| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2044371
![]()
Chemical current sources
Name of the inventor: Stanko V.H .; Mataruev VN
The name of the patentee: Cooperative Innovation Center "Advanced technologies"
Address for correspondence:
Starting date of the patent: 1993.04.22
Application: gas-liquid chemical sources of power supply for stand-alone systems with limited service.
The inventive device comprises a gas-diffusion positive electrode made of carbon having hydrophobized barrier layer, a metal negative electrode with a catalyst selected from the group consisting of platinum, palladium, rhodium, gold, silver, nickel, particularly Raney nickel, and the fuel and electrolyte mixture wt. glycerol 15 40; 30 water and potassium hydroxide 50 30 45. This power supply has a higher specific electrical characteristics in the temperature range from -30 to + 80 ° C.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to electrical engineering and can be used in the manufacture of chemical current sources (CCS) anode with liquid reagents.
Known gas-liquid HIT comprising platinized carbon air electrode and the fuel electrode-electrolyte fuel mixture of 6N sulfuric acid and methanol. The disadvantage of this is the presence of HIT corrosive acid electrolyte and a limited operating temperature range of the high volatility of methanol [1]
From the prior art closest to the combination of material features is the gas-liquid HIT comprising porous metal positive electrode, a negative metal electrode coated with a layer of rough platinized nickel, and the mixture alkaline with liquid fuel, for which methanol can be used, formaldehyde and hydrazine [2] The disadvantage of this ZIT is the instability of the electrical characteristics due to the poisoning of the positive electrode reaction products. In addition, the shortcomings of this HIT include the toxicity of the fuel used.
The aim of the invention is to provide a gas-liquid HIT having improved electrical performance and enhanced functionality in terms of operating temperature range.
This object is achieved in that the gas-liquid HIT containing positive gas diffusion and liquid metal electrode with catalyst and fuel and electrolyte mixture as a positive electrode using a carbon electrode with hydrophobized barrier layer, as a liquid negative electrode catalyst using a metal selected from the group consisting of platinum, palladium, rhodium, nickel, gold and silver, as well as fuel and electrolyte mixture is a mixture of glycerin, water and potassium hydroxide in the following ratio, wt. Glycerin 15-40 Water 30-50
Potassium hydroxide 30-45
Thus the metal catalyst used in the form of a Raney metal.
In the claimed new HIT is the use of the carbon electrode with hydrophobized layer, the metal electrode with the catalyst Raney-metal from the group consisting of platinum, palladium, rhodium, nickel, gold and silver, in combination with a glycerine-base mixture with Content, wt. glycerol 15-40; 30-50 water and potassium hydroxide 30-45.
Comparative analysis with the prototype showed that the proposed technical solution has the presence of new components (electrodes, electrolyte fuel mixture). Thus, the claimed invention meets the criterion HIT "novelty." Comparison of the claimed solution with other technical solutions show that in themselves are known components. Coal gas diffusion electrodes and a liquid metal used in other electrochemical systems such as zinc air (Electrochemical energy. III of the All-Union Scientific Conference. M. 1989, p.29), and a liquid fuel cell (fuel cell. / Some problems of science and theory. M. Science, 1964, p.148). However, their use in the claimed electrochemical system leads to improved electrical performance and expand functionality, which allows to conclude that the criterion of "inventive step".
The achieved technical result can be achieved only by the totality of essential features and is not the result of simple summation of the individual known signs, as not shown when using any of them individually in the known solutions.
 |
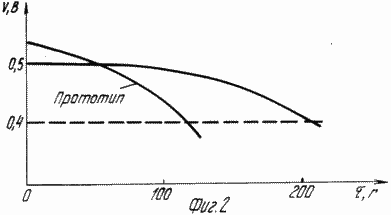 |
1 schematically shows the proposed CCS; 2 is a discharge characteristic at HIT toke1 mA / cm 2 in comparison with the prototype.
HIT is a housing 1 "pocket-like" with the air electrode 2, with the current collector 3, filled with a mixture of fuel and electrolyte 4. Inside the housing is located a liquid negative electrode current collector 5 to 6. When using CCS at the anode there is an interaction of glycerin with hydroxyl ions to form water and aldehydes and release electrons at the cathode and oxygen is ionized by interacting with the water, forming hydroxyl groups, which diffuse to the anode. Current-producing reaction is as follows:
anode C 3 H 5 (OH) 3 + 3OH - _--> C 3 H 5 O 3 + 3H 2 O + 3e -
cathode 1,5O 2 + 1.5H 2 O + 3e - _--> 3OH -
The resulting reaction water accumulates in the electrolyte, causing its dilution.
Selection of the potassium hydroxide content of 30-45 wt. water and 30-50 wt. determined, on the one hand, the solubility limit of KOH at normal temperature, on the other hand, in order to ensure long-term operation and thus discharge at the end of the electrolyte concentration due to dilution should not extend beyond the lower working limit. The lower limit of the content of glycerin in the fuel and electrolyte mixture is determined by the operating time and lower operating limit of the electrolyte concentration. The upper limit is restricted to excessive viscosity of the mixture, which hinders the diffusion processes in the HIT and restricting its electrical characteristics.
Using the positive electrode on the carbon electrode with water-repellent barrier layer provides stability characteristics of HIT due to Coal inertia to glycerol, sufficient activity in the oxygen reduction reaction and prevent flooding of the active layer by hydrophobic. The active layer usually contains a mixture of carbon black, activated carbon and PTFE binder. Hydrophobized manufactured by overmolding layer on the gas side electrode fluoroplastic film or applying PTFE emulsion, followed by drying.
The negative electrode using a metal as a catalyst metal selected from the group: platinum, palladium, rhodium, nickel, gold and silver. These catalysts have sufficient activity and durability at operating conditions HIT. The catalyst is used in the form of metal, mobile or Raney metal. The catalyst is applied to the electrode by chemical or electrochemical deposition, or mixed with a binder. Metal called Raney metal powder obtained after leaching of a suitable catalyst with the aluminum alloy. Raney metals have high specific surface area and sufficient activity in the oxidation of glycerol.
The characteristics of the experimental sample claimed HIT. As the positive electrode used in two-layer carbon electrodes with a PTFE binder and a nickel mesh current collector. The hydrophobic barrier layer is coated onto the gas side of the electrode in the form of a concentrated emulsion of PTFE with subsequent drying.
As a negative electrode used in a sintered nickel electrode and Raney nickel mesh platinized chemically. As the fuel and electrolyte mixture, the mixture weight. glycerol 20; Water and potassium hydroxide 40 40. HIT nickel anode was discharged at a current density of 1 mA / cm 2 for 200 hours. A typical discharge curve in comparison with the prior art is shown in Figure 2. HIT with platinized grid allowed the discharge at a high current density to 10 mA / cm 2. The discharge curve has a similar character. Research has shown that oxidation of glycerol can be realized container 1 Ah / g. The energy density of the claimed HIT is estimated at 60-80 Wh / kg, depending on the purpose and use of construction materials. HIT experimental sample was tested in the temperature range from -30 to +80 ° C without failure of performance. With increasing operating temperature specific power characteristics of HIT increase.
CLAIM
- Galvanic cell comprising a gas diffusion positive electrode, a metal negative electrode with a catalyst and toplivoelektrolitnuyu mixture comprising potassium hydroxide, water and alcohol, characterized in that the positive electrode is made of carbon, a barrier layer is hydrophobized, as a negative electrode catalyst taken metal selected from the group consisting of platinum, palladium, rhodium, nickel, gold and silver, as well as the alcohol in the fuel and electrolyte mixture glycerol taken in the following ratio, wt.
Glycerin 15 40
Water 30 50
Potassium hydroxide 30 45 - Current source according to claim 1, characterized in that the nickel catalyst of the negative electrode is made of Raney nickel.
print version
Publication date 10.12.2006gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.