| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2285148
![]()
Wind turbine (Wind turbine)
The name of the inventor: Shalupov Sergey Grigorievich (RU); Shalupov Vyacheslav Sergeevich
The name of the patent holder: Shalupov Sergey Grigorievich (RU); Shalupov Vyacheslav Sergeevich
Address for correspondence: 456020, Chelyabinsk Region, Ashinskiy District, Sim, ul. Revolution, 12, ap. 38, S.G. Shalupova
Date of commencement of the patent: 2003.12.29
Wind turbine belongs to the field of wind power. To increase the coefficient of wind force utilization and to reduce the threshold of wind speed that ensures operability, in a windmill containing windwheels with arcuate blades having air channels formed by arcuate partitions and lower and upper covers, fastened together, the wind wheels have three arcuate blades arranged at an angle 120 ° with respect to each other, each blade having an even number of arc-shaped air channels identical to adjacent blades, one half of which is inextricably linked to the air channels of the adjacent blade, located clockwise, and the other half of the air arc-shaped channels are inextricably linked to the air channels Adjacent blade, counter-clockwise. The upper and lower covers of the windscreens have a concave arcuate edge of equal radius in the part forming the blade of the wind wheel along the radius line, and the radial centers are spaced apart from each other at an angle of 20 ° to 50 °, in one half of the windrows the center of the arcuate concave edge of the bottom cover in relation to The center of the arcuate concave edge of the top cover is offset clockwise, and the other half is counter-clockwise. The windmill is assembled in such a way that the concave arcuate edges of the blades of the upper covers of the underlying wind turbines are combined with the concave arcuate edge of the blades of the lower covers of the overlying wind turbines, forming three helical, wind-engaging cavities on the side surface of the wind turbine.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to devices by means of which wind power can be used for the environmentally friendly production of various types of energy, for example electrical, thermal or mechanical for economic purposes.
A windmill tower is known, comprising a housing with windows and rotary valves installed therein, wherein the housing is made in height by a composite of cylindrical rings and is provided with vertical posts connected thereto, and the valves are annular in soft material and cantilevered from the inside of the rings above the windows / See, for example, SU 1451332, 1989 (1) is an analogue of /.
A frame support of a wind turbine is known in which the central barrel is hollow and provided with blocks in contact with the cable ropes located in the upper part of the barrel cavity and a traction mechanism located in the lower part of the barrel cavity and connected to the struts (see, for example, SU 1451333, 1989 (2) is an analogue of /.
A wind turbine is known that has a vertical shaft with a base and a wind wheel with arcuate blades offset one against the other to form an air channel divided by partitions. The internal cavities of the blades with the partitions perceive the energy of the wind and cause the wind wheel to rotate. The bottom cover of the wind wheel is equipped with rollers, the base with a support disk. The windmill has additional wind wheels, which are offset relative to each other in the circumferential direction, and the upper and lower covers of adjacent windwheels are interconnected (see, for example, SU 1451328, 1987 (3) - closest analogue).
The disadvantages of these constructions are:
1. The windmill tower can be used only in wind turbines of low power, since with a large diameter of the wind wheel the air flow will not reach the opposite side of the wind wheel. This wind power plant will have a low coefficient of wind power use because the air entering the interior of the tower will raise the pressure there and press the ring-shaped valves against the wall, and having an outer cylindrical shape, it will easily flow around the wind by entering the inner cavity A narrow vertical strip created by open valves. The windmill tower will not be effective in regions where winds prevail at a speed of less than 6 m / s, since at such wind speeds the high-speed wind wheels stand.
2. The frame support of the wind farm is a bearing structure for a number of high-speed wind turbines, which during operation represent for the wind resistance of one order with the resistance of the sail. Such resistance to the wind will create a large force of the tipping point, presenting to the frame support of the wind installation the requirements of increased strength and installation on a powerful support, which will increase the cost of the wind farm. A lot of windmills will create a high level of noise, which will not allow the construction of such wind farms in the human habitat. This wind power plant will be inefficient in areas with winds prevailing, having a speed of less than 6 m / s, because it uses traditional high-speed wind wheels, which at low wind speeds are inactive.
3. The wind turbine has the disadvantage that each wind wheel from which it is composed operates autonomously, without affecting in any way the operation of other wind turbines in order to improve the performance of the windmill. Due to the presence of only two blades of wind turbines, their air passages are located in the inactivity area in relation to the direction of the wind twice, in one turn, which gives the impellers impulse nature of operation. The external shape of the wind turbine created by the set of wind turbines has a stepped upward rising surface, along which the wind smoothly changes direction, without giving the wind turbine an essential part of its energy.
The task, the solution of which is directed to the invention, consists in obtaining more power and increasing the coefficient of wind force utilization with respect to existing wind turbines with a vertical axis of rotation with equal dimensions and wind speed. The increase in power not only improves the economic indicator, but also reduces the threshold of wind speed at which the wind farm starts working. In areas where a weak wind prevails, this quality is of fundamental importance.
The above object is achieved in that in a wind turbine comprising windwheels with arcuate blades having air passages formed by arcuate partitions and a lower and upper cover, fastened together, wherein the wind wheel lying in the base is rigidly connected to the vertical shaft, the wind wheels have three arched Blades positioned at an angle of 120 ° with respect to each other, each blade having an even number of arc-shaped air channels identical to adjacent blades, one half of which is inextricably linked to the air channels of the neighboring blade clockwise and the other half of the air arcuate channels Is inextricably linked to the air channels of the adjacent blade counterclockwise, the upper and lower covers of the wind turbines having a concave arcuate edge of equal radius in the portion forming the blade of the wind wheel along the radius line, and the radius centers of the arcuate edges are spaced apart from each other at an angle of 20 ° Up to 50 °, in one half of the windscreens, the center of the arcuate concave edge of the bottom cover with respect to the center of the arcuate concave edge of the top cover is offset clockwise, while the other half of the windscreens are offset counterclockwise by the same angle, with wind turbine assembling by imposing windscreens On each other and their fastening with each other is carried out in such a way that the concave arcuate edges of the blades of the upper covers of the underlying wind turbines coincide with the concave arcuate edge of the blades of the lower covers of the overlying wind turbines, forming three winding-like wind-driven cavities on the lateral surface.
From the closest analogue, the windmill differs significantly in the wind resistance in the working area, which increases the air pressure in the channels and the speed of its movement, which increases the power of the windmill. The design of the wind turbine makes it possible to practically exclude the impulse character of the torque depending on the position of its sides relative to the direction of the wind.
Drawings are attached to the application material.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |
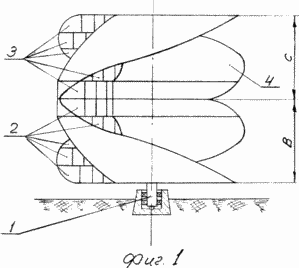
1 shows a general view of a wind turbine with the designation of the main elements of which it consists.
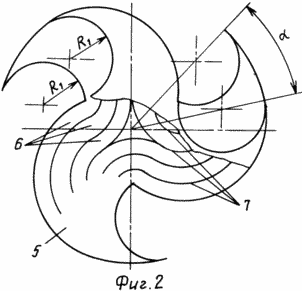
2 depicts a wind wheel 2 (Fig. 1) with a designation of the elements contained in a given wind wheel. View from above.
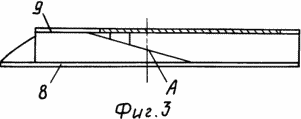
Fig. 3 shows a side view of the wind wheel 2 / Fig. 1 / with the designation of additional elements.
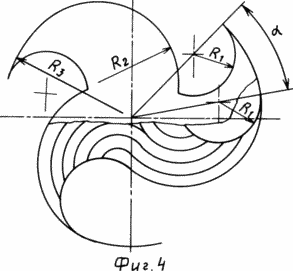
FIG. 4 is a top view of the wind wheel 3 (FIG. 1) showing the features of its design.
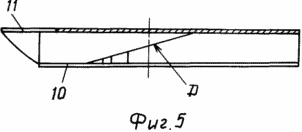
FIG. 5 shows a side view of the wind wheel 3 (FIG. 1) with a designation of its constituent elements.
The wind turbine, the general view of which is depicted in FIG. 1, comprises a shaft 1 on which a package of two types of windbreaks, fixed in a fixed manner, is fixed to one another: wind-wheels 2 and wind-wheels 3 covered by fairings 4.
Wind turbines 2 and 3 contain three blades 5 consisting of air channels 6 formed by partitions 7, a lower cover 8 and an upper cover 9 at the wind wheel 2, and at the wind wheel 3 - consisting of air channels 6 formed by partitions 7, bottom cover 10 and upper The lid 11. The blades 5 have air channels 6 of arcuate shape, one half of which is inextricably connected with half of such air channels of the adjacent blade, located clockwise, and the other half of the air channels 6 of each blade 5 - with half of similar air channels of the neighboring blade opposite Hour hand.
At the bottom cover 8 of the wind-wheel 2 and the upper cover 11 of the wind-wheel 3, the outer edge of the blades 5 is formed along the radii R2 and R3. The partition 7, passing along the outer edge of the blades 5, cuts diagonally along the outer edge of the radius R3, forming the edge "A" at the wind-wheels 2, and the edge "D" at the wind-wheels.
The upper cover 9 of the windscreens 2 and the lower cover 10 of the windscreens 3 are identical and differ from the covers 8 and 11 of the windscreens 2 and 3 in that the outer edge of the said covers is made only by the radius R2 to the point of connection with the radius R3, that when making the windrows the centers of the radii R1 of the upper and The bottom covers of each wind wheel carry on an angle , Selected from 20 ° to 50 °, by biasing the side edge of the radius R1 of the blades 5 of the upper cover 9 with respect to the side edge of the radius R1 of the lower cover 8, for example clockwise at the windscreens 2, and at the windrows 3 the lateral edge of the radius R1 of the upper The cover 11, in this case, biases the bottom cover 10 counterclockwise.
The windmill is assembled in such a way that the side edges R1 of the blades 5 of the windscreens 2 and 3 of the upper covers are aligned with the side edges R1 of the windscreens 2 and 3 of the lower covers when the windrows 2 and 3 are superimposed in a strict sequence: first the wind-wheel group 2, then the wind-wheel group 3 , Rigidly connecting the wind wheels with each other. Due to this sequence of wind turbine assemblage, the helical-shaped, wind-engaging cavity "VS" is formed, consisting of two halves: the lower helical, rising from the bottom up to the middle of the windmill along the vertical "B", and the helical upper, descending from the top down to the middle of the windmill along the vertical "C" .
Thus, on the side surface of the windmill, three exciting winds are formed, consisting of two helical parts "B" and "C" of the "BC" cavity. In the assembly of the wind wheel 2 and 3 are closed by the fairing 4.
Wind turbine operation is as follows. Wind of any direction is captured by the "BC" cavity facing it, changing the direction from below upwards in the lower half of the windmill and from top to bottom in the upper half, creating a high pressure in the catching zone. Under the influence of the created pressure, the air inside the windmill moves through the air channels 6. Due to the plurality of partitions 7, the contact area of the windmill with the air flow increases, and the three-bladed wind wheels 2 and 3 provide the maximum number of operating air channels 6 as compared to the two-bladed or four- and more-blade Wind wheels, which increases the force of torque and improves the coefficient of use of wind power.
CLAIM
A wind turbine comprising wind wheels with arcuate blades having air passages formed by arcuate partitions and a lower and upper cover, fastened together, while the wind wheel lying in the base is rigidly connected to a vertical shaft, characterized in that the wind wheels have three arcuate blades arranged At an angle of 120 ° to each other, each blade having an even number of arc-shaped air channels identical to adjacent blades, one half of which is inextricably linked to the air channels of the neighboring blade clockwise, and the other half of the air arc-shaped channels are inextricably linked to the air channels Of the neighboring blade counterclockwise, the upper and lower covers of the windwheels having a concave arcuate edge of equal radius in the portion forming the blade of the wind wheel along the radius line, and the centers of the radii of the arcuate edges are spaced from each other at an angle of 20 to 50 °, Half of the windscreen, the center of the arcuate concave edge of the bottom cover with respect to the center of the arcuate concave edge of the top cover is offset clockwise, while the other half of the windscreens are offset counterclockwise by the same angle, while assembling the windmill by placing windscreens against each other and attaching them With the other is carried out in such a way that the concave arcuate edges of the blades of the upper covers of the underlying wind turbines coincide with the concave arcuate edge of the blades of the lower covers of the overlying wind turbines, forming three wind-shaped wind-driven cavities on the lateral surface of the windmill.
print version
Publication date 31.01.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.