| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2114318
![]()
ELECTROGASODYNAMIC WIND-AGGREGATE-3
The name of the inventor: Makashev Andrey Porfirievich
The name of the patent owner: Makashev Andrey Porfirievich
Address for correspondence:
Date of commencement of the patent: 1996.04.03
Designed for the direct conversion of natural wind energy into electrical energy, consists of a channel with a dielectric housing with an expanding section containing one or more sequentially arranged sections with electrode sets and a general commutation, each section includes: ionizing electrodes at the input, creating positive pulsating corona discharges Or negative ions: stabilizing a flat or bulk capacitor located inside a space charge, retarding the ion distance, surrounded by a screening grid; Collector at the output. On the inner surface of the body there are transverse stabilizing volumetric charges electrodes - the capacitor's lining, on the outer surface a continuous electrically conductive coating - the second electrode, grounded. On the surface of the unit there are nozzles with windows in the body with intervals between them, directing an additional flow of external air into the channel, in the window openings it is ionized by the corona meshes under the voltage of the transverse electrodes. Air at a reduced speed, free of ions, through the slits in the body, located behind the collector, comes out. A part of the air flow is fed through the slots in the surroundings of the volumetric condenser, the inner part of the slits is covered with isolac. At initial start-up, the corona power is supplied by a source of constant low-power voltage, in operating mode - by a pulsating voltage with self-excitation from the collector via voltage and pulse converters, with a stabilizing capacitor included in the corona circuit. The pulling electrode is switched in-phase with the corona through the relay. Electrodes, other than ionizing and collector - electrically conductive coatings on plastic.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The published papers [1, 2, 3] describe devices with direct conversion of the natural wind energy into electric energy on the basis of the idea that dispersed charged particles, positive or negative, or air ions are transported by natural wind against the electric field, settling on the collector , They recombine, increase its tension.
However, the efficiency of such facilities is very low, and for all the simplicity of the idea, the practical implementation of it is very difficult.
The author developed theoretical and experimental studies [4], in which, for a pulsating corona discharge, air ions form a space charge of sufficient density with minimal losses in the ionization and ion transfer processes by the airflow to the collector.
The closest analogs of the invention are [4], in which aggregates are described, which, however, can consist not only of one but also of several consecutive sections, which provides increased power and efficiency of the units.
It should be noted that when working in these installations, there will inevitably be a reduction in the air flow rate. Obviously, the power can be further increased if an additional intake is made to the inside of the unit for fresh attracted air, while simultaneously venting air to a lower speed.
This proposal solves the problem of increasing the capacity of the unit by additional intake of fresh air into the flow, creating a structure for efficient operation at large and very high wind speeds, for example, at high altitude, creating a capacitor on the casing that improves operating conditions and improves safety.
The essence of the invention is as follows:
- an intake system is created for the additional flow of ionized air, which has a high hydrodynamic head, through the window in the casing, while at the same time removing from the unit a certain part of the air with a reduced velocity that does not contain ions (after the collector);
- a variant of the unit design is created for operation in wind conditions with high speed, operating at energetically effective altitudes;
- for ease of operation, the unit is assembled from self-contained joining sections, each with a full set of electrodes;
- A transducer is created from the transverse electrodes on the inner surface of the casing and the electrically conductive coating of the outer surface, which contributes to the improvement of operating conditions and the enhancement of safety measures;
- for occasional works a small power and small-sized wind turbine is created, equipped with load-bearing planes and simple height controls, rises to a height like a kite with sufficient wind force.
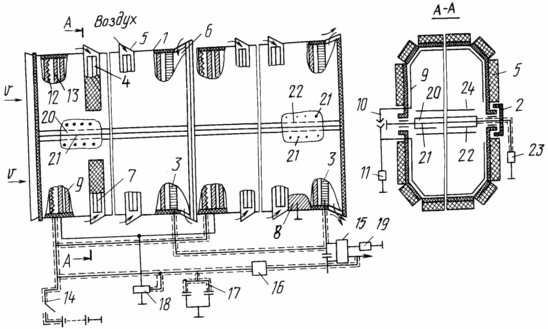
1. The figure shows schematically an EHD wind turbine consisting of one or more sections arranged in series in a channel with a dielectric expansion chamber 1 that is detachable along the median plane with fastening clamps 2. The length of each section is determined by the creation of sufficient collector voltage 3 with an average wind Speed. On the outer surface of the case, above the windows 4, there are original nozzles 5 guiding the flow of external air with a higher hydrodynamic head than the internal one into the channel, and at the outlet, after the collector there are transverse slots 6 for partially discharging air to the outside with a reduced speed that has lost its charges. The strength of the body is provided by the presence of gaps between the nozzles. In the openings of the windows there are rare nets of fine wire 7, which are under tension of transverse electrodes, which coronae into the channel in the flow of additional air.
The entire outer surface of the casing, including the nozzles, is covered with an electrically conductive coating (capacitor plate) closed to ground 8, transverse electrodes on the inner surface 9 - the second lining. The electrodes of the upper and lower part of the housing are connected by detachable contacts 10 and through the additional load 11 are closed to ground. Such a capacitor equalizes the electric field strength in the channel and raises the level of safety engineering.
At the input of each section, corona 12 and pulling electrodes 13 are installed. The corona electrodes are connected at the start by means of a switch 14 to a low voltage power supply, and in the operating mode, the power is self-excited from the collector 2 through voltage converters 15 and pulses 16, The condenser 17, which stabilizes the corona discharge, is constantly switched on. The pulling electrodes 13 through the relay 18 in in-phase with the corona are connected to the crown circuit.
The collectors 3, consisting of conductive plates or a grid, are located at the output of each section of the unit, carefully insulated, connected in parallel or in series, and through the above voltage converters 15 and pulses 16 with the corona electrodes 18 and the load 19.
Inside the space charge along the center line, in each section, there are stabilizing flat capacitors 20 consisting of an inner grounded cover plate 21 and an insulation outer cover of the transverse partitioned electrodes 22, each electrode 22 through an additional load 23 is grounded. Lining - electrically conductive coatings applied to the dielectric. Above the condenser surface there is a screening grid made of thin transverse wires 24, which inhibit the deposition of ions on the electrodes 22.
Instead of stabilizing flat capacitors, it is possible to use volumetric capacitors having an internal cavity open at the inlet and closed at the outlet. If there are several sections in the unit, the internal cavity at the outlet is closed only at the condenser of the last section. In the capacitor plates there are transverse slits covered with isolac, through them the flow of external air from the internal cavity enters the channel, to some extent preserves the air flow rate in it and slows the deposition of ions on the electrodes of the outer liner.
In what follows, for the sake of definiteness, it is assumed that the unit operates on positive ions. Ions from the ionization zone from the corona electrodes 12 and through the windows 4 on the surface of the housing from the corona wires 7 are discharged into the transfer zone by the air flow. The process of inhibition of the scattering of volume (transverse stabilization) consists in the following.
As a result of electrostatic induction of the space charge, negative charges are formed on the outer surface of the transverse electrodes 22 of the stabilizing capacitor 20, positive charges of the inner lining go to the ground; In this case, positive charges on the inner surface of the transverse electrodes 22 are preserved, since They are connected by negative charges of the inner plate 21. During the operation of the unit, both of them increase and the voltage between the plates rises to the limit and a discharge occurs after additional load 23, this process is cyclic.
The transverse electric field induced on the outer face of the negative charges is directed against the transverse field of the positive space charge surrounding the capacitor and largely compensates it. The total transverse field of the space charge system and induced negative charges, according to the Gauss theorem:
( F DdS = S q)
Where,
D is the vector of electrical induction;
S is a closed surface;
Q are charges inside S,
Will have the expression:
S E 1 (h) » Eq o.z. ^ (H) + Eq ns. ^ (H)
here -
S E ^ (h) is the total electric field of the space charge and negative charges induced on the capacitor at the level h;
... Eq o.z. ^ (H) is the transverse electric field of the space charge at the level h;
Eq n.e. ^ (H) is the induced electric field at the outer electrodes of the stabilizing capacitor;
H is the level of the layer of the space charge spaced from the surface of the capacitor.
For example, at the level of h max , i.e. At the outer surface of the space charge, in the ideal case, S E ^ (h max ) » 0, i.e. The scattering of ions into the volume will be negligible, only diffusion of ions will act, but it is relatively small.
At the same time, the transverse electrodes 9 on the inner surface of the body, having charges from the ions that precipitated from the volume and the voltage automatically set, in each section of the transfer zone, maintain the average value of the counterfield of the collector, which is confirmed by the tests of the prototype of the unit.
Naturally, in addition to the interaction of the fields, there is also a direct exchange of charged particles. The positive ions of the inner layers of the space charge (h » 0), where there is a significant imbalance of the transverse fields (| Eq o.z.^ (0) | <| Eq ns (0) |) are directed to the negatively charged outer surfaces of the electrodes Condenser 22 are deposited, recombined and, under the influence of the same electrostatic induction, positive charges are immediately discharged to the ground, the cycle is repeated, the charge accumulates on the capacitor, as mentioned above, which causes cyclic discharge through the additional load 23. The charging and discharging processes of the stabilizing capacitor in According to the laws of commutation of transient processes occur automatically (oscillatory processes). In this case, the induction rate is many orders of magnitude higher than the rate of ion settling from the volume, therefore, negative charges will always predominate on all the transverse electrodes of the capacitor 22, the transverse field of which, as already mentioned, inhibits the scattering of the space charge. The pulsating current of the stabilizing capacitor has an energy close to the energy of the fraction of the space charge that has settled in the form of ions in each cross section of the aggregate, this energy rises as ions approach the collector, i.e. The energy of the ions that settle on the stabilizing capacitor is utilized, but to a lesser extent than on the collector, to which the main overwhelming fraction of ions enter.
The process of ion deposition on electrodes 22 is effectively inhibited by the field of the screening grid 24 located above the stabilizing capacitor. With the floating potential of the grid, the degree of deceleration will be set automatically, but when regulating it (as in an electron tube), the ion deposition rate can be brought to a very low level.
The decrease in the air flow velocity in the unit, resulting from the expenditure of energy to overcome the resistance of the counter electric field to the movement of ions and the friction of the air on the surface of the electrodes, is slowed by the intake of additional outside air under a higher hydrodynamic head through nozzles 5 and windows 4 on the body and in the presence of a stabilizing Not flat) volumetric capacitor, through the slots 6 in the body of a part of the air of a reduced velocity that has lost its charges.
In the unit with several sections (see diagram), in the first section the slits 6 can be absent.
The wind turbine consists of paired blocks, the dimensions of one block in the cross section can be up to several m 2 , the length - depending on the number of sections up to 4-5 m.
In the unit, wind can be used at a speed of 3-4 to 40-50 m / s and higher, which is impossible for winged wind power plants.
According to preliminary calculations, it is expected that the unit, consisting of 2-3 sections, with a wind speed of about 8-9 m / s, will have an efficiency of up to 65-70% and produce a specific power:
- To the cross-sectional area up to 300-400 W / m 2 ;
- Specific weight not more than 50-60 kg / kW;
- Output voltage with parallel connection of collectors of sections 50-60 kV;
- With a serial connection of 120-150 kV.
A very important advantage of the unit is the absence of moving rotating parts; Wind wheels often do not withstand the load, require repair, are limited in size.
Due to the fact that the surfaces of the hull and the stabilizing condenser, in contrast to the winged wind turbines, are only flowed by a stream of air with minimal friction, with a relatively small frontal aerodynamic load, it is possible to make it from light, cheap materials, mainly plastics, with a specific material consumption and weight Below the corresponding values of the vane generators. Its reliability is much higher.
The structural and mechanical part of the unit is simple, it can be manufactured in any specialized workshop. As a support, lightweight structures can be used, for example, tubular masts with stretches.
2. For the convenience of carrying out the operations of installation, operation, repair, EHD, the wind turbine constructed in accordance with paragraph 1 instead of one common housing has several self-contained sequentially joined sections, including each complete set of electrodes with a general commutation between the electrodes of the sections.
3. EHD wind generator, made in accordance with par. 1, 2, having a streamlined design, relatively light weight, being straight-flow, without torque, with full automation integrated with a fixed aerodynamic balloon. At altitude, the wind speed is much higher and more constant than in the surface layers of the atmosphere (specific wind power ![]() , Where r - air density kg / m 3 , V - wind speed, m / s), the specific power of the unit increases accordingly. For example, at a speed of 20 and 30 m / s (and constant), the specific power of the wind flow increases by 8 and 27 times compared to the power at a speed of 10 m / s, naturally, the specific power of the unit will increase accordingly.
, Where r - air density kg / m 3 , V - wind speed, m / s), the specific power of the unit increases accordingly. For example, at a speed of 20 and 30 m / s (and constant), the specific power of the wind flow increases by 8 and 27 times compared to the power at a speed of 10 m / s, naturally, the specific power of the unit will increase accordingly.
In general, at high wind speeds, the electric field strength in the aggregate will be very large and can reach the electric strength of the air, which will cause a leakage of charges. To prevent this phenomenon, and to increase the specific power when operating in areas with high air speed and at altitude, the unit must have sections shortened by 2-5 times or more, in comparison with conventional surface installations. The linear density of the sections n / L, where n is the number of sections in the installation, L is the length of the transfer zone, should increase approximately in this ratio, the specific weight of the unit (kg / kW) and the specific consumption of materials will accordingly decrease. To create vertical traction (weight reduction), the unit is equipped with bearing planes and elevator controls.
4. The EDG wind turbine of low power (N @ 1 kW), made in accordance with paragraph 1, is equipped with the simplest bearing planes and elevator wheels. The surface of the housing is a carrier. It rises to the height occasionally in the presence of wind, like a kite.
Possible applications of EDG wind turbine:
- when working with negative ions, the unit can release part of the ions into the surrounding space, and negative ions are known to be a therapeutic factor, so it is possible to use it in sanatoria, hospitals or in public institutions for air enrichment;
- in agriculture, on farms, etc .;
- on some types of sea-going vessels, for example, on the bases of the fishing fleet, etc .;
- in the distance from urban areas, in expeditions;
- for domestic needs;
- the use of large-scale aggregates with a working area of hundreds and thousands of m 2 and power of up to many mW, will be effective, especially in combination with traditional grid-based power plants (HED wind farms);
- when the unit is combined with a streamlined aerodynamic balloon, it is possible to use high-power wind power at energetically favorable altitudes.
Currently, under the project of the inventor and with the financing of the Department of Electricity Problems of the Russian Academy of Sciences, a prototype of a wind turbine is manufactured in the factory.
INFORMATION SOURCES
1. US Patent 3,508,085, Cl. H 02 3/00, publ. 1970.
2. Rubashov IB, Bortnikov Yu.S. Electrogasdynamics, Atomizdat, 1971.
3. D. Renzo. Wind power. -M .: Energoatomizdat, 1982.
4. Makashev A.P. Electrogasdynamic generator of direct current. Patent of the Russian Federation No. 1276218, 1993.
CLAIM
1. An electrogasdynamic wind turbine comprising a channel with an expanding section, electrodes with a corona power supply upon initial start-up from an auxiliary low-power voltage source, characterized in that the channel comprises a dielectric split housing, includes one or more sequentially arranged sections, on the inner surface of the housing in each section A plurality of transverse electrodes are provided at the entrance of each section, the former forming positive or negative ions, with the power supply of the crown in operating mode, a pulsating voltage with self-excitation from the collector via a voltage converter and a relay, with stabilization of a capacitor permanently connected to the circuit Corona, and at the outlet of the collector, there are nozzles on the outer surface of the housing that guide an additional air flow through the windows in the housing with a high hydrodynamic head, and air at a reduced speed that does not contain ions through the lateral slots in the housing located after the collector comes out , While in the openings of the windows there are rare grids of fine wire, under tension of transverse electrodes, corona in the flow of additional air, on the outer surface of the case there is a grounded capacitor plate, transverse electrodes, on the inner surface - the second coating, Inside a stabilizing flat or volumetric hollow capacitor consisting of an internal closed-to-ground cover and an outer cover of a plurality of transverse electrodes, however, with the volume capacitor installed, through the slits on the plates and insulation, an additional air flow enters the unit, the slots are covered with isolate, over the stabilizing capacitor Screening grid that slows the settling of ions on its surface, the collector is connected to the load via a voltage converter or a pulse converter, the pulling electrode is connected to the corona circuit in phase with the corona electrode through the relay.
2. A wind turbine according to claim 1, characterized in that, for ease of installation and operation, it consists of self-contained successively connected sections, each with a complete set of electrodes and a general commutation.
3. Wind power plant according to. 1 and 2, characterized in that for operation at altitudes where the wind speeds are significantly higher than those in the near-ground zone, it is built into a streamlined aerodynamic balloon, has sections shortened by at least 2 to 5 times compared to surface facilities, an increase in the linear density Sections of the aggregate n / L, where n is the number of sections, L is the length of the transfer zone, along with the increase in the specific power limits the limiting value of the electric field in the installation against possible leakage of charges; at the same time, it is equipped with bearing planes creating a vertical traction, .
4. Wind power plant according to. 1 and 2, characterized in that it has relatively small dimensions and power, is equipped with load-bearing planes with the simplest rudders of height, rises to the height occasionally with a wind of sufficient strength, like a kite.
print version
Date of publication 02.04.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.