|
Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2075643
![]()
MOBILE WIND POWER PLANT AND METHOD OF ITS INSTALLATION
The name of the inventor: Zabegaev AI; Gorbunov Yu.N .; Naumov VV; Chernyshov SK; Smirnov S.L .; Novak Yu.I .; Sobol Ya.G .; Demkin V.V.
The name of the patent holder: Limited Liability Partnership - Obshchemash-engineering; Research and Production Association "Vetroen"
Address for correspondence:
Date of commencement of the patent: 1995.01.31
Use: The invention relates to wind power and concerns relocated and mobile wind power plants and methods of their installation. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION: The mobile wind power plant comprises a sectional mast, a hoisting device, a wind wheel with blades, a gondola, a generator, a transmission, flexible towers and is provided with adjustable supports, a power cage, a series of support groups and peripheral supports; each of the support groups is in series consecutive A lever and a peripheral truss, in the support group, the levers are rotatably and fixably supported at their peripheral ends to the ground, forming a gap between the ground and the lower portions of the cage in height and width of a definitely greater height and width by a transport platform for transporting the wind power plant, Sectional mast is made of the same type of modules, the lower one of which is mounted and fixed inside the cage, the shape and cuts of which are designed to move the module forward through an opening in the central part of the cage, and the flexible links are equipped with tension mechanisms and connected at their ends to the peripheral support of each of the groups of the support Mechanism, and others with the top module of the mast. Each flexible rod can be equipped with a mechanism for changing its length, including the mechanisms of preliminary and final tension, and self-tension when its length is changed. The load-lifting device includes a pair of "rack-wheel" gear connected to a drive located on the body, which is designed to be mounted on a power cage. Peripheral supports are adjustable in height, and at least one peripheral support is provided with a pin adapted to penetrate into the ground. Mobile wind power plant is installed in a way that includes transportation to the place of installation of the components of the installation and the base, the installation of the wind wheel and the gondola, the gradual lifting of the component parts of the installation by the load-lifting device. The base of the installation is made in the form of a power cage with a through channel, beforehand, a part of the installation is assembled, including the power cage, the quarrying farm and levers, prior to transportation, placed on the transport platform and supported on the transport platform by the lower side of the cage, the transport platform is moved to the place of installation until the base coincides With a nominally necessary position and temporarily fixed, then the linkage of the power cage to the ground is carried out with the help of an emergency truss and the lever, the mounted platform is mounted on the base relative to the transport platform, then the transport platform is removed, and the lifting device of each of the mast modules is lifted through the through channel At the base of the installation, the lifting being carried out step-by-step in the component part of the assembly in assembly, at least one of the modules to be lifted is provided with means for locating and fixing the functional tooling thereon. On the peripheral supports, the support elements are made in the form of containers for liquid or under a free-flowing medium. The lifting of the installation mounted on the base of the installation relative to the transport platform is carried out with the help of adjustable supports.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to wind power and concerns relocated and mobile wind power plants (VEU), oriented primarily to work in the low-speed wind range.
A mobile wind power plant of low power is known, in which the support is made in the form of separate air-filled elastic toroidal sections, the cavities of which are communicating with each other via a flexible hose (see authsp., N 164854, 01.13.1962, cl. F 03 D 11/00).
This known technical solution requires special equipment: assembling of special equipment: compressor, pipelines and pneumatic fittings, which reduces the mobility of the installation and its scope, complicates the technology of the work.
In addition, this embodiment of the support from the air-elastic elements predetermines its large cross-section, which worsens the interaction of the propeller with the support when the wind wheel rotates in the air flow and limits the efficiency and technological parameters of the wind turbine.
Known is the method of mounting vertical structures (see aut.svid.SSSR No. 1219767 of 04/07/84 class E 04 H 12/00), in which the upper section is raised above the foundation to the height necessary to bring the bottom section under cultivation upright. After the design connection of the upper and the undergrowth of the lower sections, the lower level braces are transferred to be fastened to the lower part of the upper section and to be re-stitched for the next lift.
This known technical solution for the considered class of wind turbines has shortcomings that limit its effectiveness.
This method of installation is suitable primarily for permanently installed structures, because It contains a laborious operation of joining up the sections to be welded together, transferring the braces and rearranging.
In addition, it is associated with laborious work on the organization of a supporting contour of the erected structure, which is carried out from flexible tractors moored into the ground for effective perception of wind loads. Quick dismantling of the assembled structure is simply impossible.
For this class of mobile and quickly installed wind turbines, first and foremost, a simple and operational technology for deploying a wind turbine at the installation site and a technology for relocating a wind turbine are required.
An important point is to ensure the perception of dynamic wind loads, as wind turbine windmill during operation creates a great aerodynamic resistance, which, given the dynamic nature of the wind load and its greater magnitude, creates significant difficulties for the operation of the wind turbine.
Known for avt.svid. USSR N 1219767 of 04/07/84 cl. E 04 H 12/00 The method of installation, despite its progressive nature, does not solve the problems discussed above.
A mobile wind power plant is known (see USSR Authorship No. 1546700 dated April 27, 1998, F 03 D 11/04), containing a supporting mast, attached to the ground by flexible rods, a rotor windmill mounted on it with horizontal traverses and pivoted to Their blades and an electric generator located at the base of the mast and kinematically connected to the windmill by means of a reducer and a transmission shaft installed in the mast cavity, a mobile platform. The transmission shaft and supporting mast are telescopic. The latter is articulated on the platform and equipped with lifting and extension mechanisms, horizontal traverses are mounted with the possibility of folding to the mast, and the electric generator and the reducer are mounted on the platform.
Known by avt.svid. N 1546700 a mobile wind power plant excludes construction work on the erection of the foundation, increases the speed of deployment and ensures its installation directly on the transport platform used as a support for the entire operation of the installation, i.е. As in its transportation, installation, so, and this is important, in the process of work.
According to the function and the result to be achieved, such a wind power installation and the method of its installation are closest to the claimed wind power plant and the method of its installation and are chosen as a prototype for the device and method.
The installation of a mobile wind power plant (see above description for USSR USSR No. 1546700 dated April 27, 1998) is carried out initially in the factory. After that the wind power plant permanently connected to the mobile (transport) platform is transported in a mobile folded state on the transport platform.
In place of work, turn the telescopic mast from horizontal to vertical position due to the lifting mechanism. Support the transport platform on the ground through a pair of height-adjustable supports. Connect the upper part (section) of the telescopic mast with flexible rods. A telescopic section having a smaller diameter is projected from the lower section of the mast having a larger diameter.
This wind power plant has the following drawbacks: the transport platform is constantly moving, mounting and generating electricity is a mobile or fixed support under its mast. The operation of the wind turbine can not be provided without a transport platform; Because of the availability of a "permanently unused" transport platform, has a high cost, both the wind power plant itself and the electricity generated by it, which increases the payback period of the wind turbine; The universality is not enough, since the design of the wind turbine is essentially unchangeable, which requires the factory installation of a wind turbine on the transport platform. When arriving at the site, its parameters, for example maximum height, can not be changed based on specific terrain and wind flows; Insufficient reliability primarily due to a large number of articulated mechanisms and assemblies, including a retractable mast and a platform in the power circuit of the installation, which have low reliability, all the more taking into account the specific operation of the wind turbine under the influence of variable loads, climatic factors and, as a rule, insufficient Qualification of the attendants; The binding of the wind turbine to the anchored supports for flexible links impose certain restrictions on the types of soils used. For example, in rocky soils, the securing of flexible rods requires special technology compared, for example, with soft (sedimentary rocks) soils. At the same time, on loose soils, for example sandy soils, there is a difficulty in anchoring the supports in view of the fragility of the ground. Similarly for peat and marshy soils.
This limits the use of a known device and a known method for installing a wind turbine.
The purpose of the invention is: to reduce the cost, weight, material consumption of the wind power plant by completely eliminating the vehicle from the plant in the operating mode when generating electricity; Shortening of the installation time of the windmill and the number of personnel; Increase of universality due to the possibility of installing wind turbines on loose and rocky soils without their preliminary preparation, but also due to the use of modular assemblies during installation; Providing the possibility of changing the maximum height of the wind turbine when it is installed in a working position in specific local conditions and wind flows; Optimization of transport dimensions of wind turbines and its components; Increased reliability; Reduction of the payback period and reduction of the cost of generated electricity;
The claimed goal is achieved by the fact that a wind power plant comprising a sectional mast, a load-lifting device, a wind-wheel with blades, an electric generator, a transmission, a gondola (with a rack), flexible traction, is equipped with a power cage, a series of support groups in the form of consecutively connected consecutive truss, lever and peripheral In the support group, the arms are rotatably and fixed in the rest position by their peripheral ends to the ground, forming a gap between the ground and the lower portions of the cage for the height and width of the definitely greater height and width of the transport platform for the transportation of the wind power plant. The mast is made of the same type of modules , The lower of which is mounted and fixed inside the cage, the shape and dimensions of which are designed to move the module forward through an opening in the central part of the cage, and the flexible links are equipped with tension mechanisms and connected at their ends to the peripheral support of each of the groups of the support mechanism, and the others to the upper Mast module.
Further differences of the claimed device consist in the fact that: each flexible rod is provided with a mechanism for changing its length, including the mechanisms of preliminary and final tension, the load-lifting device includes a pair of rack-wheel pairs connected to a drive located on the housing to which Is configured to be mounted on the power cage, the peripheral supports can be made to be adjustable in height, wherein at least one peripheral support is provided with a pin configured to be grounded. The claimed method of mounting a mobile wind power plant includes transportation to the installation site of the component parts of the installation and the base, the installation of the wind wheel and the gondola, the gradual lifting of the component parts of the installation by means of load-lifting equipment, the base of the installation is first carried out in the form of a power cage with a through channel and before collecting a part of the installation Clip, coarse truss and levers, place it on the transport platform and lean against the transport platform with the bottom side of the cage, the transport platform is moved to the place of installation until the base coincides with the nominally required position and temporarily fixed, forming an arched opening under the power cage, then removed from Of the opening of the transport platform, and lifting of the lifting means of each of the mast sections is effected through a through channel in the base of the installation, the lifting being performed step-by-step in the component part of the assembly, and at least one of the raised sections is provided with means for locating and fixing on them a functional tooling .
Further differences of the claimed mounting method consist in the fact that on the peripheral supports the support elements are made in the form of containers for liquid or bulk medium, and the formation of the opening under the base of the power cage and the lifting of the mounted part of the installation relative to the transport platform is carried out by means of adjustable supports.
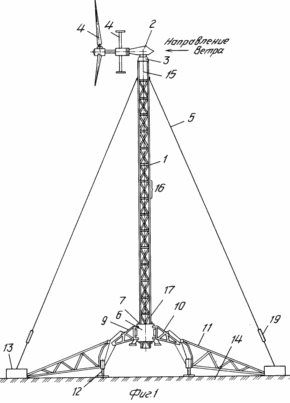
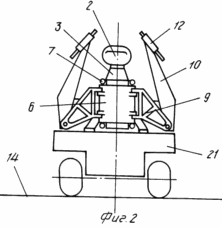
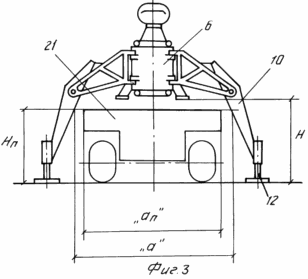
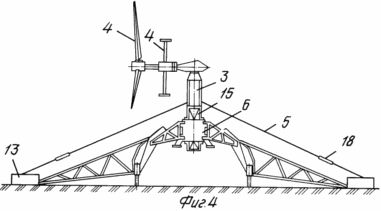
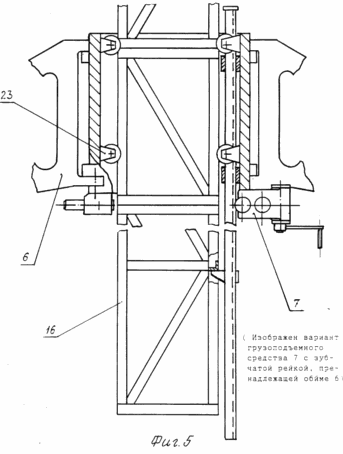
The attached drawings show: FIG. 1 general view of the mobile wind power installation in the assembled state; FIG. 2 general view of the mobile wind power plant in the transport position. FIG. 3 - scheme for supporting the power cage on the ground after forming the internal contour of the supports and removing the transport platform from under it. FIG. 4 - wind power plant in the intermediate stage of installation of the state with the pushed peripheral supports and the formed external supporting contour. FIG. 5 power clip with a lifting mechanism for the extension of the mast. FIG. 6 top of the wind power plant. Release of flexible links to the upper module to the gondola stand of the wind turbine. FIG. 7 diagram of the load action from the weight of the wind power plant, the wind flow and the load perception by the external and internal support circuits.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
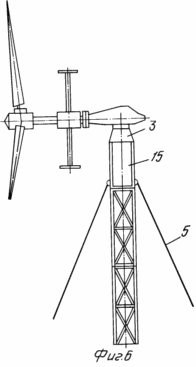 |
In the drawings and in the materials of the applications the following is indicated: the sectional mast of the wind turbine 1; Gondola 2; Gondola stand 3 upper module 15 mast 1; Wind wheel 4; Flexible links 5; Power clip 6; A load-lifting device 7; Support groups 8; An ordinary farm 9; Lever 10; Peripheral truss 11; Support (adjustable in height), mounted on the end of the lever 12; Peripheral support 13; Soil 14; Upper mast module 15; A typical mast module 16; Lower mast module 17; Tension mechanism of flexible links 18; Mechanism for changing the length of flexible links 19; A pin 20 on the peripheral support 13; Transport platform 21; Drive of load-lifting device 22; Guides 23 of the power cage 6; Containers 24 for liquid or bulk media on peripheral supports 13.
A mobile wind power plant, see FIG. 1.4, 5, contains a sectional mast 1, a gondola 2 with a stand 3, a wind wheel 4, an electric generator and a transmission, flexible links 5 and is equipped with a power cage 6 with a central hole and a lifting device 7, supporting groups 8, for example four, each Which is made in the form of consecutively connected prefabricated truss 9, lever 10 and peripheral truss 11, the primitive truss 9 at one end is connected to the cage 6, and the outer one is articulated to the center-close end of the lever 10, which is pivotally and vertically fixed and Which has a height-adjustable support 12 at the peripheral end, the peripheral truss 11 is connected at one end to the peripheral end of the lever 10, and the outer end to the outer peripheral support 13, the levers 10 are pivotally and fixably mounted in the support position by the peripheral edge to the ground 14 through A height-adjustable peripheral support 12, forming between the ground 14 and the lower portions of the casing 6 a height H and a width "a" of a definitely higher height H n and an "an" width of the transport platform for the transportation of the wind power plant, nacelle 2 (provided at the bottom 3) is connected to the upper module 15 of the mast which is made in the form of rigidly interconnected modules of the same type 16, the lower of which 17 is mounted and fixed inside the cage 6, the shape and dimensions of which are designed to move the modules 16 through the hole in the central Parts of the cage 6, each flexible rod 5 is provided with a tensioning mechanism 17 and is connected at one end to the peripheral support 12 of each of the support groups, and the other to the post 3 of the nacelle 2 (upper mast module 14).
The movable wind power plant can additionally be provided with mechanisms for changing the length of the flexible rods 5. Depending on the service life and operating conditions, it may contain mechanisms for preliminary and final tension of the flexible rods, as well as for the mechanisms of self-tensioning of the rods during the extension of the mast, respectively, when the length of the flexible rods is changed. In addition, the wind power plant is equipped with nodes for securing the power cage on the transport platform.
The peripheral supports 13 are adjustable in height, at least one of them being provided with a pin 20 which is adapted to penetrate into the ground 14.
The load-lifting device 7 includes a rack-and-wheel pair of wheels connected to a drive 22 located on the housing, see FIG. 4, which is designed to be mounted on the power cage 6.
In the assembled state of the windmill, the mast base (lower module 17) is fixed in the enclosing power cage 6, which is connected with the support groups symmetrically diverging at an angle to each other, for example, four in the form of a consecutive fixed farm 9, a lever 10 and a peripheral truss 11, The truss 9 is connected at one end to the power cage 6 with one end and the other external is pivotally connected to the proximal end of the lever 10, which is pivotably mounted and fixed in a vertical plane and having a height-adjustable support 12, for example a screw, at the peripheral end.
The primitive trusses 9 are connected to the cage 6 with the possibility of turning each truss 9 in a horizontal plane and then fixing it in the working radially oriented position.
The levers 10 are mounted on the prefabricated truss 9 with the possibility of their rotation and fixation in the vertical plane in at least two positions in the transport, raised up, see FIG. 2, and working, turned down, see Fig. 1.
The levers 10 in the working position are fixed in the position of supporting the peripheral edges of the ground 14 through an adjustable screw 12 to form a power cage 6, four coarse trusses 9 and four arms 10 of the power structure with an arched opening along the height H and a width B, Than the height H 1 and the width B 1 of the transport platform 21 used to transport the unit in disassembled form to the installation site and the subsequent operation of the wind turbine.
The mast of the wind turbine is a sectional dismountable structure, each section is a single module 16 in the form of a volumetric design with elements of intermodule fixation along the upper and lower ends. The cross section of each module 16, 17, the nacelle post 3 is made for the central opening of the power cage 6 and its guides 23 for free passage through the cage 6. The guides 23 and the height of the module H 3 are selected from the condition of free movement in the archway, i.e. Must be definitely less than the latter.
The implementation of the sectional mast module of the windmill is not considered in this application and the implementation of the cable devices of the windmills that are laid out during the installation as well as the start-stop devices of the windmill are not considered, which are independent technical solutions known from the technical literature and not being the subject of this application .
Details of the module design, implementation and method of installation of vertical structures made up of sections are considered in a separate application of the same applicant for "Method of mounting vertical structures made up of sections and a sectional module for mounting vertical structures" sent to VNIIGPE ref. N 5 / 1-95 dated January 30, 1995
In the present application, it will be noted that the section module comprises an upper and a lower base connecting their skeleton, intermodule attachment points on the bases, and provided with guides fixed to the skeleton for interacting with a load-lifting device, the module skeleton being in the form of a bulky power structure, On the bases are arranged in pairs on each and diagonally opposite to the rotation of the diagonals on the bases by an angle, for example, 90 ° relative to each other.
The method for mounting a mobile wind power plant is that the installation base is made in the form of a power cage 6 with a through channel, pre-transported, a part of the installation consisting of a power cage 6, primitive trusses 9 and levers 10 is assembled, placed on a transport platform 21 And they are supported on the transport platform 21 by the lower side of the cage 6, the transport platform 21 is moved to the mounting site until the base coincides with the nominally required position and is temporarily fixed, after which the power casing 6 is connected to the ground 14 by means of primitive trusses 9 and levers 10, and the assembled On the base (power cage 6) part of the installation relative to the transport platform 21, forming an arched opening under the power cage, then the transport platform 21 is removed from the opening, and the lifting device 7 of each of the mast modules 16 is produced through the through channel in the base of the power cage 6 of the installation, Wherein the lifting is carried out in a step-wise integral part of the assembly in assembly, and at least one of the modules to be lifted is provided with means for locating and fixing functional attachments thereon.
Additionally, on the peripheral supports 13, the supporting members are made in the form of liquid or liquid containers 24, and the lifting of the installation mounted on the base 6 with respect to the transport platform 21 is performed by means of adjustable supports 12 on the arms 10.
Preliminary operations of the method, including assembling a part of the windmill from the power cage 6 with through channels, preliminarily shaped forms 9 and levers 10, a lifting device 7 fixed with a casing on the power cage 6, the upper mast module 15, which is placed in the load-lifting device 7 and fixed, and executed In the form of a rack 3 with a gondola 2 and a wind wheel 4 in the folded state, guarantees high quality of assembly and reliability of the windmill during operation.
In order to guarantee non-damage during transportation and relocation of the windmill, the assembled part of the installation is supported to the transport platform by the lower side of the cage by means of special support units.
Pribooboimennye farm 9 set in the most convenient for transportation position. The levers 10 are turned into the transport position "up" and fixed.
Upon arrival of the transport platform 21 with parts of the windmill directly to the installation site of the installation, the transport platform is moved to coincidence in the plan of the power cage 6 with the required position, the platform itself is fixed in this position.
In each of the support groups 8, the lever 10 is fixed and set up in a vertical plane relative to the connection with the coarse farm, turning from the transport position "up" to the working position "down". In this case, the lever 1 is taken out beyond the dimensions of the platform 21 itself and rests its peripheral end through the adjustable support 12 on the ground 14. In the operating position "downwards", each lever 10 is fixed, the corresponding length of each of the screw supports 12 is selected and, by screwing or screwing It is achieved the nominally necessary alignment of the position of the power cage 63 and sufficient equalization of the pressure of each of the adjustable supports 12 directly on the ground 14. The vertical axis of the power casing 6 is placed in the nominally required vertical position by means of a level, plumb or level. The peripheral truss 11 is connected at one end to the peripheral end of the lever 10 and its outer end is connected to the peripheral support 13. Both ends of the peripheral truss 11 are rigidly fixed at the peripheral end of the lever 10 and the peripheral support 13, respectively.
Install the blade of the wind wheel 4 in the working position on the gondola 2. One end of each flexible link 5 is connected to the power stand 3 under the gondola 3 and through the constant tension mechanism 18 the opposite free end of the flexible link 5 is closed and form a power triangle from the column 2, the power cage 6, An unobstructed truss 9, a lever 10, a peripheral truss 11, a peripheral support 13, and a flexible link 5 with a mechanism 18 and / or 19. Change the geometry and components of the power triangle during installation or operation. The lifting device 7 (can be performed in various ways, for example in the form of a gear connected to a rail or a friction pair: a rail guide rail) is connected to the power cage 6. The mobile transport platform 21 is withdrawn from under the arched opening formed by the power cage 6, Coarse trusses 9 and levers 10 with adjustable supports 12 on the ground 14. The gondola 2 is dismantled with the stand 3 relative to the power cage 6. After that, the upper mast module 15 has the possibility of translational movement relative to the guides 23 on the load-lifting device 7 fixed to the power cage 6. The same type of mast modules 16 are made to a height that is definitely less than the height H of the opening formed by the power cage 6 of the coarse farm 9 and the lever 10.
In the operating position, each of the modules 16 is alternately moved in a plan, aligned in cross-section with the pass-through section of the central channel of the cage 6, raised above the ground 14 in an upright position to the lower end of the upper portion, which for the first of the mounted modules 16 will be the lower end of the post 3 or Upper mast module. The blades of the wind wheel are installed in the working position, after which the modular casing-mounted part of the windmill is hoisted, the free end of each flexible link 5 connected to the power rack by the upper module 14 under the gondola 2 is closed through the mechanisms 18, 19 on the peripheral support 13, A variable power triangle and supporting in it the nominal forward forces in the course of installation, the lifting of the gondola 2 and the assembly of the mast are carried out stepwise simultaneously.
For this purpose, modules 16, for example, bolted connection, each subsequent module 16 with the previous one, are rigidly connected to each other, at least at diagonally located points. After each connection, the connected gondola 2 with the rack and the modules 16 by the height (length) of the module 16 are alternately lifted by the load-lifting device 7. The lower of the connected modules 17 rigidly at several points (for perception of the moment) is fixed in the power cage 6. For The account of the mechanism 19 changes the length of the rod 5 during the extension of each module 16. In this case, the gaps between the same modules 16, the support 3 and the connecting elements between the module modules are selected. If necessary, adjust the nominal voltage in the system of the components of the windmill modules to the nominal required by the tension of the flexible links 5. At each stage of installation, any of the modules 16 is changed as the geometry of the power triangle formed by the mounted part of the mast, the truss 9, the levers 10, and its components, those. The power triangle is forced to change in space.
To stretch the rods 5 and change their length during the lifting of the structure, devices are used in the form of special mechanisms. As a simple mechanism for tension, for example, a lanyard can be used, which, when screwed, changes the length of the rods. In order to regulate the length and tension of the flexible links when the mast extends, a more complex mechanism can be applied from the known, for example, manual rescue firefighting device, which allows the cable to be drawn up to a length of up to 30.50 meters with a resistance force of up to 125 or more "kgf" at ambient temperature ± 50 o . (A brochure describing this rescue mechanism is attached). ["Rescue firefighters individual device: USPI 4-50, USSR Ministry of Internal Affairs, Institute of Fire Defense, M, 1991.
When pulling the cable at a certain adjustable speed (from 0 to 3 m / s), the device creates a tension force of up to 125 kgf. The strength of pulling the cable in its nature is inelastic dissipative and is created due to the organization of viscous drag of liquid in the device. (Other variants of this device are possible for considerably greater efforts up to hundreds of "kgf" and up to tons.) This technical solution is independent, known, so detailed consideration is not given.)
In combination with the lanyards, such and similar tensioning devices in the claimed method effectively solve the problem of creating an axial compressive force both during the extension of the structure and at the end of the extension.
The dismantling of the wind power plant is carried out in the reverse order described, successively lowering the modules and disconnecting them from each other and from the gondola rack. Transport platform 21, after it is removed from the opening, even one can be practically used for installation, maintenance, etc. An unlimited number of wind power plants produced on the basis of this complex invention; It can be, for example, a returnable vehicle.
At the same time, a number of wind turbines can be installed on one transport platform, for example, two, three. Five or more. In this case, after installing the first of the wind turbine modules on the ground and removing the platform from the archway, it can be transported to the installation site of the second windmill module, etc.
Since the transport platform 21 is only needed for transportation, the cost of the wind turbine and its installation is dramatically reduced. Moreover, the claimed mobile wind turbine does not require a foundation, or practically no preparatory work on the installation site. The type of soil is also indifferent. Loose soil (sandy, sandy loamy, peaty) will require only an enlarged diameter of the support part of the peripheral support 13.
One (at least one) of the lifting sections of the mast modules, the upper 15 or the standard 16 module is provided with means for locating and fixing the functional rigging thereon. In the simplest case, the functional accessories are the nodes for securing the flexible links 5. Other options are possible, for example, nodes for fixing lighting devices, electrical cables, etc.
In essence, in the claimed device, two support circuits are formed in the claimed device from the supports 12 and external from the peripheral supports 13. The execution of the peripheral supports 13 in the form of containers for liquid or granular media allows to efficiently solve the problem of balancing aerodynamic loads in the operation of a wind turbine in a nonfundamental design of a wind turbine, Allows significantly reduce the transported mass of wind turbines. For example, the support 13 in the form of a container with a volume of 1 m3 at its own weight of 50.100 kg makes it possible to obtain a weight of 1, OT when filled with liquid (water), and when filling with ground to 2.2.2.7 tons, which effectively solves the problem of the stability of the wind turbine at Work.
The internal supports 12 and the peripheral supports 13 are adjustable, which allows for equalization of loads during installation. First, when the inner support loop is formed, the weight of the modular part of the wind turbine mounted on the transport platform is transferred onto it, while the lifting cradle relative to the transport platform is lifted by means of adjustable supports 12.
Consider the scheme of loads applied to a mobile windmill when operating in a wind flow.
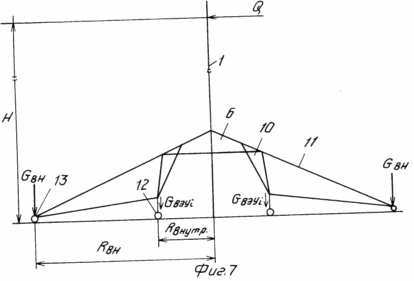
When the wind flow is affected, the resistance force Q (see Figure 7) tends to overturn the wind turbine. The developed external support circuit does not allow to overturn the wind turbine.
As can be seen from the circuit of FIG. 7, the weight of the wind turbine and the peripheral supports resist the tipping.
The equilibrium condition for the non-rolling of the wind turbine is approximately written in the form: ![]()
Where: H is the height of the axis of the wind wheel; Q force of aerodynamic resistance of windwheel to wind flow during operation of wind turbine; K safety factor, taking into account the gustiness of the wind and other random factors;
(K @ 1.3 ... 1.5)
N GBn reaction from the weight of the i-th support of the outer contour;
R Bнi is theprojection of the radius of the installation of the i-support of the external reference contour on the direction of the wind flow;
N number of supports of the external reference contour;
G veu weight of the wind turbine;
R is the distance from the vertical axis of the wind turbine to the nearest external support in the projection to the direction of the wind flow.
As can be seen from equation (1), the weight of the outer peripheral support applied on the larger arm than the weight of the wind turbine generates a large counter-torque. Therefore, the desire to reduce the weight of wind turbines due to the organization of two support circuits
Internal, perceiving mainly the load of the weight of the mounted design of the wind turbine, and the external one from the condition of perception of mainly functional loads, in particular side loads from the wind turbine of the wind turbine, is justified and expedient. This allows us to achieve a reduction in the material consumption, the cost of the installation, ensure the convenience of transporting the windmill and does not conflict with the task of ensuring the stability of the assembled structure under various disturbances, including wind disturbances.
For example, for
H = 15.0 m, n = 4, R вн = 3.0 m Q = 1.0 Tc, R Bn = 6.0 m, G veu = 1.0 Tc, effective torque M = Q H = 15 Tm is balanced as follows:
Due to the weight of the wind turbine with the direction of the wind flow at an angle of 45 ° between the supports,
M Gwey = 3.0m × cos 45 oh 1.0 tc = 2.1 tm, which, with the use of classical solutions, requires anchoring of flexible bonds in the ground on a considerable base for perception of the external acting moment M = 15 tm;
Due to the weight of the outer (peripheral) supports
MG BH 12, Ohm C cos 45 oh 2.0 Tc = 17.0 tm, thus, the efficiency of using an external supporting circuit with supports in the form of tanks for liquid or bulk filler is obvious.
Mounted wind turbine is subjected to the following main types of loads:
- From the weight of the wind turbine in the non-operating state;
- Lateral aerodynamic load from the resistance of the wind wheel in the operating mode of operation at power output;
- Lateral aerodynamic load during storm modes; wind turbine does not work, storm V = 44.60 m / s (at mast height 15 and according to SNIP V max = 44 m / s, mast height 30 m V max = 52 m / s);
- Lateral loads from the wind during installation.
To ensure the perception of lateral loads, the mast of the wind turbine must be constantly loaded with an axial compressive load. This is achieved by tensioning the flexible connections 5, which are stretched both during the operation of the windmill (in the assembled state) and during the installation of the wind turbine in step-by-step lifting due to the presence of tension mechanisms 18 and changes in the length 19 in the chain "upper module 15 of the mast peripheral support 13" and Thus forming a closed power triangle. The compression force of the mast may be different depending on the solution of the nodes of the inter-module connection of the sections. In the simplest case of their implementation with the organization of simple support of the sections in the longitudinal direction and fixing them from the horizontal displacement to ensure the stability of the composite mast, the tension of the flexible supports must be sufficient to perceive the external acting torque: in the example under consideration, at a moment M = 15 m, the tension force of the flexible Connections should be 2.7 tons. The longitudinal compressive number applied to the mast, at the same time, is 10 tons, which is sufficient to ensure high rigidity of the structure thus stressed.
Depending on the requirements for the rigidity of the assembled structure, the amount of tension of the pre-tension of flexible rods can be set differently. For example, if the upper module of the mast is allowed to move by 0.1.0.2 mm in the horizontal direction, the value of the pre-tension force of the flexible masts can be reduced by 3.8 times, which will lead to a reduction in the rigidity of the entire assembled structure (depending on the requirements)
The height of the mast of the mobile windmill during installation according to the claimed method can be adjusted to the specific conditions of the terrain and the characteristics of the wind flow. It can be increased if the terrain is "cluttered" with structures or trees, i. E. When the boundary layer is high, and, on the contrary, is reduced when the terrain is open.
The problem of perceiving the increased loads on the wind power due to the increase in the height of the mast in this case is effectively solved by increasing the weight of the peripheral supports 13.
The height of the mast is increased by simply adding additional modules to the modules.
Important issue in the operation of the wind turbine is the issue of grounding, tk. A lonely standing vertical metal structure is exposed to electric lightning discharges.
To improve the grounding of the wind turbine, it is sufficient to provide at least one of the peripheral supports with a pin that is capable of penetrating into the ground.
The claimed method and device are oriented primarily for use in conditions of low-speed wind flows, for which the requirements for wind turbines are much more stringent than in classical cases. For example, a wind turbine windmill that efficiently operates in low-speed winds and possesses considerable sailing capacity, in strong and storm winds, creates loads 2.5 times greater than those for classic wind turbines designed to deliver rated power at speeds 2.5.4 times the average annual Speed in the area of application of wind turbines.
In addition, the mobility of the wind turbine is of particular importance. This applies to installations used for the needs of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Emergency Situations, expeditions, when energy supply in uninhabited areas is required, when objects are relocated, i.e. In situations where the wind turbine is dismantled in the last place, and in the new place is installed first.
The claimed windmill is mobile, compact in transportation and transported on two cars or one car with a trailer, the first transport module comprising a power cage with supporting groups and composite lifted parts of the windmill (folded or bladed in the transport container), a second transport Module is a set of sections of mast modules, peripheral trusses and peripheral supports.
The windmill is mounted with a minimum number of personnel.
As the design developments and calculations of technological time showed, installation of the wind turbine as a whole can be carried out with the help of two people per hour. This requires minimum lifting equipment, for example, for a 10 kW wind turbine, the mass of one sectional mast module does not exceed 20 kg, the mass of the peripheral support is 100 kg, the peripheral supports, depending on the embodiment, 50,100 kg.
Thus, the claimed mobile wind power plant and the way of installation of the mobile wind power plant are progressive, and their use creates a positive effect, which consists in the following:
- Reduces the cost, weight, material consumption of the wind power plant due to the complete exclusion of the vehicle from the structure of the installation in the operating mode when generating electricity;
- Shortens the terms of installation of the windmill and the number of personnel necessary for this;
- Extends versatility by providing the possibility of installing wind turbines on loose and rocky soils without their preliminary preparation, but also by using modular assemblies during installation;
- Provides the possibility of changing the maximum height of the wind turbine when it is installed on a working position in specific terrain conditions and wind flows;
- Allows to optimize the transport dimensions in the wind turbine and its components;
- Improves reliability by providing factory assembling of the most important components of VCU and effective perception of loads during operation of wind turbines in various operating modes, including storms and operation in strong winds;
- Shortens the payback period and reduces the cost of generated electricity, especially in low-speed winds due to lower installation costs and the cost of the wind turbine construction.
CLAIM
1. A movable wind power installation comprising a sectional mast, a load-lifting device, a wind-wheel with blades, a gondola, a generator, a transmission, flexible towers and equipped with adjustable supports, characterized in that it is provided with a power cage, a series of support groups, in the form of consecutively connected consecutive trusses , The lever and the peripheral truss, in the support group, the levers are pivotable and fixed in the rest position by their peripheral ends to the ground, forming a gap between the ground and the lower portions of the cage in height and width of a definitely greater height and width of the transport platform for transporting the windmill, Is made of the same type of modules, the lower one of which is mounted and fixed inside the cage, the shape and dimensions of which are designed to move the module forward through an opening in the central part of the cage, and the flexible links are equipped with tension mechanisms and connected at their ends to the peripheral support of each of the support groups, and Others with upper mast module.
2. Installation according to claim 1, characterized in that each flexible rod is provided with a mechanism for changing its length.
3. An installation according to claim 1, characterized in that each flexible rod is provided with a pretensioning mechanism and a final tensioning mechanism.
4. Installation according to claim 1, characterized in that each flexible rod is provided with a self-tensioning mechanism with a change in its length.
5. Installation according to. 1 4, characterized in that the flexible rods are provided with tensioning mechanisms and changing their length, connected in series.
6. An installation as claimed in claim 1, characterized in that the load-lifting device includes a rack-and-wheel pair of wheels connected to a drive located on the housing, which is configured to be mounted on a power cage.
7. An installation according to claim 1, characterized in that the peripheral supports are adjustable in height.
8. Installation according to. 1 and 7, characterized in that at least one peripheral support is provided with a pin adapted to penetrate into the ground.
9. A method for mounting a movable wind power plant, comprising transporting the components of the installation and the base to the installation site, installing a wind wheel and a gondola, successively lifting the components of the plant by lifting means, characterized in that the installation base is in the form of a power cage with a through channel, Assembling a part of the installation including the power cage, the primitive truss and levers, placing it on the transport platform, and resting on the transport platform with the underside of the cage, the transport platform is moved to the place of installation until the base coincides with the nominally required position and temporarily fixed, Trusses and levers connect the power cage to the ground, raise the mounted part of the installation against the transport platform, then remove the transport platform, and lift the load-lifting device of each of the mast modules through a through channel in the base of the installation, the lifting being performed step-by-step in the assembly part of the assembly , At least one of the modules to be lifted is provided with means for locating and fixing functional attachments thereon.
10. The method of claim 9, wherein the support elements are provided in the form of liquid containers on the peripheral supports.
11. The method according to claim 9, characterized in that the support elements are provided on the peripheral supports in the form of containers for a bulk medium.
12. The method according to claim 9, characterized in that the lifting of the installation mounted on the base of the installation relative to the transport platform is performed by means of adjustable supports.
print version
Date of publication 02.04.2007gg




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.