| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2119093
![]()
Windmill
Name of the inventor: Cheboksarov VV .; Zmeu K.V.
The name of the patentee: Far Eastern State Technical University
Address for correspondence:
Starting date of the patent: 1996.12.03
The invention relates to wind power engineering and allows to exclude special turning mechanisms and to increase the working range of rotation of the bearing base, in which the blades actively operate. The rotary blades are mounted on the carrier system with the ability to rotate about the horizontal axes, which are oriented along the radii of the carrier system and through the plane of the blades. The transverse section of the blade is trough-shaped, the axis of rotation of each blade passes along the chord of the chute through the center of gravity of the blade perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the chute. Part planes relative to the pivot axis are made with a condition S 1× r S1 № S 2× r S2, where S 1, r S1 - turning radius area and the center area of one portion of the plane; S 2, r S2 - turning radius area and center area of the other plane portion. At the same time the blade with the parameters set themselves automatically rotated by up to 90 o from one stop to another, one of which corresponds to the vertical position, and the other - horizontally.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to wind power engineering and can be used to create large wind power plants.
There is a known wind turbine with rotating cylinders on the supporting structure, which rotate about the horizontal axis by means of a special cam mechanism with a weather vane (see AS No. 1694976, class F 03 D 3/02, 1991).
The drawback of this device lies in the complexity of the rotation mechanisms of the blades, the need to determine the direction of the wind.
A wind turbine is also known, comprising rotary blades arranged to rotate on radial horizontal axes mounted on a supporting base (see EPO application No. 0270136, cl. F 03 D 3/06, 1989).
The disadvantage of this device is the complexity of the design. In this case, the blades operate only on one half of the circle, while on the other they create additional resistance.
The task, the solution of which is directed to the proposed invention, is to increase the reliability and efficiency of the device.
The technical result, which is achieved in solving the task, is expressed in simplifying the design by eliminating special turning mechanisms, and in increasing the working range of rotation of the bearing base, in which the blades actively operate.
Said technical result in the implementation of the invention is achieved by the fact that a wind turbine comprising rotary blades rotatably mounted on radial horizontal axes mounted on a supporting base is characterized in that the cross section of the blade is provided with a trough shape, the axis of rotation of each blade passing along the chord Trough the center of gravity of the blade, perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the trough, where parts of the planes of the blades relative to the axis of their rotation are made with the condition
S 1B r S1 № S 2× r S2,
Where
S 1, r S1 - turning radius area and the center area of one portion of the plane;
S 2, r S2 - turning radius area and center area of the other plane portion.
In addition, the supporting base is in the form of a ring, each blade being arranged to interact with an abutment placed on the radius of the ring and made in the form of an elastic rod, one end of which is fastened to a part of the blade with a smaller area, and the free end is directly connected to the carrier Ring.
A comparative analysis of the essential features of the claimed solution and the characteristics of analogs and prototype testifies to its compliance with the criterion of "novelty".
At the same time, the following functional tasks solve the characteristics of the inventive part of the claims.
The sign "... the transverse section of the blade is given a trough shape ..." allows to provide additional force in the direction of rotation of the carrier system with blades, as well as rapid lifting of the blade after passing the passive section towards the air flow.
The sign "... the axis of rotation of each blade passes along the chord of the chute, through the center of gravity of the blade, perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the chute ..." defines the condition ensuring the ease of turning the blades with the established parameters under the influence of aerodynamic forces.
Conditions 1 S H r S1 № S 2× r S2 provides a rise in the operating position of the blades under the action of aerodynamic forces.
The set of distinctive features of the second claim of the invention provide additional rotatable blades under full wind load to 90 o from the vertical toward the palm protection system in stormy weather. In this case, the emergency inclination of the blade leads to an additional effect - clamping the carrier system against the supporting surface, which increases the stability of the structure.
The proposed technical solution is shown in the drawing, where 1 is the carrier system; 2 - supporting surface; 3 - rotary blades; 4 - axis; 5 - an abutment defining the horizontal position, and 6 - an abutment defining the vertical position of the blade.
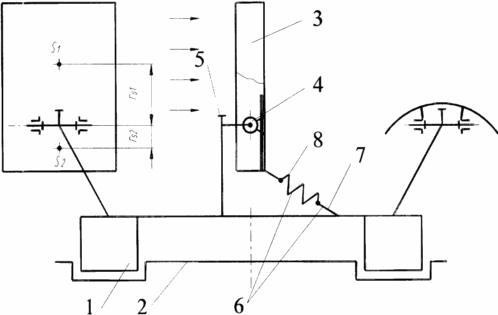
The carrier system 1 is in the form of a ring, one side of which is supported on the supporting surface 2. On the other, the rotary blades 3 are rotatable about the horizontal axes 4, which are oriented along the radii of the carrier system. The plane of the blades 3 in a section parallel to the pivot axis is trough-shaped. The axis of rotation of each blade passes through the chord of the chute through the center of gravity, dividing the plane of the blade into two parts according to the formula. The free rotation of the blades is limited by the stops 5 and 6. The latter is a steel cable 7 connected to a bearing ring with a restraining spring 7 fastened to a part of the blade with a smaller area.
The device works as follows. Under the action of the wind vane 3 is automatically rotated about the axis 4, driving the carrier surface 1. In this case, the blades are rotated within 3 to 90 o from lock 5 corresponding to the horizontal position with the least resistance to air flow, the stop 6, which corresponds to the vertical position of the blade With the greatest perception of wind force. If the wind force exceeds the limit, the limiting spring 8 is stretched and the blade takes an inclined and then horizontal position.
CLAIM
A wind turbine comprising rotatable blades rotatably disposed on radial horizontal axes mounted on a supporting base, characterized in that a transverse section of the blade is provided with a trough-shaped shape, the axis of rotation of each blade passing along the chord of the chute through the center of gravity of the blade, perpendicular to the longitudinal Axes of the trough, the parts of the blade planes relative to the axis of their rotation being made with the condition
S 1B r S1 № S 2× r S2,
where S 1, r S1 - turning radius area and the center area of one portion of the plane;
S 2, r S2 - turning radius area and center area of the other plane portion.
2. Wind turbine according to claim 1, characterized in that the supporting base is made in the form of a ring, each blade being arranged to interact with a stop located on the radius of the ring and made in the form of an elastic rod, one end of which is fastened to a part of the blade with a smaller Area, and the free end is connected directly with the bearing ring.
print version
Date of publication 02.04.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.