| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2253037
![]()
VETROPNEVOTURBINNAYA INSTALLATION WITH A WIND-MOTOR HAVING A DIFFUSER AND A COMPRESSOR IN THE PNEUMAMS
The name of the inventor: Janson R.A. (RU); Gasilov A.V.
The name of the patent holder: Janson Richard Alexandrovich (RU); Gasilov Alexey Vladimirovich
Address for correspondence: 121309, Moscow, ul. B. Filyovskaya, 17, apt.148, R.A. Jansson
Date of commencement of the patent: 2003.05.29
(EN) The invention relates to wind power and is used in horizontal axial wind installations with a pneumatic method of transferring wind power from a wind turbine to a consumer (electric generator). The technical result is an increase in the efficiency of the pneumatic transmission, an increase in the coefficient of wind energy use, a decrease in the mass of the hollow blade, which is achieved, firstly, by installing a compressor between the inlet to the hollow blades of the windmill and the outlet from the pneumatic highway and, Due to the placement of a wind turbine inside the atmospheric diffuser at the entrance to it. The diffuser has an annular slot for injecting the external wind flow and an end flange. When the wind turbine rotates, the useful power developed by it is expended for pumping air inside the hollow blades and for rotation through the compressor's step-up reducer. The compressor has a device for regulating the air flow through it. As a result of the combined action of the two stages of air compression (hollow blades and compressor), a pressure below the atmospheric pressure is established in the pneumatic highway, which enables the ground-based air turbine to operate due to a pressure drop between atmospheric pressure and pressure in the pneumatic highway. The air turbine drives the electric generator.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of power engineering, namely wind energy installations.
It is known a device (wind turbine-turbine plant) that converts the energy of the air flow into the mechanical power of the electric generator drive by means of a free-running horizontal-axial wind wheel with hollow blades mounted on the mast-pipe, a ground-based air turbine and connecting them by means of a mast-pipe of a pneumatic highway with air pressure below atmospheric pressure [1] is a prototype. The drawbacks of this wind turbine include an increased chord chord size and a lower efficiency of pneumatic transmission, which is about 0.5. The increase in the size of the chord of the blade, especially on its periphery, is due to flow inside the blade with an allowable speed of the required amount of air. An increase in the chord of the blade causes an increase in profile losses, which leads to a decrease in the efficiency of the windmill, and reduces the design value of the aerodynamic coefficient of the lift force of the profile Cy, which leads to an overload of the wind turbine with an increase in wind speed above the design value. The reduced efficiency of pneumatic transmission is largely due to the fact that in the prototype it is impossible to use the kinetic energy of the air jet leaving the blade.
A device is known that converts the energy of the air flow into the mechanical power of the electric generator drive by means of a horizontal-axial wind turbine with a wind turbine having a diffuser ([2], p. 134 et seq.). One of the disadvantages of this wind generator is the location of electromechanical equipment on the tower, above the ground, which complicates installation, maintenance and repair.
The objective of the invention, which is addressed by the following technical solutions, is to increase the efficiency of the horizontal axial wind farm with the pneumatic method of transferring the power of the wind flow to the consumer using a windmill with hollow blades in which the air compression process takes place, the ground air turbine in which the Obtaining useful work in the process of expanding in it atmospheric air, and connecting pneumatic paths, the air pressure in which is less than atmospheric.
The technical result is an increase in the efficiency of pneumatic transmission, an increase in the coefficient of use of wind energy, a decrease in the mass of the hollow blade.
The solution of the set task on achievement of the declared technical result is carried out in the following ways:
1). In the pneumatic transmission scheme of the prototype [1], a second compression stage of the air is added in the form of a compressor, for example, an axial or centrifugal (with a regulating device of the air flow going through it) located in the pneumatic highway, directly in the gondola, at the entrance to the hollow blades of the wind wheel, and mechanically bound With a wind wheel by means of a speed-increasing reducer. Unlike the prototype, a two-stage air compression scheme makes it possible to increase the discharge behind an air turbine, i. E. The value of the degree of reduction of the total pressure in the air turbine at a constant set value of its power. This makes it possible to substantially (approximately 1.3 ... 1.6 times) reduce the air flow inside the blade, as a result of which the total loss of kinetic energy leaving the air blades decreases, the chord of the blade decreases, its mass decreases, profile losses decrease and in As a result, both the efficiency of the wind turbine and the efficiency of the pneumatic transmission increase, despite the need for additional power costs to overcome the mechanical losses in the reducer and the compression process in the compressor. In addition, with a small absolute value of the reduction in the total pressure in the air turbine (in the prototype of the order of 1.05 ... 1.08), its increase raises the efficiency of the air turbine. At the same time, a decrease in the chord of the blade leads to an increase in the coefficient of lift Cy and allows to reduce the overload of the wind turbine when the wind speed is increased above the calculated speed.
2). An atmospheric diffuser is added to the prototype wind turbine layout [1]. Just as in the case of the analogue [2], the installation behind the diffuser's windmill makes it possible to reduce the static pressure behind the windmill, increase the air flow through it and the power extracted from the air flow. An increase in the feed speed ahead of the wind turbine makes it possible to increase the circumferential velocity at the periphery of the blade while maintaining the optimum value of the high-speed coefficient. In contrast to the analogue in question [2] with a wind turbine having continuous blades, this leads to the achievement of a new technical result, namely, to an increase in the degree of pressure increase in the process of compressing air inside the channel of the hollow blade, i.e. To an increase in the degree of pressure reduction in the air turbine and ultimately to the same positive result as in the previous paragraph 1).
The installation of a diffuser in a wind turbine with hollow blades, in contrast to an analogue [2], having a wind turbine with continuous blades, leads to the achievement of a new technical result, namely, it improves the energy indices of the process of increasing the static pressure in the diffuser by using the kinetic energy of the air jets emerging From hollow blades. Forming inside the diffuser near its inner walls a helicoidal vortex sheet, air jets act as vortex generators, turbulizing the flow at the entrance to the diffuser, which, as is known, increases its efficiency at large angles of wall opening.
The figure shows a schematic structural diagram of a wind turbine-turbine plant with a windmill having a diffuser and a compressor in a pneumatic highway.
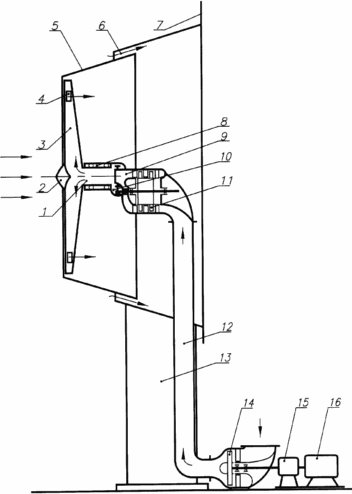 |
The wind turbine-turbine plant consists of the following main units: a wind turbine 2, a compressor 11 located inside the diffuser 5 between the entrance to the hollow blades 3 of the windmill and the outlet 9 of the air motor 12 with an air flow control device, an atmospheric diffuser 5, an air line 12 connecting the hollow blades of the wind wheel and an air turbine 14, a terrestrial air turbine 14 generating a useful power of an electric generator 16. The wind turbine 2 has a hollow rotor 1 and hollow blades 3, in the peripheral part of which there are air outlet holes 4. The rotor 1 rotates in the bearing supports 8 and is mechanically connected by means of a step-up reducer 10 to the compressor 11. The hollow blades 3 through the hollow rotor 1 and the branch pipe 9 are connected aerodynamically with the flow-through part of the compressor 11, which in turn is aerodynamically connected via a pneumatic duct 12 to the air Ground turbine 14. The turbine 14 is mechanically, possibly via a reducer 15, connected to an electric generator 16. The wind turbine-turbine plant works as follows. With the help of a rotatable support 13, the wind turbine is oriented to the direction of the wind. The wind turbine winds the wind turbine 2, as a result of which the useful power developed on the rotor 1 is expended for pumping air inside the hollow blades 3 and for rotation through the reduction gear 10 of the compressor 11 from which the compressed air through the pipe 9 is guided into the inside of the hollow rotor 1 and further to the hollow blades 3. As a result of the combined operation of the two air compression stages (hollow blades 3 and compressor 11), pressure in the airway 12 is set lower than atmospheric pressure, which makes it possible for the ground air turbine 14 to operate by using a pressure drop between atmospheric pressure and pressure in the pneumatic 12. An air turbine 14 rotates the electric generator 16. To increase the efficiency of the compression process, an annular slot 6 is provided in the diffuser 5 for blowing through the walls of the diffuser 5 of the outer wind flow and an end flange 7 to increase the discharge behind the diffuser 5. The regulation of the air flow through the compressor 11 (for example, Rotary blades) is an additional way to regulate the windmill. |
The possibility of carrying out the invention is confirmed by using, as a prototype and analog, devices that were previously manufactured and successfully operated. According to the patent [1] (prototype) in 1953, the English company Enfild Cables Ltd produced a wind turbine with pneumatic transmission, which has an electric generator with a power of 100 kW [3]. According to the scheme of the wind turbine with a diffuser (analog) in 1996 in New Zealand was installed and put into operation wind turbine Vortec-7 with an electric generator with a power of 1000 kW [4].
INFORMATION SOURCES
1. German patent number 900079, cl. F 03 D 11/02.
2. "Wind power". Ed. D. de Renzo: Translated from English. Ed. Ya.I. Shefter. - Moscow: Energoatomizdat, 1982. - 272 p.
3. Wind-Generated Electricity. Prototype 100-kW Plant "Engineering". V.180, No. 4652, 1955, (March 25, 1955). - P.371-374.
4. Vruce Cole. New turbine could be offered low cost wind power. "Modem Rotor Systems". August 1977. - P.27-30.
CLAIM
A wind turbine-turbine plant with a wind turbine having a diffuser and a compressor in a pneumatic main, comprising a wind wheel with hollow blades, an atmospheric diffuser, an air turbine located on the ground and generating useful power, and a pneumatic highway connecting the hollow blades of the wind wheel and the air turbine, Gondola, a compressor is installed between the entrance to the hollow blades of the windmill and the outlet from the pneumatic highway, with a control device of the air flow going through it and driven by the wind wheel through the step-up reducer.
print version
Date of publication 05.04.2007gg




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.