| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2118701
![]()
WIND POWER PLANT (OPTIONS)
The name of the inventor: Ognev Vladimir Vasilievich; Vasilenko Stanislav Efimovich
The name of the patent holder: Ognev Vladimir Vasilyevich; Vasilenko Stanislav Efimovich
Address for correspondence:
Date of commencement of the patent: 1996.05.29
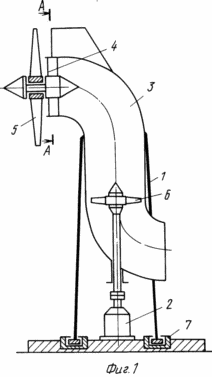
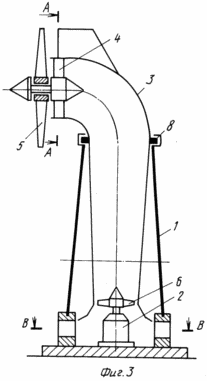
The wind power plant is designed to generate electricity when using wind power. In the cavity of the tower 1 with an outlet in the lower part there is an air duct 3. At its entrance the guide device is fixed 4. On the shaft of the apparatus 4, outside the air duct 3, a wind wheel 5 with a diameter greater than the diameter of the air duct 3 is freely fixed. On the shaft of the generator 2 there is a wind wheel with The possibility of aerodynamic interaction with the wind wheel. 5. Two more variants of wind power plants are described. In the second variant, a wind wheel 5 with a diameter greater than the diameter of the air duct 3 is freely mounted on the shaft of the apparatus 4. Outside the inlet cavity on the other side of the air duct 3, a fan wind wheel 10 is mounted, and a second guiding device 11 is fastened to it. On one shaft with a free wind wheel 5, a driving wind wheel 12 is installed. By installing several wind turbines with the possibility of their aerodynamic interaction, the specific energy of the flow increases and the efficiency of the installation is increased.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of wind power, namely to power plants.
Wind power plants are known (see, for example, RF patent No. 2018028, class F 03 D 1/00, USSR autos Nos. 1682621, 1560781, 1471709, 1242636, class F 03 D 1/00, patent Germany No. 2932293, class F 03 D 1/02) containing a tower (mast), one or more self-aligning windscreens, a generator mounted directly on the wind wheel on one axis with it and transmitting the connection using a generator installed at the base of the tower.
The disadvantage of the examined wind turbines is a relatively low efficiency.
A wind power plant is known (see German patent No. 3604448, class F 03 D 1/02 - prototype), containing a supporting tower (tower) installed on the base, an air duct whose upper and lower extremities are bent in opposite directions in a horizontal Direction; Installed in the middle part of the duct cavity on the generator shaft of the turbine, including one or more windscreens and guiding devices. The generator is installed inside the base.
The disadvantage of the considered wind power plant is also a relatively low efficiency due to large energy losses at the inlet and outlet of the air duct and, correspondingly, a small differential pressure, and in connection with significant dynamic loads on the generator.
The task of the proposed technical solutions is to increase the efficiency of the wind power plant by increasing the specific energy of the flow and significantly reducing the dynamic loads on the generator.
Variant 1. The stated task is achieved by the fact that in a wind power plant containing a hollow tower with an outlet in the lower part and a generator mounted on the base of an air duct, two wind turbines located in the cavity of the tower, one of which is mounted on the generator shaft with the possibility Aerodynamic interaction with another wind wheel, guiding device, another wind wheel is proposed to perform a diameter larger than the diameter of the air duct and to be installed freely, outside of it, on the shaft of the guide device fixed at the inlet of the duct.
Variant 2. The stated task is achieved by the fact that in a wind power plant containing a hollow tower with an outlet in the lower part and a generator mounted on the base of an air duct, three wind turbines located in the cavity of the tower, one of which is mounted on the generator shaft and The duct is designed to be T-shaped, while at one end of its upper part, on the outside on the axis fixed in the support, to install a driving wind wheel whose diameter is greater than the diameter of the duct, at the other end of the upper part of the duct, in its cavity, at The same axis to fix the guiding device and the fan wind wheel with the possibility of its aerodynamic interaction with the wind wheel installed on the generator shaft.
Variant 3. The stated task is achieved by the fact that in a wind power plant containing a hollow tower with an outlet in the lower part and a generator mounted on the base of an air duct, three turbines located in the cavity of the tower, one of which is mounted on the generator shaft With the possibility of aerodynamic interaction with other wind turbines and two guiding devices, it is proposed to make the air duct T-shaped, with the upper part of it being equipped with an additional internal duct of conical shape and with one end fixed together with the first guide on one inlet. On the axis of the first guide, outside, freely, with a diameter larger than the diameter of the duct, install a second wind wheel. On one axis with the second guiding device, fixed in the cavity of the other end of the additional internal duct, freely, inside the cavity from the side of the other inlet of the duct, install the third wind wheel.
In addition, in the wind turbine a hollow tower can be installed on the base movably, and the duct can be fixed in the cavity of the tower (option 1) or installed in it with the ability to rotate (in any version), wind turbines can be equipped with an additional curved outlet duct, , For example, with respect to the surface of the cavity of the tower and duct.
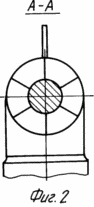
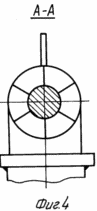
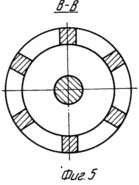
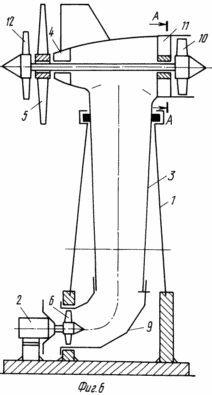
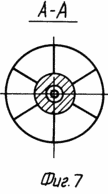
In Fig. 1 and 3 are a general view of the wind turbine (option 1); In Fig. 2 is a cross-sectional view taken along line AA of FIG. 1; In Fig. 4 is a cross-sectional view taken along line AA of FIG. 3; In Fig. 5 is a section of BB in FIG. 3; In Fig. 6 - general view of the wind turbine (option 2); In Fig. 7 is a sectional view of AA in FIG. 6; In Fig. 8 shows a variant of the arrangement of the free and driven wind turbines of the wind turbine in Fig. 6; In Fig. 9 - general view of the wind turbine (option 3).
The wind turbine (option 1, Figures 1 to 5) contains a hollow tower 1 with an outlet at the bottom and a generator 2 mounted on the base. An air duct 2 is located in the cavity of the tower 1. A guide apparatus 4 (section of Figures 2, 4) is fixed at its entrance. On the shaft of the apparatus 4, outside the air duct 3, a wind wheel 5 with a diameter greater than the diameter of the air duct 3 is freely fixed. On the shaft of the generator 2, a wind wheel 6 is mounted with the possibility of aerodynamic interaction with the wind wheel 5. The following design differences in this embodiment may be provided. The hollow tower 1 can be mounted movably in the supports 7 on the base, the air duct 3 can be installed in the cavities of the tower 1 rotatably in the supports 8. The hollow tower 1 can have one outlet or several ones formed along its perimeter. Wind wheel 6 can be placed directly in the outlet of duct 3 (Figure 3) or inside duct 3 at the end of its rectilinear part (Figure 1).
The wind power plant (option 2, Figures 6-7) contains a hollow tower 1 with an outlet at the bottom and a generator 2 mounted on the base. The air duct 3 is T-shaped, the lower part is located in the cavity of the tower 1 and is rotatably mounted. On one side of the upper part of the duct 3 is fixed the support 4. On its axis outside, a second wind-wheel 5 with a diameter greater than the diameter of the upper part of the air duct 3 is freely fixed. On the shaft of the generator 2, the first wind wheel 6 is mounted.
The wind turbine is provided with an additional curved outlet duct 9, which is arranged concentrically, for example, with respect to the surface of the cavity of the tower 1 and the duct 3. The exit of the hollow tower 1 can be made as a single hole or several perimeters (see Figure 5). On the axis of the support 4 and the wind wheel 5 in the entrance cavity of the other side of the upper part of the air duct 3, a fan wind wheel 10 is mounted, and a second guiding device 11 (section of Figure 7) is fixed in front of it. A driving wind wheel 12 (see Figures 6, 7) is mounted on the same axis with a free wind wheel 5 (either before or after it).
The wind power plant (option 3, figure 9) comprises a hollow tower 1 with outlet holes at the bottom and a generator 2 installed on the base. The air duct 3 is T-shaped and the lower part is arranged in the cavity of the tower 1 to rotate. In the cavity of one end of the upper part of the duct 3, the first guide device 4 is fixed. On the axis of the guide apparatus 4, a free wind wheel 5 is installed externally with a diameter larger than the diameter of the upper part of the duct 3. A wind wheel 6 is mounted on the shaft of the generator 2. Inside the cavity of the other inlet of the upper part The air duct 3 is provided with a fan wheel 10 and a second guide apparatus 11 fixed in an additional duct 13 located in the upper part of the duct 3 and having a conical shape. Moreover, with a larger diameter, the additional air duct 13 is fixed together with the first guide device 4 at the inlet to the air duct 3.
The wind power plant (option 1, Figures 1-5) operates as follows.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Under wind pressure, for example, using the aerodynamic plane, the air duct 3 is deployed parallel to the flow if it is rotatably mounted in the tower 1 (Figure 3) or it is deployed together with the tower 1 (Figure 1) if it is rotatably mounted. The wind winds up the wind wheel 5, which, for example, ventilates (sucks) the air flow through the guiding device 4, for example. The forced ventilation creates a superior pressure drop in comparison with the dynamic wind pressure on the wind wheel 6, to which the air stream entering The lower extremity of the duct directly or through the openings in the tower 1 (Figure 5), communicating its cavity and the extremity of the duct 3 with the external environment. Wind-wheel 6 twists the drive shaft of generator 2, converting the rotation into electricity for the consumer.
Wind power plant (option 2, Figures 6 - 8) works as follows.
 |
 |
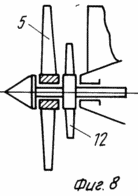 |
The wind flow unfolds the air duct 3, which is rotatably mounted in the tower 1, parallel to the wind flow. Reversal can occur both by means of an aerodynamic plane, and due to asymmetry of performance of the top part of the T-shaped air line 3. The air stream untwists a wind-wheel 5 of free rotation which in its pritulochnyj part creates a pressure support in front of a driving windwheel 12, untwisting it. Wind wheel 12 rotates the fan wheel 10 mounted on the same axis with it, on which, and on the other hand, an incident airflow acts which, through the guide apparatus 11, acts on the wind wheel 6. Thus, a stream having a high pressure enters the lower part of the duct. The resulting air stream rotates the wind wheel 6 with increased frequency and power (with relatively small dimensions) and drives the generator 2. The rotation of the windscreens 5 and 12 (Figure 8) creates an excessive negative pressure, which leads to improved aerodynamic interaction with the other wind turbines of the plant .
The wind power plant (option 3, figure 9) works as follows.
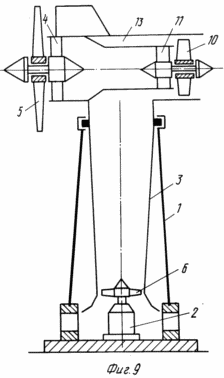 |
The wind flow unfolds the air duct 3, which is rotatably mounted in the tower 1, parallel to the wind flow. The wind stream untwists the freely installed windwheels 5 and 10. The wind wheel 5 with its breech piece (for example) ventilates (sucks) the air flow from the cavity of the additional air duct 13. Forced ventilation with the wind wheel 5 creates a vacuum behind the bushing part 10. Due to this vacuum and the dynamic head of the wind, the wind wheel 10 Unwinds. At the same time, its peripheral part ventilates the air flow with excess pressure into the structurally formed diametral gap (between the surface of the upper part of the duct 3 and the surface of the additional duct 13) forming a unitary part with the duct 3. The thus generated high energy flux in the air duct 3 of tower 1 untwists the wind wheel 6 on the drive shaft of the generator 2, and then exits outward from the lower extremity of the duct and the openings in the tower 1. Wind power plants of the proposed design can be represented by a series of capacities and sizes depending on the energy demand and climatic conditions of operation, i.e. Do not undergo icing and work even from weak winds, thanks to the design of the installation as a whole and the closure of the windscreens in the air inlet, in particular. |
CLAIM
1. A wind power plant comprising a hollow tower with an outlet at the bottom and a generator mounted on the base, an air duct disposed in the cavity of the tower, two wind wheels, one of which is mounted on the generator shaft with the possibility of aerodynamic interaction with another wind wheel; In that another wind wheel with a diameter larger than the diameter of the air duct is mounted freely outside it, on the shaft of the guide apparatus fixed to the inlet of the duct.
2. A wind power plant comprising a hollow tower with an outlet opening at the bottom and a generator mounted on the base, an air duct, three bottom wheels located in the cavity of the tower, three wind wheels, one of which is mounted on the generator shaft, and a guide apparatus, characterized in that the air duct T-shaped, while at one end of its upper part, outside the axis fixed in the support, a driving wind wheel and a free wind wheel with a diameter larger than the diameter of the duct are installed on the other end of the upper part of the duct, in its cavity, on the same Axis fixed guiding apparatus and fan wind wheel with the possibility of its aerodynamic interaction with the wind wheel installed on the generator shaft.
3. A wind power plant comprising a hollow tower with an outlet in the lower part and a generator mounted on the base, an air duct, three bottom wheels located in the cavity of the tower, three wind wheels, one of which is mounted on the generator shaft, and two guiding apparatuses, characterized in that The air duct is T-shaped, the upper part of which is provided with an additional internal conical air duct, one end fixed together with the first guiding apparatus at one of its inputs, on the axis of the first guide apparatus, a second wind wheel is mounted outside, freely, with a diameter larger than the diameter of the duct, On one axis with a second guide device fixed in the cavity of the other end of the additional internal air duct, a third wind wheel with the possibility of aerodynamic interaction with the wind wheel mounted on the generator shaft is installed inside the cavity from the other inlet of the duct.
4. Installation according to claim 1, characterized in that the hollow tower is mounted on the base movably, and the air duct is fixed in the cavity of the tower.
5. Installation according to claims 1 to 3, characterized in that the air duct is rotatably mounted in the turret cavity.
6. An installation according to claims 2 to 3, characterized in that it is provided with an additional curved outlet duct, which is arranged concentrically, for example, with respect to the surface of the cavity of the tower and the air duct.
print version
Date of publication 10.04.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.