| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2269674
![]()
Windmill
The name of the inventor: Atamanenko Michael Eduardovich (RU); Tischenko Oleg Nikolaevich (RU); Svetlakov Sergey Sergeevich (RU)
The name of the patent holder: Atamanenko Michael Eduardovich (RU); Tischenko Oleg Nikolaevich (RU); Svetlakov Sergey Sergeevich (RU)
Address for correspondence: 121351, Moscow, ul. Polotsk, 8, kv.30, ME Atamanenko
Date of commencement of the patent: 2004.02.19
The invention relates to the field of wind energy. The technical result consists in the creation of a compact, full-turn around the vertical axis of the structure, increasing the efficiency of the wind turbine, providing modularity and the ability to operate over a wide range of speeds of the incoming wind. The windmill includes a two-link coaxial vertical shaft connected to a generator located on the ground, a confuser with a weather vane and a device regulating air flow through it, a rotor with two tiers of blades separated by a horizontal plane, according to the invention, and is an energy module including a horizontal wind wheel , Rigidly connected with the vertical shaft and representing a flat circle, along the edge of which, on its two sides, the blades are attached in two tiers to which they adjoin, covering all or part of its area, covered with casing, confusors, mounted on the shaft and able to rotate freely Around it, and equipped with ribs and planes of rigidity, simultaneously forming a high-speed flow inside the confusors, in addition, there are rollers fixing the wind wheel between the confusers, an apron that holds the confusors together and protects both tiers of the blades from the external wind. After passing the exit channels of the confusers, Comes into contact with the blades of both tiers at the optimum angle to the vector of their circumferential speed, rotating the shaft and the electric generator connected to them.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of wind power and can be used for power supply to various consumers.
Analogs of the claimed invention are the following:
1. Wind turbine (RF patch No. 1783144, F 03 D 3/04), located in the surface plane and containing a number of air ducts with full-swing intake devices converging into one confuser and further into the working channel in which an air turbine is located, Its minimum diameter. The exhaust air is discharged through full-turn devices. The positive qualities of the windmill are:
- Using a confuser to produce high-speed airflow.
- Presence of several intake devices working on one turbine.
- Ability to work in a wide range of wind speeds, and any of its directions. Disadvantages of a wind turbine.
- Use only ground, usually weakened air flow.
- Large aerodynamic drag and dynamic dynamic head, high operating costs of auxiliary devices.
2. Wind turbine (RF pat. No. 2156885, F 03 D 3/04), containing successively located in the direction of the wind: an air intake device with a divider, twisting air flow, a confuser with a working channel, a wind turbine, a regulator of its rotation, equipped with gears, a diffuser , A weather vane. All this is placed on a turntable, which can freely rotate around a vertical shaft placed inside a stationary tower. In addition, the two gear rotary assemblies sequentially change the direction of the axis of rotation of the turbine for its connection to the generator.
Positive qualities of the windmill.
- Creation of an accelerated and swirling air flow, having a reduced frontal dynamic head.
- Automatic windmill orientation in the wind.
- Placement of an electric generator on the ground.
- Presence of devices that regulate air flow. Disadvantages of the wind turbine:
- The impossibility of increasing the power due to the operation of several motors per shaft.
- Large linear dimensions and the presence of gears, complicating the solution of issues of economy and reliability.
As a prototype, the applicant selected a wind turbine (RF patent No. 2028504, 6 F 03 D 3/02), which is the closest to him in terms of the aggregate of essential characteristics.
The windmill contains a two-link, coaxial vertical shaft, which, together with an electric generator located on the ground, is located inside the tower as a tower. In the upper part of the inner link of the shaft there is a chamber divided in half by a horizontal partition. In each half there is a rotor, around which there are guide blades. Rotors independently rotate the connected links of the shaft in opposite directions. The chamber, together with its confuser and weather vane, rotates freely around the vertical axis. Air flow, passing the confuser and the blade-guide, falls on the rotor blades. With strong gusts of wind, excess air is discharged through the side openings on the confuser.
The positive qualities of the prototype.
- Use of a concentrator-accelerator of air flow.
- Presence of a two-link shaft.
- The location of the generator on the ground.
- The presence of devices that cut off excess air in the presence of strong gusts of wind.
Disadvantages of the prototype.
- There is no reserve for increasing the capacity of the installation due to the increase in the number of rotors on one shaft along the vertical.
- Large aerodynamic resistance due to the presence of guiding blades and a complicated route of air flow inside the chamber.
- Low coefficient of acceleration of the air environment due to the arrangement of the overall windscreen in the exit channel of the confuser.
- High capital costs for construction.
The object of the present invention is:
- Effective use of energy of low-speed, diffused wind flow.
- Ability to work in a wide range of speeds of incoming wind and power generation capacity.
- Low capital and operating costs.
- High reliability and environmental safety.
The technical result of the developed invention can be considered as follows:
- Compact, full-turn around the vertical axis design, automatically catching, concentrating and accelerating the wind from either side.
Appendix No. 2 to the decision to grant a patent for an invention under application No. 2004104736/06
- High efficiency of wind energy use due to optimal conditions of interaction between wind wheel blades and wind environment, high speed of concentrated airflow, low aerodynamic resistance.
- Modular design and the ability to create individual engines with a power (1-5) kW, with winds from 5 m / s and up to tens of thousands of kW, when several vertical motors are located on one vertical shaft.
- Ability to work in a wide range of incident wind speeds, provided by the regulation of airflow through the installation; A durable, streamlined and compact form of the power module, which makes it possible to use a cable fastening system.
- Construction of large factory readiness.
- Wind turbine does not create electrical interference, it is environmentally safe. The solution of the problem indicated above is achieved by the fact that the windmill contains a two-link coaxial vertical shaft connected to a generator located on the ground, a confuser equipped with a weather vane and a device regulating air flow through it, a rotor with two tiers of blades separated by a horizontal plane. In this case, the windmill is an energy module including a horizontal wind wheel rigidly connected to a vertical shaft and constituting a flat circle at the edge of which, on its two sides, are attached blades forming two tiers adjoining, covering all or part of it Its areas covered with a casing are the two main elements of the construction - confusers, mounted on the shaft and able to freely rotate around it and equipped with ribs and planes of rigidity, simultaneously forming a high-speed flow inside the confusors, besides, rollers fixing the wind wheel between the confusers, an apron firmly fastening Confusers along the contour of the power module into one unit, protecting both tiers of the blades from the external wind, which, after passing the exit channels of the confusers, comes into contact with the blades of both tiers at the optimum angle to the vector of their circumferential speed, rotating the shaft and the generator connected to them.
Inside the crown of the blades of each tier of the main wind wheel rotating the shaft, an additional wind-wheel with its own tier of blades is placed, coaxial with it, which can freely rotate around the common vertical shaft, but in the other direction, using an accelerated air flow from the chamber of the existing confuser divided by a solid wall into two compartments , And the other part of the flow, having the opposite direction, acts as before, and on the main wind wheel, while the emerging reactive forces on the confuser from the flows from different compartments quench each other, which facilitates the orientation of the energy module relative to the external wind, and placed in Gap between the wind wheels the reversing device allows to fill the generated power loss on the main wind wheel, which has arisen due to the separation of the flows.
 |
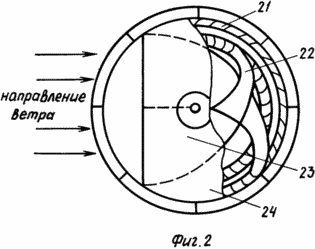 |
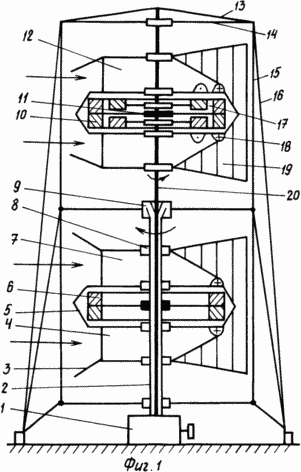
Fig. 1 shows a two-link shaft with two power modules, one of which (the upper one) is equipped with additional wind pulleys.
- Shaded nodes of rotation - rigid connection.
- Signs (+) and (-) - directions of the accelerated flow from the confuser's chambers relative to the observer.
FIG. 2 shows the arrangement of the mutual arrangement in the power module of the main and additional windscreens and a two-chamber confuser.
The figures contain:
1. Electric generator.
2. The lower link of a two-link vertical shaft.
3. The regulator of the expense of air.
4. Lower confuser of the lower energy module.
5. Apron.
6. Two tiers of main rotor blades.
7. Upper confuser of the lower energy module.
8. Node of free rotation.
9. The assembly releasably connecting shaft units.
10. Scoops auxiliary windscreens.
11. Rigid fastening of the main wind wheel to the shaft.
12. Power module with additional wind turbines and two-chamber confusers.
13. - 16. The variant of fastening a two-link shaft.
17. Reversing device.
18. Cross-sections of working channels from a two-chamber confuser.
19. Weathercock.
20. The upper link of the two-link shaft.
21. Main and auxiliary wind wheels.
22. Working channels.
23. Confuser chambers.
24. Casing.
Wind turbine works as follows.
Thanks to the weather vanes 19, the confusers 7 and 4 of the lower power module, which is movably connected to the lower link of the shaft 2, and the same confusers of the upper energy module, and movably connected to the upper link of the shaft 20, are oriented by their input sections towards the wind using the free rotation nodes 8. Depending on The capacity of the external flow device 3 (for example, the damper) is programmed to occupy a certain position, setting the air flow through the confuser from zero to the optimum. In this case, the influence of the external environment on the wind wheel 21 is eliminated by the presence of an apron 5. Passing both the confuser of the power module, air in the form of two narrow high-speed flows falls on the two-tier blades 6 rotating the wind wheel, rigidly connected to the lower link of the shaft 2. Similarly, in the upper energy module 12 the main The wind wheel, rigidly connected to the upper link of the shaft 20, rotates it, but in the opposite direction, with respect to the link 2. At the same time, the air flow leaving the confusers will deflect the power module from its optimum position relative to the direction of the wind due to the emerging reactive force. To smooth out this effect, you can arrange the weather vane 19 at some angle to the external wind speed vector. And in order to minimize the disorientation of the module relative to the direction of the wind, it is proposed to make the confuser two-chamber 23, the outputs of which 18, 22 are directed in opposite directions, thus ensuring the rotation of the main windwheel 6 and auxiliary 10. This, on the one hand, will lead to mutual compensation Reactive forces on confusers, and on the other hand, using the rotation of auxiliary wheels and reversing devices, will make up for the loss of power on the main wind wheel resulting from the separation of the flow.
CLAIM
1. A wind turbine comprising a two-link coaxial vertical shaft connected to a generator located on the ground, a confuser equipped with a weather vane and a device controlling the airflow through it, a rotor with two tiers of blades separated by a horizontal plane, characterized in that the windmill is an energy module, Including a horizontal wind wheel, rigidly connected to a vertical shaft and constituting a flat circle, at the edge of which two blades are attached on its two sides, forming two tiers to which they adjoin, covering all or part of its area, Confusors planted on the shaft and able to freely rotate around it, equipped with ribs and planes of rigidity, simultaneously forming a high-speed flow inside the confusors, in addition, rollers fixing the wind wheel between the confusers are provided, an apron firmly fixing the confusors along the contour of the power module into one and protecting both The tier of the blades from the external wind, which, after passing the exit channels of confusers, comes into contact with the blades of both tiers at the optimum angle to the vector of their circumferential speed, rotating the shaft, and the electric generator connected to them.
2. Wind turbine according to claim 1, characterized in that within each tier blade crown main propeller, the rotating shaft, and further placed coaxially with its tier wind wheel blades, which is able to rotate freely around a common vertical shaft, but in the other direction, using the accelerated air flow from the chamber existing confuser divided solid wall into two compartments and the other portion of the flow having an opposite direction is supplied, as before, to the main wind wheel, with the resulting reactive force on the confusor of flows from different compartments cancel each other, power module facilitates orientation with respect to the external wind, and placed in the gap between the propeller thrust reverser lets you fill the resulting power loss in the main propeller, which arose due to flow separation.
print version
Date of publication 11.01.2007gg




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.