the direction of the wind [2]).
The wind wheel is driven into rotation by a vortex syringe. Directly in the pipe. It is more advantageous to use a wind wheel with a wing device, rather than a lobed one. The wings are fixed at the optimal angle in the most vortical vp. And are connected to the shaft by bridges, which will be in the central part of the pipe, where there is no movement of the HP. The number of wings in wind turbines, as well as the wind chocks themselves, will depend on how much during the interaction of the vortex in. Etc. with its wind-wings, its structure will be violated. In wind turbines, the number of wings can be one with a counterweight (the counterweight will again be in the zone where there is no movement of the HP), two, etc. The distances between the wind wheels, the optimum height (the higher the tube, the greater the thrust) and The diameter of the pipe (the larger the diameter, the greater the velocity of the vortex vp) should be determined experimentally on the layout. To reduce the vortex resistance in. The shaft through the bearings is fixed by profile plates located parallel to the motion of the vortex alternating current.
The above arguments allow us to conclude that the claimed technical solution meets the criterion of "essential differences".
The technical solution is explained by the drawings.
 |
 |
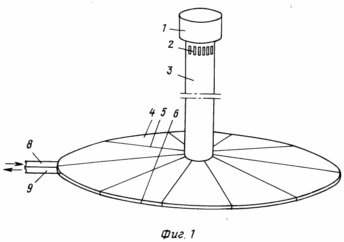
In Fig. 1 shows a general view of the TVE with a "tent", where in the upper part there are a deflector and an auxiliary vortex generator. The roof of the tent, mounted on the stiffeners, which are supported by the racks. Simultaneously, the stiffeners are an additional support for the pipe.
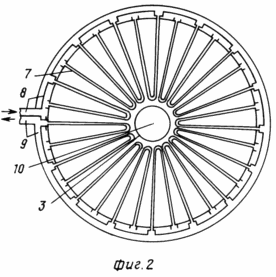
In Fig. 2 shows the heating system under the "tent". Hot water or steam is supplied to the batteries (grates) and diverted from them through the pipes.
 |
 |
 |
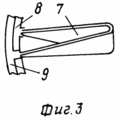
3 shows one section of the battery of the air heating system.
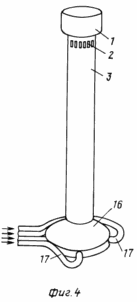
4 shows a general view of the fuel cell with direct supply of warm air from four sides through the hopper directly to the pipe.
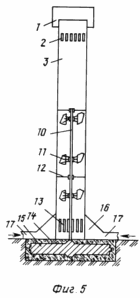
5 shows a TVE in section with a direct supply of warm air. The disk generator is placed in the foundation on which the pipe rests. The generator shaft is brought to the maximum possible height. On the shaft, which is fixed through the bearings by profile plates, several wind wheels with wing devices are placed. At the bottom of the pipe is the main generator. In the upper part of the pipe there are a deflector and an auxiliary vortex generator. The hopper simultaneously serves as an additional support for the pipe.
 |
 |
In Fig. 6 shows a pipe in cross-section with an exemplary arrangement of zones of high-voltage. Where the advantage of putting the wind wing in the vortex vp zone is evident. At the optimum angle.
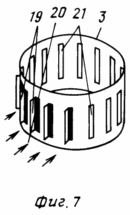
In Fig. 7 shows a part of the pipe with an auxiliary vortex generator, where vertical slits with automatically adjustable guide vanes are seen that open from the direction of the wind (indicated by arrows) and are set at an angle determining the formation of a vortex vortex. Inside the pipe. In the main vortex generator all the blades are open and fixed at a constant angle necessary for the formation of a vortex vortex. The vertical slots of the vortex generators will weaken the mechanical strength of the pipe, but because the main generator is at the base of the pipe where it is fastened, and the auxiliary vortex generator is located at its uppermost part, there is no need for amplification in the places of the slits.
The TVE consists of: a tube 3 with a main 13 and an auxiliary 2 vortex generators, a "tent" 4 mounted on the stiffeners 5, having an external perimeter 2 meter inlet for intake of external air 6, an air heating system comprising an inlet 8 and an outlet 9 Pipes and sections of batteries (grates) 7, hopper 16 with supply pipes 17 (for TVE with direct warm air), disk generator 15 (other types of generators can be used) with shaft 10, on which wind wheels with wing devices 11 and Elements for fixing the shaft 12, the deflector 1, the foundation 14, the counterweight 18, the vertical slots with the open 19 and the closed 21 guide blades, the arrows 20 shows the direction of the wind.
The weight of a metal pipe is 20 times lighter than a similar structure made of reinforced concrete.
In TVE, instead of the traditional cylindrical generator, it is advisable to use a powerful slow-speed disk (carousel) generator ("Carousel electric machine", a positive decision on application No. 4540025/07, reference N 16476 dated November 27, 1991), located horizontally below the surface of the earth. The vertical shaft of the generator, on which several wind wheels are fixed, is brought to the maximum possible height and without coupling devices (reducers) is connected to the disk-rotor. The angular rotation speed of the shaft is from 10 to 50 rpm. It is possible to use other types of generators.
Due to the length of the pipe, the temperature difference between its bottom and the top obtained by using excess heat from the enterprises, the work of the auxiliary vortex generator and deflector is achieved by traction (the first stage). Heated under the "tent" or with direct supply of warm air rushes through the slots of the main generator of the vortex into the tube, where, thanks to the guide vanes, it acquires a vortex motion. Vortex vp Occupying a certain position in the pipe (for different pipe diameters it will be different), interacting at an optimum angle with the wings of the wind wheels, rotating the generator shaft. The number of wings of the wind wheels, their shape, dimensions should be chosen in such a way that the vortex alternating current. After partial destruction, when approaching the next wind wheel, was restored.
Vortex velocity in. Within the pipe will be constant, because The insignificant effect of the auxiliary vortex generator and deflector caused by the variability of the wind speed will be smoothed out by a massive rotor disk that simultaneously acts as a flywheel.
The proposed TVE is completely environmentally friendly, takes up a small area for its construction, moreover, if existing powerful wind installations using wings of a large area interfere with local TV-radio reception, then electromagnetic oscillations created by friction About the wings of the windwheels, will be shielded by a metal pipe.
The set of the above-mentioned technical solutions will allow creating a wind power plant of such capacity, which will be sufficient for the rotation of a rotor disk of large diameter and weighing several tens of tons.
Thus, the proposed technical solution in comparison with the prototypes [1] and [2] will have the following advantages:
1. Due to the use of excess (waste) from the enterprises or natural heat with the thermal insulation of the "tent" or "bunker", the surface of the ground under the "tent", a much larger difference in air temperature between the bottom and the top of the pipe is achieved (especially in winter), those. Traction is much increased.
2. The vortex motion, in comparison with the ascending one, several times increases the velocity of the vortices.
3. Putting the wing of the wind wheel into the vortex vp zone. Directly in the pipe at the optimal angle creates the condition for the most beneficial use of the HP.
4. The use of an auxiliary vortex generator operating due to an external wind supports the vortex motion of the vortex. In the pipe and increases traction.
5. Using the deflector increases traction.
6. If a 1/3 of all slits are used in the vortex generator operating due to the external wind, which are opened only from the direction of the wind, then in the main vortex generator air enters the pipe through all the slits at the same time, which significantly increases the power of the vortex Gt;
7. With the use of several wind wheels, evenly distributed on the shaft, more efficiently used. And the force on the shaft increases.
8. The use of wind blades instead of blades (with the incoming HP only used lobed wind wheels), the wings of the large working surface dramatically increase the power of the wind farm.
9. Since the vortex c.p. Does not touch the inner surface of the pipe, then to reduce friction losses, there is no need for careful processing (grinding).
10. When using a low-speed disk generator, where the disc rotor is driven through the shaft directly, and not through a reducer, in which about 25% of the power is lost.
11. Due to the massive disk-rotor, which simultaneously performs the role of the flywheel, the speed of its rotation will be constant and will not depend on short-term changes in wind speed.
CLAIM
A teplogortical power plant comprising a pipe with a vortex generator, a wind wheel mounted on a vertical shaft, and an electric generator, characterized in that the power plant is provided with an additional vortex generator, a deflector and an air heating system with pipes, wherein the wind wheels are mounted directly in the pipe, and the wings of the windrows are located in the zone Vortex air flow.
print version
Date of publication 17.03.2007gg




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.