| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2193687
![]()
Wind turbine
Name of the inventor: Keselo BA .; Bashirov AA .; Voskoboynikov DV
The name of the patentee: Limited Liability Company Scientific and Production Enterprise "Air transport"
Address for correspondence: 420103, Kazan, and / I 155, D.V.Voskoboynikovu
Starting date of the patent: 2001.01.03
The invention relates to wind power engineering and can be used to convert wind energy into other forms of energy. The technical result consists in increasing the lift coefficient and the efficiency and the simplification of the construction is ensured by the fact that the wind wheel turbine is designed as a connected by radial spokes of the rim and the hub on which a freely rotatable round spokes axes and movable along the axis of said spokes Savonius rotor made. Moving rotors along the axes of the spokes is carried out by a two-armed lever, one arm of which is connected via a rocker mechanism with a lower support Savonius rotor and the second, spring-loaded relative to the shaft propeller located load with the possibility of adjusting the centrifugal force, the pair of blades of each rotor tier are displaced relative to adjacent these blades at an angle of 60 o in the spiral direction and separated from adjacent blades separating discs with a diameter greater than the diameter of the cylinder formed by the rotation of the rotor ends paired blades Savonius 5-8%.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to wind power engineering and can be used to convert wind energy into other forms of energy.
Known wind turbine having impeller blades made in a Magnus rotors. Rotors are made in the form of cylinders of different diameters. Magnus rotors are driven by a special motor (see. AS USSR 1402707, MKI F 03 D 1/06, for the 1988 Bull. 22).
The disadvantage of this device is the complicated launch of a wind turbine connected to an electrical load shutdown and the inclusion of compulsory drive rotors Magnus, which reduces the efficiency of wind energy and wind turbines requires a fairly sophisticated management system.
Known wind turbine blade comprising a pen airfoil associated with the wind wheel. Provided Perot cavity, which houses single storey Savonius rotor, wherein the rotor axis is parallel to the axis of the pen (see. AS USSR 1776868, MKI F 03 D 1/06, 1992 for, at Bul. 43).
This design has the following drawbacks:
First, the Savonius rotor is mounted freely in terms of its own direction of rotation, is capable of generating lift due to the Magnus effect, which will reduce the lift of the airfoil wind wheel and brake.
Secondly, when placing the Savonius rotor so that the lift profile vector and the lift vector Magnus same direction, is diverted to the optimum blade angle of attack by the torque relative to the center of pressure profile formed Magnus lift.
This phenomenon reduces the lift coefficient profile strength.
Third, the installation of the electric generator directly into the blades on one shaft with the rotor Savonius significantly worsen the starting properties of the entire propeller, since a significant portion of wind energy will be spent on the joint promotion of the Savonius rotor with the rotor of the generator, and at the same time, require design complexity through the use of special current collectors in electric power transmission from the rotating blade with the generator to the stationary part of the wind turbine.
Fourth, the efficiency of this design due to a turbulent flow profile. A source of said pulsation mode Savonius rotor is mounted in any area of the profile. This phenomenon was confirmed experimentally (see. The works of ASME. Modern Engineering Series A 10, 1989, article Mondi, Frenando "Characteristics of Savonius wind turbine," p. 146, fig. 19), taking place in the rotor profiles wrapping zone Savonius - a central vortex.
Known wind turbine comprising a supporting structure and the turntable device towards the orientation of the wind, the impeller with radial vanes, made in the form of Savonius rotor coupled with the PTO shaft (sm. FR, A1 2566466, cl. F 03 D 1/02 27.12.1985) the essential features adopted as the closest analogue of the invention (prototype).
The disadvantage of this wind turbine is a low efficiency, design complexity, low reliability in the regulation in the event of a significant increase in wind speed (hurricane, storm, etc.).
The technical result consists in increasing the lift coefficient and efficiency but also simplify the structure is ensured by the fact that a wind turbine comprising a supporting structure with a rotary table and the device orientation to the wind direction, the impeller with radial vanes, made in the form of Savonius rotor coupled with the PTO shaft, according to the invention operating the wind wheel, formed as a streamlined hub and coaxial thereto rim interconnected uniformly spaced on radial spokes circumference coaxially to the axes of which are rotatable in the same direction around the axes of the spokes and move along the axes of these spokes in the direction of axis of the hub to the rim and back tier rotors Saviniusa, twin blades tier are installed with angular deflection of 60 o with respect to the pair of blades adjacent tiers in the helical direction, and between the ends of each tier and at the ends of each rotor are perpendicular to the rotor axis of rotation of the separating discs with a diameter greater than the diameter of the cylinder formed by the rotation of the paired ends of the blades, by 5-8%, and neighbors to support a streamlined rotor hub Savonius connected by wings with double-arm lever, bearing hinges which are mounted on a propeller shaft power take-off, and on the free, spring-loaded relative to the PTO shaft ends of double-arm levers are arranged to adjust the amount of centrifugal force loads.
 |
 |
 |
|
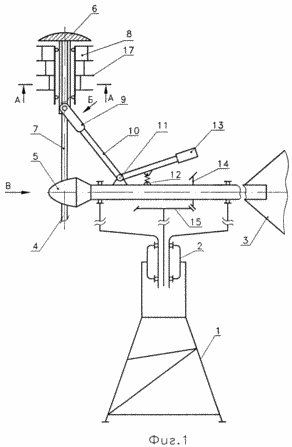
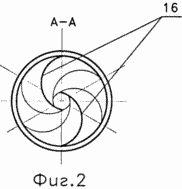
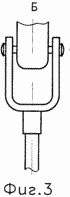
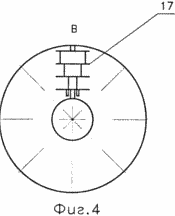
Figure 1 is a schematic view of a wind turbine. Figure 2 - A-A section of a wind turbine 1. Figure 3 - D view of a wind turbine 1. Figure 4 - In view of the wind turbine 1. |
 |
Wind turbine, comprises a support structure - 1 with a rotary table - 2, the orientation of the device in the direction of the wind - 3, impeller - 4 with a streamlined hub - 5, rim - 6, radial spokes - 7 Savonius rotor - 8, the rocker 9, double-arm lever - 10, two-armed support arm - 11, spring - 12, Georgia - 13, for the transmission power take-off of the bevel gears 14 and 15, the blades - 16 Savonius rotor and wheels - 17.
Wind turbine operates as follows:
In the absence of wind flow Savonius rotor - by springs 8 - 12, and the goods - 13, acting via a two-armed lever - and rocker mechanism 10 - 9 are located in a position close to the rim - 6.
When exposed to the wind flow to the impeller - Savonius rotor 4 - 8 come into rotation, while a force caused by the Magnus effect, which gives a unidirectional torque acting on the wheel - 4.
At the same time, being at the upper end of the spokes - 7 Savonius rotors - 8 provide enhanced starting torque, contributing to a rapid propeller being driven away - 4. After dialing the appropriate speed by the centrifugal force loads - 13 moves from its initial position and by means of backstage - 9 and two-armed lever - 11 moved Savonius rotor - 8 spoke - 7 in the direction of the hub - 5 against the spring force - 12. at the same time increase speed propeller - 4.
Thus, the wind turbine allows for a stage start to have a significant starting point, the working stage of significant momentum, without opening and closing the PTO transmission. In turn, offset binary Savonius rotor blades in an amount of 60 o arranged to ensure uniform rotation of the rotor, and the protrusion of the separation discs - 17 outside the cylinder formed by the ends of the paired rotating blades 5-8%, performed in order to maximize the lifting force on blades of the rotor Savonius (see. directory ![]() v.1, ONTI, 1936, p. 462).
v.1, ONTI, 1936, p. 462).
The value of 5-8% is obtained by the authors based on the results of experimental models of blowing wind turbine. These results suggest that increasing the diameter of the separation discs - 17 to 5% in the range up to 8% abrupt increase in observed values of lift. The magnitude of the excess separating disc diameter of more than 8% is impractical due to the conditions of co-location Savonius rotors in the space between the rim - 6 and streamlined hub - 5.
In addition to these advantages allows for wind turbine Magnus effect without auxiliary energy required for forced rotation of the rotors.
CLAIM
Wind turbine comprising a supporting structure with a rotary table and the device orientation of the wind direction, the impeller with radial vanes, made in the form of Savonius rotor coupled with the PTO shaft, characterized in that the impeller is designed as a streamlined hub and coaxial thereto rim interconnected uniformly spaced on radial spokes circumference coaxially to the axes of which are rotatable in the same direction around the axes of the spokes and movable along the axis of said spokes, the direction of the hub axis to the rim and back tier rotors Savonius paired blades tier are installed angularly 60 o offset relative tier adjacent pair of blades in the spiral direction, and between the ends of each tier, and at the ends of each rotor are perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the separating rotor disks with a diameter greater than the diameter of the cylinder formed by the ends of the paired rotating blades, 5-8%, and proximal to the streamlined hub Savonius rotor support wings connected by a double-arm levers, pivot hinges which are mounted on the propeller shaft PTO, and on free, spring-loaded relative to the PTO shaft ends two-armed levers adapted to adjust the magnitude of the centrifugal force loads.
print version
Publication date 30.01.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.