| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2171397
![]()
Windmill
The name of the inventor: Oleynikov Yuri Mikhailovich
The name of the patent holder: Oleynikov Yuri Mikhailovich
Address for correspondence: 357560, Stavropol Territory, Pyatigorsk, pos. Goryachevodsky, st. River, 13, Yu.M. Oleinikov
The effective date of the patent: 1997.02.26
The invention relates to wind power, namely to wind turbines that convert wind energy into electrical energy in areas where winds are often or constantly blowing. The technical result, consisting in simplifying the design, increasing the efficiency and profitability of the wind turbine application, is achieved due to the fact that in the windmill containing the rotor in the form of a straight circular cylinder with a power wheel inside it, the rotor housing is horizontal or vertical, the power wheel is located on bearings And is made in the form of a mill water wheel with power blades, and in the direction of the rotor body there are upper and lower openings-channels, in the slots of which there are movable damper-shutters, overlapping these channels in pairs.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to wind power, namely to wind turbines, which convert wind energy into electrical energy.
A wind turbine is known, comprising a housing with an inlet confuser, a neck, an outlet diffuser, a shaft, a turbine and a rotor blade, guiding blades of a confuser and a second rotor blade (see SU, 1590626 A1, class F 03 D 1/04, 07.09.1990, 2 from.).
The shortcomings of the windmill include low engine efficiency and design complexity.
A vane motor is known comprising a housing and an impeller mounted thereon with radial blades provided with a rotating gap along their input and output edges with rotating rolls connected by a mechanical conical transmission with a fixed axis, radial shafts and blades rotatable by means of a drive relatively Radial axes (see SU, 1539387 A1, cl. F 03 D 7/02, 30/01/1990, figures 1, 3).
The drawbacks of the engine include power regulation on the output shaft of the motor due to the increase in the structural elements (rollers or rollers), and the low reliability of the blade rotation drive relative to the radial axes.
A wind turbine is known, which contains a rotor in the form of a straight circular cylinder with a power wheel inside it, accepted as the closest prototype analogue of the essential features of the invention (see US 3,924,966 A, cl. F 03 D 1/06, 09.12.1975, Figures 1-3, 4 s).
The shortcomings of the windmill include low efficiency from 0.01 to 1-2%, low profitability of application and complexity of the design.
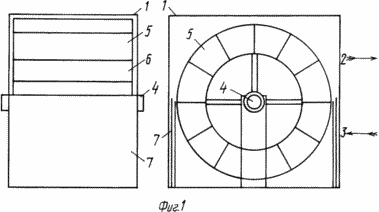 |
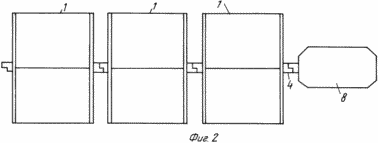
The technical result, consisting in simplifying the design, increasing the efficiency and profitability of the wind turbine application, is achieved due to the fact that in a wind turbine comprising a rotor in the form of a straight circular cylinder with a power wheel inside it, according to the invention, the rotor housing is horizontal or vertical, the power wheel is located On the bearings and is made in the form of a mill water wheel with power blades, and in the direction of their rotor body there are upper and lower openings-channels, in the slots of which there are movable shutters - blinds overlapping these channels, and the ends of the shaft of the power wheel are made in the form Nodes for connection to other shafts. In Fig. 1 shows a wind turbine (general view); In Fig. 2 - wind turbine connected to the generator and power elements. The wind turbine consists of a housing 1 in the form of a straight circular cylinder with through-going upper 2 and lower 3 holes-channels rotating on a shaft 4 with bearings (not shown), a power wheel made in the form of a mill water wheel 5 with power blades 6. In the grooves of the holes 2,3 of the housing 1 there are movable blinds-louver 7, which can overlap these channels in pairs. At the ends of the shaft 4 are the connection nodes (not shown), one of which is connected to the shaft of the generator 8, and the other is used to connect to other power elements. |
 |
WINDROWER WORKS AS FOLLOWING
When assembled, it is fastened to the base of the foundation (not shown) so that the upper 2 and lower 3 holes-channels coincide with the direction of the prevailing wind in the given terrain. Then, when the wind moves, the upper channels 2 are covered by shutters-louvers 7, and the lower channels 3 are open at this time. In this case, the direction of rotation of the blades 6 remains the same and the generator 8 operates in the previous mode, since the braking effect of the wind is eliminated by the fact that one half of the blades 6 of the wheel 5 rotates, creating a torque, while the other half of the blades 6 is closed by the louver 7.
With a different wind direction, the upper channels 2 open, and the lower channels 3 are closed at this time.
To increase the power of the generator 8, several wind turbines of the same type can be installed on the same shaft 4 (with a horizontal arrangement of the housing).
The rotation of the blades 6 of the mill water wheel 5 is transferred to the shaft 4 connected to the generator 8, where the electric energy is generated when the axis of the generator 8 rotates.
CLAIM
1. A wind turbine comprising a rotor in the form of a straight circular cylinder with a power wheel located therein, characterized in that the rotor body is arranged horizontally or vertically, the power wheel is located on the bearings and is made in the form of a millwheel water wheel with power blades, and in the direction thereof in The rotor body has upper and lower openings-channels, in the slots of which there are movable damper-shutters, overlapping these channels in pairs.
2. Wind turbine according to claim 1, characterized in that the ends of the shaft of the power wheel are made in the form of nodes for connection to other shafts.
print version
Date of publication 30.01.2007gg




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.