| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2170366
![]()
Wind turbine
Name of the inventor: Zeldin Julius Rafailovich; Eugene Savinov Rafailovich
The name of the patentee: Zeldin Julius Rafailovich; Eugene Savinov Rafailovich
Address for correspondence: 153012, Ivanovo, st. Bubnov, 72, kv.96, Yu.R.Zeldinu
Starting date of the patent: 1998.04.06
The invention relates to devices for the wind energy by converting it to other forms of energy. The technical result consists in simplifying the construction of a wind turbine, increasing the reliability of its operation and increasing the degree of wind energy is achieved due to the fact that the wind turbine comprising at least two blades in a rotor Savonius, each consisting of two half-cylinders mounted on shafts with the possibility of their turn, the engine further comprises a frame, Savonius rotor mounted on a turntable with a vertical shaft, and their axis kinematically connected to the core turbine. Wherein the axis of each of the semi-cylinders arranged in the center of gravity and each of the half-cylinders fitted with a load, fixed to its surface.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to devices for the wind energy by converting it to other forms of energy.
Known wind turbines carousel containing vertical rotary blades with the mechanism of their rotation (AS USSR N 1486623, MKI F 03 D 3/06; N 1483081, MKI F 03 D 3/02; MKI F 03 D 7/06, 3 / 02, and others.). These constructs contained according to the descriptions of many open kinematic transmission, fine details and mechanism of the orientation of the blades relative to the wind direction, which can not guarantee a reliable and long-lasting their work, especially during the rains and snowfall.
Known wind turbine carousel containing several (at least two) Savonius rotor, each consisting of two half-cylinders mounted on axles rotatably (Pat. SU 19164 A, cl. F 03 D 7/06, 1931 YG).
By the principle of action of this wind turbine is close to the proposed and accepted as a prototype. To operate the prototype device should have its optimum orientation with respect to the wind direction.
The disadvantage of the prototype is the presence of the device and the need to orient the blades relative to the wind. This complicates the design of the wind turbine and reduces reliability.
It is known that such a wind turbine starts operating at a wind speed of three meters per second, which prevents its use in areas with a predominance of low wind.
The purpose of the invention is to simplify the turbine design and reliability of its operation. Another object is to increase the degree of wind energy.
These and other objects are achieved in that the wind turbine comprising at least two blades in a rotor Savonius, each consisting of two half-cylinders mounted on axles rotatably, the inventive engine comprises a frame, Savonius rotor mounted vertically on a turntable shaft and its axis kinematically connected to the backbone of the wind turbine, the axis of each of the semi-cylinders arranged in the center of gravity and each provided with a load semicylinders fixed to its surface.
 |
 |
 | |
 |
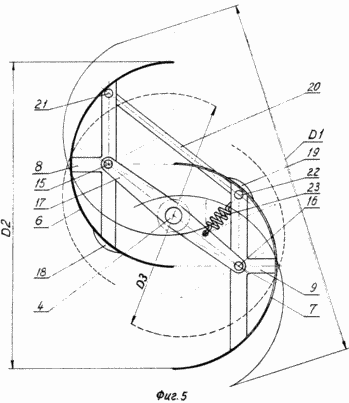 |
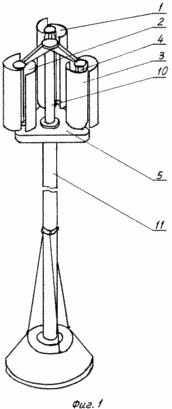
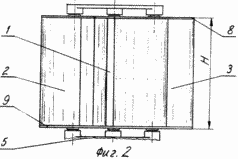
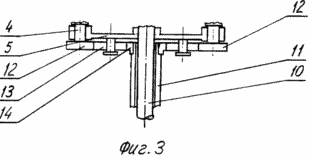
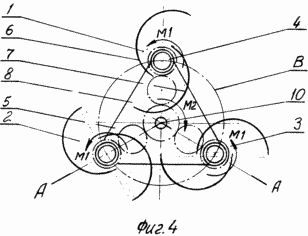
A possible embodiment of a wind turbine is illustrated by drawings, which show in Fig. 1 - a view of the wind turbine in perspective; FIG. 2 - side view of the rotary blades of a wind turbine; FIG. 3 - section along axis A-A of the platform; FIG. 4 - a top view of a wind turbine; FIG. 5 - cross section of one of the rotors.
Wind turbine (Figs. 1-5) comprises a blade 1, 2 and 3 (the number of blades may be different), mounted on the vertical axis on the platform 4, 5. Each of the blades 1, 2 and 3 is designed as a Savonius rotor, consisting of two half-cylinders 6 and 7, the relative location of which is shown in FIG. 4 and 5. Semicylinders 6 and 7 are equipped for the stiffening crossmembers 9 and 8.
The platform 5 is fixed on a vertical shaft 10 mounted in bearings (not shown) of the core 11. At axles 4 fixed gear 12 which, through satellites 13 kinematically connects all blades with central pinion 14 rigidly fixed on the frame 11.
Semicylinders 6 and 7 (FIG. 5) are mounted on shafts 15 and 16 mounted on brackets 17 and located in the center of gravity of each of the semi-cylinders and are provided with weights 18 and 19 are fixed on the surfaces of semi-cylinders 6 and 7. The brackets 17 are fixed on the axes 4 . Cross members 8 and 9 are connected to each other a connecting rod 20, the distance between the axes 21 and 22 is equal to the distance between the axes 15 and 16 so that the elements 8, 9, 17 and 20 together form a hinged parallelogram. The bracket 17 and the cross member 9 are interconnected by a spring 23.
Wind turbine operates as follows.
Acting on each of the blades 1, 2 and 3, wind, regardless of its direction, the worm Savonius rotors from which these blades, the torque M1. Gears 12, 13 and 14 transmit the time backbone wind turbine 11, because of which on the platform 5 there is a reactive torque M2 rotating shaft 10. Rotation of the shaft 10 may be used to transmit power from any of the potential customers.
Axis 4 of each of the Savonius rotor while rotating platform 5 are moving in a circle B. In this half circle each rotor Savonius moves against the wind, in the other half - in the wind.
It is known that the rotor of the wind power developed by the rotor is proportional to the cube of the velocity Savonius (YI Shefger use of wind energy, - M .: Energoizdat, 1983), i.e.
N = k · (V in +/- V p)3,
where N - power developed by the rotor Savonius;
V in - wind speed;
V p - the speed of the rotor axis 4 Savonius forward (+) or (-) wind;
k - coefficient of proportionality.
It can be shown that the areas of motion axis 4, for which the velocity V in and V p are added, capacity increases to a somewhat higher value than the power reduction in the areas in which these velocities are subtracted, and the gain in developing capacity in comparison with a fixed axis 4 is
N = 3 · k · V in · V p2,
ie installation of axes 4 Savonius rotor on a rotating platform 5 can increase the degree of energy wind turbines wind.
The wind speed is known, a value significantly changing over time. The most favorable to the consumer will have the job of a wind turbine when it is functional in a wide range of wind speed variation (from 1.5 - 2 m / s to 30 - 35 m / s instead of 5 - 25 m / s, as it is now).
This proposed structure is provided as a weak wind, its power is small, the rotor turns are reduced, and the spring 23 by cutting translates semicylinders 6 and 7 from the main operating position shown in FIG. 5 double solid lines to the position shown in the same thin lines.
Semicylinders 6 and 7 the rotor as it rotates, in this case the swept area of the rotor defined by the product of the height H (FIG. 2) to the diameter D1 (FIG. 5). With increasing wind speed of the rotor relative to the axis 10 increases and the centrifugal force increases, developed loads 18 and 19. By overcoming the resistance of the spring 23, this force rotates the half-cylinders 6 and 7, and at the rated wind speed at which the work on the wind turbine is designed translates them in a position determined by the diameter D2.
If too strong a wind speed of rotation of the rotor increases, the centrifugal force of the goods 18 and 19 increases even more, turning half-cylinders 6 and 7 to the position determined by the diameter D3. The wind load on the rotor while significantly decreases as the overall configuration of the rotor approaches the shape of a cylinder.
CLAIM
1. Wind turbine comprising at least two blade Savonius rotor as consisting of two semi-cylinders each mounted on their axes with the possibility of rotation, characterized in that the engine further comprises a frame, Savonius rotor with vertical shaft mounted on a turntable, and their axes kinematically connected to the backbone of the wind turbine.
2. Wind turbine according to claim 1, characterized in that the axis of each of the semi-cylinders arranged in their center of gravity, each equipped with a load of half cylinders, fixed on its surface.
print version
Publication date 30.01.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.