| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2076947
![]()
ENERGY CONVERTER
Name of the inventor: Zubarev Konstantin; Zubarev Alexander K.; Medvedev Valentin
The name of the patentee: Konstantin Zubarev; Zubarev Alexander K.; Medvedev Valentin
Address for correspondence:
Starting date of the patent: 1994.06.07
Use: wind energy, hydropower, but also in vehicles. energy converter comprises farm 1 mounted therein rotatably vertical shaft 2 which tiered strengthened horizontal crosspiece with rotating elements 5, each lower pair of traverses 4 deployed horizontally relative to the top, and each rotary member 5 is composed of a pair of mesh scaffolds 19 20 sleek, reinforced with the possibility of mutual displacement along the traverses 4 frames 19, 20 are covered with grids of 21, 22 with different-sized meshes. One of the grids 21, located on the outer side, is a supporting and has a smaller-sized meshes. The second grid 22, the interior, with a larger mesh size, is equipped with a sail elements 23 fixed to one side of each mesh. Each of the sail members 23 is made of an elastic material with a size corresponding to the size of the mesh.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The alleged invention relates to the energy sector, in particular to the energy converters operating from air or water streams.
There are many different energy converters pivoting planes of plates and vanes which are pivotably fastened in different positions, in optimal aerodynamic regarding how to create resistance towards and against the working environment. These converters operate, as a rule, at a relatively stable working environment parameters, which in real terms is extremely rare and can significantly increase the efficiency (up to 25%).
Known "Carousel windmill" [1] containing a vertical shaft with radial blades, which are made in the form of frames. On each of the frames with pivotable about horizontal pivot axes reinforced elements in the form of plates with bent edges. The known device, simple in design, it has a major drawback not effectively converts the energy of the medium flow, it does not provide flow control possibilities as conditions change and process fluid parameters. The device has a limited power range. Increasing its result in a substantial increase in the area of the radial blades.
Known and "wind turbine" [2] containing a vertical shaft, on which the rotating elements are reinforced with flexible blades. The blades are made as thin-walled panels with internal cavities. This device and inefficiently because of the limited his opportunities. When freezing performance and working environment considerable elastic deformation of the material of the blades do not provide the intended not only efficiency but also the long-term operation.
The closest to the claimed is "wind turbine" in our opinion [3]
Known wind turbine comprising: a farm mounted therein rotatably vertical shaft on which tiered horizontal crosspiece fastened with rotary elements, and the device and software turn kinematically associated with the rotary elements. Moreover, the kinematic connection device software have different gear ratios with rotary blades of different series and in the form of chain drives.
The main disadvantage of this device when it is constructive complexity and low efficiency in its significant environmental fluctuations (temperature, wind, precipitation), since numerous kinematic connection, in particular chain transmission can not guarantee stable operation in these conditions. It is doubtful, and the reliability of the device because of the increased complexity.
The main task, which set themselves the authors of the present invention is to increase the energy efficiency of both air and water flow. Along the way, the task is to create a simple in construction and reliable in operation.
This object is achieved by the fact that in the proposed design, farm comprising mounted therein rotatably vertical shaft on which tiered horizontal crosspiece fastened with rotary elements each traverse the lower pair of rolled angle with respect to the upper 35-55 o, and each rotatable member made consisting of a pair of mesh scaffolds sleek, reinforced with the possibility of mutual displacement along the traverse, and the scaffolds covered with nets with different mesh size, of which at least one is provided with a sail elements. At the same time one of the grids located on the outer side and having a smaller size meshes, is the support and the second, internal, with a larger mesh size, is equipped with a sail elements, fixed on one side of each mesh. Moreover, each of the elements of the sail is made of an elastic material with a size corresponding to the size of the mesh.
Installation of each successive pair of traverse reversal with respect to the upstream can more fully take into account the change in the air flow direction.
Performing rotary elements as a pair of mesh scaffolds streamlined shape, arranged in series in one direction, pivotable about a vertical shaft, allows to create a torque equal to the difference of resistance of the working medium "solid" and open the sails. This resistance arises difference is the main component of the driving force (component efficiency) power converters.
Performing as scaffolds aerodynamically streamlined sail can significantly improve the work, particularly the proposed semi-cylindrical shape allows to improve the result by 10-20% compared to a flat sail.
The support grid and sailing in the operating position are located close to each other, and when exposed to the working environment by sailing sailing mesh grid feathers are pressed against the reference grid and form a "one-piece sail." Under the influence of the working environment on the part of the reference grid feathers (patches) are rotated or bent (open), providing significantly less resistance to the working environment than "one-piece sail."
Setting volume of carcasses is movable relative to the traverse (at a distance of no more than the width of the flap) will allow to adjust the power of the device under various weather changes, ie reduce or turn off the power in high winds (storms, hurricanes).
Inlaid patchwork sail easy to fix on the frame bulk aerodynamic streamlined shape, which greatly improves the performance of a type-setting sails. Optimum volumetric form further worked out at the moment, but also offers a semi-cylindrical shape is different from the flat by 10-20% in favor of the bulk.
The shape of the flap (pen) and its size, as a rule, have to follow the shape and size of grid cells sailing (possible arrangement of several flaps, one in the amount of repeating the mesh grid). The main requirement to the form of patches is more dense overlapping reference grid with the free passage in the mesh grid sailing (or most dense opening).
Grid reference and sailing may be conventional metal (wire) mesh.
The material of the flap (pen) depends on the operated environment (water, current, tide or air, wind) and the air (wind) can be parachute silk, canvas or other thick cloth, soaked in moisture repellent composition or polymer films such as frost-resistant polyethylene film, that is. e. materials that meet the requirements of lightness, strength, hardiness, vlagonepogloschaemosti, flexibility, etc. requirements. To work in the water requirements for the material of the flap (pen) differ primarily reduced vlagopogloschaemostyu, resistant to soaking, and other similar requirements. Weight of material can be slightly larger than the air, i.e. water as a flap (stylus) can be used tires, light-gage aluminum alloys (in fresh water), titanium alloys, polymeric plates, plastics and other materials that are resistant to seawater.
Existing materials and processing technology theoretically allows to create a "sailing" for wind converters with an efficiency of over 50%.
 |
 |
 |
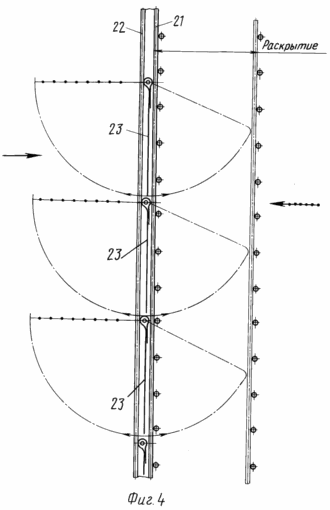 |
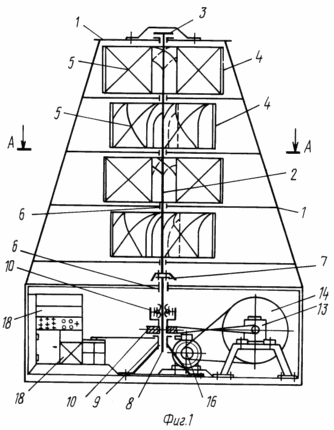
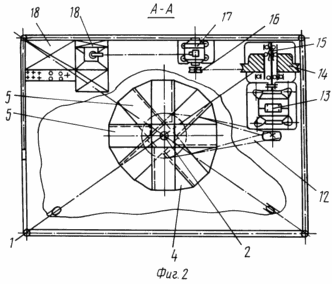
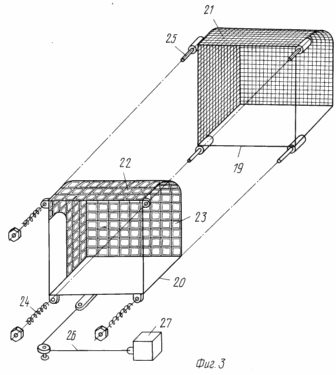
1 schematically shows a wind power plant, a side view (sectional view); -the same in Figure 2, a plan view (partially broken away); Figure 3 shows a schematic assembly of typesetting blown in one direction of the sail and its management; 4 schematically shows the work of a group of patches in two directions.
The construction of the wind power plant (1, 2) are as follows: steel truss 1, which is mounted on a vertical shaft 2, in the upper part resting on the thrust radial bearing 3. In height on a shaft rigidly fixed eight cruciate traverses 4, constituting four tiers (floors), where each tier is secured by four sails 5, i.e. sixteen sails. Each tier rotated relative to each other at 45 o. Tiered radially between shaft 6 grommets restricted lower end through a rigid coupling shaft 7 connected to the gear shaft 8 whose lower end is limited by the radial bearing 9. Thus, rotor drive hanging on the upper thrust bearing. On the transmission shaft 8 through the overrunning clutch 10 set on leading the rotor pulley 11, the transmitting torque through a belt cross-transmission 12 at a step-up gearbox 13, which is the output shaft has a pulley, flywheel 14 in the overrunning clutch 15 that transmits torque to the pulley 16, the DC generator 17. The generator 17 works in the battery pack 18, which, via the inverter 18 provides electricity to the consumer.
Inlaid blown in one direction, the sail is shown in Figure 3 and is a team structure, consisting of two rigid frames, one frame reference grid 19 and a frame 20. On the sailing grid frame supporting grid 19 fixed supporting grid 21 with a square mesh of size 30x30 mm . In the frame of the grid 20 sailing sailboat anchored mesh 22 with a square mesh measuring 100x100 mm of galvanized steel wire of 1.6 mm diameter. Each cell of the grid 22 is blocked sailing flap 23 of hardy plastic film thickness of 0.5 mm square shape, size 98h98 mm. Form frames and nets (reference and sailing) are similar and differ only in size, which allows yachting frame 20 with the grid 22 inserted into the support frame 19 with support grid 21. Mount each sailing mesh with the frame to each reference grid to the frame via the compression spring 24 three or four pins 25 welded to the support frame. This mount allows you to postpone sailing grid with frame from the reference grid on the width of the flap, ie 90-100 mm for a given effort. When assembled, operational flaps (the feathers) sailing grid are located in close proximity to the reference grid and account for one-piece sail.
The area of the flap (pen) is dependent on the material properties and should be minimized to a set of patches, i.e. Total area of sails limited to typesetting installation of required capacity and regional operating environment conditions. For example, if the reference grid with 30x30 mm mesh grid can be sailing with a mesh of 100x100 mm and 100x50 mm. At the same time the size of the flap will be 98h98 or 98h48 mm mm. Nets may be polymeric (nylon, nylon), sailing for the grid as a minimum and a maximum of galvanized stainless steel. Increased material requirements sailing mesh against corrosion resistance justified durability of the variables (atmospheric) weather conditions.
For regular or automatic shut-off when the rotor sails certain speed (the maximum), each frame of sailing through a flexible connection 26 is loaded by free load 27, which under the influence of centrifugal force makes automatic Pushing sailing grid, and the grid in the fall of the rotor speed automatically accept the operating position.
Work wind power plant is as follows: dynamic pressure of the wind on one side of the shaft 2 presses the flaps 23 to the support grid 19, forming and acting on the "solid" sail on the other shaft wind deploys flaps 23 on the purged side and with much less resistance penetrates and slits formed mesh.
The resultant resistance difference is the various efforts to "integral" and "open" the sails, resulting in a torque shaft 2 and the rotor begins to rotate in the same direction. As the rotation of the shaft of the sail change position, the next sail flaps are pressed against the reference grid to form a "one-piece" sail, and the process continues as long as there is a head wind. Location sails shaft traverses chosen so that the work is at least two full sail section and two sail to the wind in a projection constituting one full sail. With a full cross-section of "whole" of the sail 1 m and the difference in sail in different directions of motion of the rotor, ie, Closed and open sail sails as 1: 0.3, the right to expect that on opposite sides of the shaft force will occur in the same regard. On average data, 1 m continuous wall arises force to 100 kgf. Due to the partial density of solid sails resulting force will be smaller and will decrease as the capacity of the rotor speed of rotation, but the initial force can be taken not less than 0.8 times the statistical, accounting for the difference between the efforts of 80 kgf 30 kgf to 50 kgf. Since the middle of the sail is on a radius of 1 m, the torque is 50 kgm. Because the work is three sails at the same time, the torque can reach 150 kgm. At an average wind speed of 8 m / sec and an efficiency of 50% rotor speed will be: ![]()
or about 40 rev / min, which is through the ratio of torque and speed will be a power of about 6 kW.
sails Management provided by razdvizheniya sailing and support networks in the case of manual switching off, or in case of wind exceeding the rated speed, razdvizheniya nets is automatic due to the appearance of sufficient centrifugal force acting on the load and through a flexible connection to the grid sailing.
To achieve uniform rotation electric circuit provided in the flywheel, overrunning clutch, electric accumulators, converter, electric power control circuit of the generator, i.e. the problem is solved by known methods.
Experimental set having eight sails size of 1 m x 1 m 1 m 2, each arranged around a vertical shaft by four pieces in two tiers adjustment deployed by 45 o with respect to each other, showed stable operation and distinct from known author efficiency in favor of " sailing. " Feathers (patches) on the installation made size: 50 mm wide and 250 mm long, from the hardy plastic film 0.5 mm in thickness and showed good stability in all seasons. In all eight sails worked 608 patches, and all tests came time down six flaps, and at the expense of low-quality execution of fixing (soldering, welding around the wire mesh sailing). Replacement or repair of the flap does not cause difficulties.
Test models with dimensions of 100x100 mm sails and 95h25 mm pen size gave a clear result in terms of efficiency and aerodynamic shape of the sail. The model is found to be at high wind speeds, ie, at 250-400 rev / min at a radius of 150 mm grafts have time to operate in the open and close, allowing you to create portable miniustanovki power up to 100 watts, useful in expeditions, camping trips and other similar situations in the remote signaling points. Possible use of the proposed converter, for example, in the target wind turbines, where appropriate direct application of mechanical energy. These can be pump, compressor and hydraulic power, or combinations thereof up to the heat (refrigeration) installations. Inlaid blown in one direction of the sail in motor mode can be used on marine and river vessels, which do not require high travel speeds. In motor mode, these sails can be promising to create vehicles hovercraft, maholeta and other means used to move both by air and by water.
Thus, the "sail" for wind turbines provides efficiency up to 50% quiet operation, ease of construction and its control, and depending on the regional atmospheric conditions, a wide range of plants of various capacities.
CLAIM
1. Energy converter comprising farm mounted therein rotatably vertical shaft on which tiered horizontal crosspiece fastened with rotary elements, characterized in that each lower pair of traverse relative to the upper deployed horizontally, and each rotary member is composed of at reticulated least a pair of carcasses streamlined shape, mounted axially movable along the traverse frames are covered with grids of different mesh size, one of which is located on the inner side, provided with sail elements.
2. Converter according to claim 1, characterized in that one of the grids, mounted on the outer frame, has a smaller size and a supporting meshes.
3. The transducer of claim 1, wherein the sail members are made of elastic material, mounted on one side of the mesh and the internal grid are of a size corresponding to the size of the meshes.
4. The transducer of claim. 1, characterized in that each lower pair of traverse relative to the upper deployed horizontally through an angle in the range 30-55 o.
print version
Publication date 30.03.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.