| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2248466
![]()
PLANETARY TYPE WINDROVER (VETRYAK)
The name of the inventor: Gdanskiy N.I. (RU); Maltsevsky S.V. (RU); Solovyov A.M. (RU); Grigoryev R.V.
The name of the patent holder: Moscow State University of Engineering Ecology (MSUEE)
Address for correspondence: 107884, Moscow, ul. Staraya Basmannaya, 21/4, MGUIE, pro-rector for scientific work
The effective date of the patent: 2002.11.05
The invention relates to wind power and is intended primarily for use in areas with low wind speeds. The technical result consists in increasing the reliability of the wind turbine by controlling the law of motion of the blades. A planetary-type windmill includes a rotating rotating frame on the base with movable blades and a rotary shaft, the blades being connected to the rotary shaft by a transmission mechanism with a constant ratio of 1: 2, the rotary shaft being provided with a movably mounted weather vane and connected to it by a control device consisting of a crank-slider Mechanism, connecting rod, control plate and return spring, and as a transmission mechanism, a belt gear is used.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to wind power and is intended primarily for use in areas with low wind speeds.
There is a known wind power plant. The patent of the Russian Federation No. 2070659, class F 03 D 3/02, 7/06, 1994, in which a frame with vertically arranged blades is mounted on the central shaft, which can rotate about their axes and are connected by gears to a pinion gear rigidly connected With a weather vane loaded in the direction of engagement, and the ratio of the gear transmission from the weather vane to the blades is 1: 2 at normal wind speed, in the case of storm wind the transmission opens.
The main disadvantages of the well-known wind power unit are: the use of gears of rather complex construction and the discrete nature of the mechanism's operation, which protects the unit from storm winds. Gears for efficient operation require adjustment of the gearing and constant presence of grease in the contacts, which greatly complicates the design, increases its cost and reduces reliability. And transmission data significantly increase the inertia of the entire structure in the rotational motion, which reduces its efficiency at low wind speeds. The discrete nature of the triggering of the protective mechanism leads to the fact that the stopping of the unit and the orientation of its blades in the wind should be performed when the maximum possible wind speed and, correspondingly, the maximum rotations of the frame with blades are reached. In this case, significant inertial loads will occur in the structure.
The closest to the totality of features is the wind power plant of the planetary type. Patent RF No. 2030777, class F 03 D 3/02, 7/06, 1995, comprising a rotary shaft rotatable on the base with movable blades and a rotary shaft, the blades being connected to the rotary shaft by a transfer mechanism with a constant Ratio of 1: 2. The disadvantage of this design is the use of horizontally located chain drives, which for effective long-term operation require lubrication of friction parts and the presence of guiding devices that ensure the correct chaining of sprockets. And significant shortcomings are: the need for an additional device that provides orientation of the installation to the wind, and the lack of a mechanism to protect it from storm winds.
The aim of the invention is to increase the reliability of the engine by controlling the law of motion of the blades.
This is achieved by the fact that in a wind turbine comprising a rotary shaft rotating on a base with movable blades, a rotary shaft, blades connected to the rotary shaft by a constant ratio of 1: 2 in accordance with the invention, the rotary shaft is provided with a movably mounted weather vane and is connected to it by a control device , Consisting of a crank-slider mechanism, a connecting rod, a control plate and a return spring, and a belt gear is used as the transmission mechanism.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
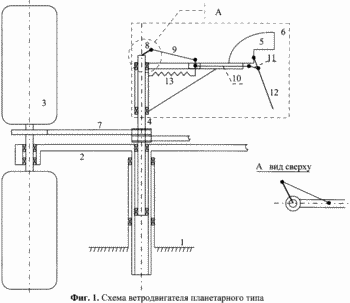
1. FIG. 1 shows a sketch of a wind turbine structure.
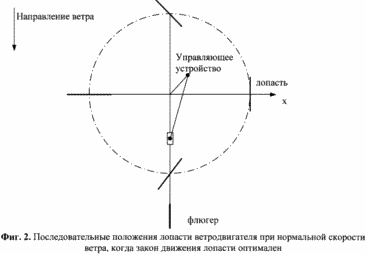
2. FIG. 2 shows the successive positions of the windmill blade at normal wind speed.
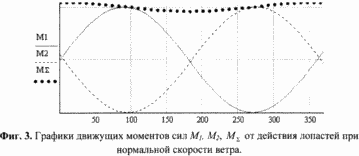
3. FIG. 3 shows the driving moments of the forces M 1 , M 2 from the action of the blades 3 at a normal wind speed.
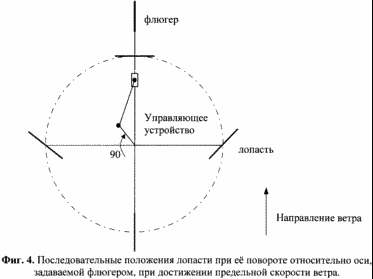
4. Fig. 4 shows the successive positions of the blade when the wind speed limit is reached.
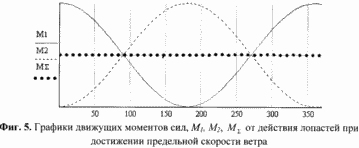
5. FIG. 5 shows the driving moments of the forces M 1 , M 2 from the action of the blades 3 when the limiting wind speed is reached.
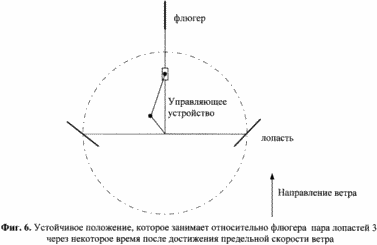
6. FIG. 6 shows the stable position of the blades 3 after reaching the wind speed limit.
The windmill consists of a fixed base 1, a rotary frame 2 mounted on it, blades 3 movably mounted on the frame 2, a rotational shaft 4 and a weather vane 5, rotatably mounted on the pivoting shaft 4 and associated with the control device 6.
Blades 3 are installed in pairs in order to balance the tipping torque of the forces.
The blades are connected to the rotary shaft by a belt gear 7 with a ratio of 1: 2 from the shaft 4 to the blades 3.
The control device 6 consists of a crank-slider mechanism including a lever 8 rigidly connected to the shaft 4, a connecting rod 9, a slider 10, and from the connecting rod 11, the control plate 12 and the return spring 13.
Wind turbine works as follows. When the wind strength is in the optimal speed range [ ![]() Min ,
Min , ![]() Opt ], the adjusting plate 12 under its weight and return spring 13 is in the lower position. In this case, the optimal law of motion of the blades 3 relative to the wind is ensured. 2 shows the successive positions of the blade when it rotates by 0, 90, 180 and 270 degrees relative to the axis defined by the weather vane. FIG. 3 shows the driving moments of the forces M 1 , M 2 generated on the rotary frame by a pair of blades 3 mounted thereon with a shift of 180 degrees, and the total moment of the forces M
Opt ], the adjusting plate 12 under its weight and return spring 13 is in the lower position. In this case, the optimal law of motion of the blades 3 relative to the wind is ensured. 2 shows the successive positions of the blade when it rotates by 0, 90, 180 and 270 degrees relative to the axis defined by the weather vane. FIG. 3 shows the driving moments of the forces M 1 , M 2 generated on the rotary frame by a pair of blades 3 mounted thereon with a shift of 180 degrees, and the total moment of the forces M ![]() From the action of both blades.
From the action of both blades.
When the wind force is increased beyond a certain value ![]() Opt under the action of the wind, the control plate 12 rises and through the control device consisting of the lever 8, the connecting rod 9, the slider 10 and the connecting rod 11, rotates the rotary shaft 4 together with the wind vane 5 together with the small pulleys of the belt gears 7 fixed thereto. In this case, the average values M 1 , M 2 and M
Opt under the action of the wind, the control plate 12 rises and through the control device consisting of the lever 8, the connecting rod 9, the slider 10 and the connecting rod 11, rotates the rotary shaft 4 together with the wind vane 5 together with the small pulleys of the belt gears 7 fixed thereto. In this case, the average values M 1 , M 2 and M ![]() Will gradually decrease in comparison with their optimum values. When the wind speed limit is reached
Will gradually decrease in comparison with their optimum values. When the wind speed limit is reached ![]() Before the adjustment plate 12 occupies the uppermost position by rotating the shaft 4 by 90 degrees with respect to the optimum position. 4 shows the successive positions of the blade when the wind speed limit is reached and rotated by 0, 90, 180 and 270 degrees relative to the axis defined by the weather vane. FIG. 5 shows the driving moments of the forces M 1 , M 2 created on the pivoting frame by a pair of blades 3 mounted thereon with a shift of 180 degrees, and the total moment of the forces M
Before the adjustment plate 12 occupies the uppermost position by rotating the shaft 4 by 90 degrees with respect to the optimum position. 4 shows the successive positions of the blade when the wind speed limit is reached and rotated by 0, 90, 180 and 270 degrees relative to the axis defined by the weather vane. FIG. 5 shows the driving moments of the forces M 1 , M 2 created on the pivoting frame by a pair of blades 3 mounted thereon with a shift of 180 degrees, and the total moment of the forces M ![]() From the action of both blades in this case. As can be seen, the average values of M 1 , M 2 and M
From the action of both blades in this case. As can be seen, the average values of M 1 , M 2 and M ![]() Are equal to zero and the windmill frame after a while stops in a stable position, at which the moments of forces on both blades counterbalance each other (Fig. 6).
Are equal to zero and the windmill frame after a while stops in a stable position, at which the moments of forces on both blades counterbalance each other (Fig. 6).
Belt gears, unlike gear and chain drives, do not require lubrication, are simpler in design and installation, which increases the reliability and durability of the entire structure as a whole. The control device 6 allows smoothly controlling the movement of the frame 2 and blades 3 in such a way that when the wind speed exceeds the threshold value, the windmill starts to decelerate due to a change in the law of motion of the blades relative to the wind flow, and stops at a limiting speed, taking a stable equilibrium state (Fig. 6).
The authors designed and manufactured a working model of a planetary type wind turbine of the claimed design with a calculated power of 400 W with wind force of 5 m / s. The model was presented at the exhibition NTTM-2002, held in June-July 2002, where she was awarded a diploma.
CLAIM
A planetary-type windmill including a rotating rotating frame on the base with movable blades and a rotary shaft, the blades being connected to the rotary shaft by a constant ratio of 1: 2 transmitting mechanism, characterized in that the rotary shaft is provided with a movably mounted weather vane and is connected to it by a control device consisting of A crank-slider mechanism, a connecting rod, a control plate and a return spring, and a belt gear is used as the transmission mechanism.
print version
Publication date 31.01.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.