| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2158047
![]()
METHOD OF RECONSTRUCTING LEAD BATTERIES
The name of the inventor: Shevchenko NP; Kochurov A.A.
Name of patent holder: Military Automobile Institute
Address for correspondence: 390014, Ryazan, Military Automobile Institute, NIO, Burobina GN
Date of commencement of the patent: 1999.06.01
The invention relates to electrical engineering and relates to the recovery of storage batteries. The invention allows the use of any rechargeable batteries for processing, regardless of their technical condition. The technical result is to increase the service life and capacity of the restored batteries, save materials and increase the yield of the product, the full use of the raw material. This is achieved by the fact that the active mass of the positive plates is not separated from the grids, and the powder obtained after grinding the used positive plates is heat treated at 450-500 ° C to yellow color. The paste is prepared by mixing in certain proportions the powder with distilled water, followed by the addition of a sulfuric acid solution with a density of 1.40 g / cm 3 with vigorous stirring. After rubbing the paste into the grate, the plates are pressed by laminating between rubber rolls, dried at 120 ° C for 20-25 seconds or held in air for 4-6 minutes, re-rolled between rollers wrapped with gauze. After pressing, the plates are kept at 45-50 ° C and air humidity 95% 16-18 hours, then at the same temperature, with a decrease in humidity from 95 to 75%, another 20 hours the plates are dried at a temperature of 68-70 ° C and air humidity no more than 20% in the course of 12-14 hours.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to electrical engineering and relates to the recovery of storage batteries.
There is a known method for the recovery of lead accumulators (USSR Authorship Certificate No. 112833, IPC N 01 M 10/12, 1956), consisting in the fact that the used battery is precharged for 4-5 hours before disassembling. After disassembling the blocks, the active mass of the positive electrodes is separated from the grids and, in pure form (without slurry and without a mass of negative electrodes and foreign binders) is subjected to grinding. The resulting powder is stirred on the working electrolyte until a pasty state and spread the paste on the grate. After that, the positive plates are pressed, re-lubricated and pressed again. Negative electrodes are restored without removing the mass from the grids by pressing plates with canvas gaskets. The restored negative electrodes are collected with positive electrodes in the block. The collected battery is subjected to a single charge at a normal current value.
Disadvantages of this method are:
1. The large amount of labor involved in separating the positive active mass from the lattices.
2. Limited capabilities of the proposed technology, distributed only to batteries that do not have such a malfunction as a short circuit or an open.
3. Low capacity (40 to 60% of the nominal) of the rechargeable batteries due to the fact that although the active mass is used in its pure form, its electrical activity is significantly reduced by the end of service due to a change in the structure of lead dioxide (PbO 2 ) and accumulation (PbO 4 ), which can not be reduced to PbO 2 in the course of a charge (Dasoyan MA, Aguf IA Modern theory of a lead accumulator (Moscow: Energia, 1975, pp. 129-130).
4. Short service life of the rechargeable batteries. After a year of service, 60-80% of the active mass of positive electrodes creep because of the poor quality of the paste obtained from the powder of the spent active mass. Only high-temperature drying (about 150 ° C) allows satisfactory adhesion of the active mass. However, with this drying, the active mass is cracked.
The invention is aimed at increasing the service life and capacity of the restored batteries, saving materials and increasing the yield of the product, completeness of the use of the raw material; Allows to use for processing any storage batteries regardless of their technical condition.
This is achieved by the fact that the active mass of the positive electrodes is not separated from the gratings, and the powder obtained after grinding the used positive electrodes is subjected to a thermal treatment at a temperature of 450-500 ° C to yellow. The paste is prepared by mixing the powder with distilled water, followed by the addition of a sulfuric acid solution with a density of 1.40 g / cm 3 based on: 1 kg of powder, 120 ml of water and 77 ml of acid. Further, the paste is rubbed into the grate, compacted by rolling the plates between the rubber rollers. After that, the plates are dried at a temperature of 120 ° C for 20-25 seconds or air-conditioned for 4-6 minutes, re-rolled between rolls wrapped in gauze. Plates are held at a temperature of 45-50 o C and an air humidity of 95% for 16-18 hours, then at the same temperature with a decrease in humidity from 95% to 75% for another 20 hours. Dry the plates at a temperature of 68-70 o C and humidity of air no more than 20% for 12-14 hours.
THE PROPOSED METHOD FOR RECONSTRUCTING LEAD BATTERIES CONCLUDES IN THE FOLLOWING
Used batteries are disassembled. The active mass of the positive electrodes with the grate is washed in distilled water, dried, ground, heat treated at a temperature of 450-500 ° C to a yellow color. After that, the paste is prepared by mixing the powder with distilled water, followed by the addition of a sulfuric acid solution with a density of 1.40 g / cm 3, based on 1 kg of powder, 120 ml of water and 77 ml of acid. The paste is rubbed into the grate, compacted by laminating the plates between the rubber rollers. After that, the plates are dried at a temperature of 120 ° C for 20-25 seconds or air-conditioned for 4-6 minutes, re-rolled between rolls wrapped in gauze. The plates are then held at a temperature of 45-50 ° C and an air humidity of at least 95% 16-18 hours, then at the same temperature, with a decrease in humidity of up to 75%, another 20 hours. After holding, the plates are dried at a temperature of 68-70 ° C and a humidity of not more than 20% for 12-14 hours.
Negative electrodes are restored without removing the mass from the grids by pressing them with canvas gaskets. The recovered negative electrodes are collected with positive ones into the block.
The collected battery is filled with an electrolyte of density 1.12 g / cm, charged at a normal current value.
The offered method is more perfect in comparison with the known one, since it provides an increase in the service life of accumulators in 2-2.5 times, capacity of batteries from 50% to 100% of the nominal.
When the powder is thermally treated, the thermal decomposition reaction proceeds according to the scheme (Malinin GV, Tolmachev Yu.M., Yadrintsev VB, "Inorganic Chemistry", 1968, Vol. 13, No. 7, p. 1746; Malinin G V., Tolmachev Yu.M., Yadrintsev VB Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 1969, Vol. 14, No. 2, P.307): 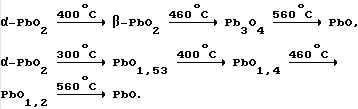
As a result of the heat treatment of the powder of the spent active mass, lead dioxide is converted into minium (the curd is an integral part of the powder for positive electrodes in the production of storage batteries), and lead sulfate changes its structure and, when formed, is easily converted to PbO 2 . When heat treatment and burnt antimony, which positively affects the self-discharge.
A high-quality paste is obtained from the heat-treated powder. The recipe for pasta preparation, as well as the methods of sealing the paste after applying it to the grate, aging and drying plates are known as promising in the production of batteries, provide good results when restoring batteries: the active mass after drying is well adhered, not cracked, not prone to rapid slipping in the process And the porosity reaches 50%.
CLAIM
A method for recovering lead accumulators, which consists in the fact that, after disassembling the blocks, the active mass of the positive electrodes is milled, stirred on the working electrolyte until a pasty state, spread the paste on the current collector, press, dry and, after assembly, the battery is charged, characterized in that an active The mass of the positive plates, not separating it from the current lead, and the powder is heat-treated at 450-500 ° C to yellow, after which the paste is prepared by mixing with distilled water, followed by the addition of sulfuric acid of 1.40 g / cm 3 with vigorous stirring Which is rubbed into the current collector once, and the compaction is carried out twice by rolling first between the rubber rolls, then after drying at 120 ° C for 20 to 25 seconds or after holding in air for 4 to 6 minutes, rolling again between the rolls wrapped Gauze, while the prepared plates are kept at a temperature of 45 - 50 ° C and air humidity of at least 95% 16 - 18 hours before drying, then at the same temperature with a decrease in humidity of up to 75% for another 20 hours, and drying is carried out at a temperature of 68 - 70 o C and humidity of air no more than 20% within 12 - 14 hours.
print version
Date of publication 24.03.2007gg




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.