| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2256278
![]()
PULSED ELECTRIC ENERGY GENERATOR
The name of the inventor: Tuchin Boris Timofeevich (RU)
The name of the patent holder: Tuchin Boris Timofeevich (RU)
Address for correspondence: 630554, Novosibirsk Region, with. Baryshevo Str. Vokzalnaya, 3-B, Apt. 6, ToT.Tuchin
Date of commencement of the patent: 2001.06.13
The invention relates to power engineering and can be used in military equipment, in the national economy and in everyday life. The technical result is to increase the power. In the excitation system of the generator, the transverse magnetic flux of the annular magnets is compressed. As a result of compression of the transverse magnetic flux in the excitation system of the generator, the duration of the induced pulse becomes much shorter than the period between pulses, so that the electromagnetic braking torque on the generator shaft counteracts the primary motor only a short "infinitesimal" time interval, and therefore the external circuit load current is not Has time to exert a braking effect on the rotor shaft. As a consequence, there is a reduction in the amount of mechanical work that is expended during the induction of emf. The installation of internal intermediate shields allows increasing the number of sections of generators, which makes it possible to increase the power of a pulsed electric power generator.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of power engineering and can be used in military equipment, in the national economy and in everyday life.
An electric power generator is known, comprising a housing with a stator with excitation windings, a rotor with electromagnets. The rotor with electromagnets serves to excite the main magnetic field of the machine, and on the stator in inductive windings an electrical charge is induced and currents pass.
V.Yu. Lomonosov. Electrical engineering. Moscow, 1990. P.292.
The disadvantage of such a pulsed electric power generator is the inadequate amount of induced electric charge and insufficient power.
The problem solved by the invention is that by changing the design of the generator, increase the amount of the induced electric charge and the power of the pulsed electric energy generator.
This task is achieved by the fact that the pulsed electric energy generator consists of a group of pulsed electric energy generators in which the stators of the extreme lateral pulse generators of electrical energy are located between the outer side bearing shields and the inner intermediate shields, and the average pulse electric energy generator is located between two internal intermediate Shields, side bearing shields and internal intermediate panels are fixed to each other by spacer tubes and studs with threaded nuts and washers, in addition, the bearing shields on the outside face contain stiffeners, and on the inside the bearing shields together with the intermediate shields on the side The surfaces contain a base ring stop and guides forming grooves that are located radially along the entire perimeter of the stator circumference at the same step distance, in the guide grooves, radially the sections of the cores of the magnetic circuits forming radially inside the stator a toroidal arcuate cavity for free rotation of the rotor, each separate section of the magnetic circuit body Consists of side rails and two arc-shaped plates made of ferroalloy and fixed with each other by threaded connection with screws, inside, between the plates, fixed with the screws of ferroalloy cores, on the cores are installed inductors connected in series, that is, the end of the conductor of the first Coil is connected to the beginning of the conductor of the second inductor, and the end of the conductor of the second inductor is connected to the beginning of the conductor of the third inductor, and so on, forming on the stator of a separate generator a circular zigzag inductive circuit that is connected in parallel with the zigzag inductive circuits of neighboring generators, The terminals of the group zigzag chain are connected to the contact terminals to which the consumers of electrical energy are connected, the cores of the magnetic circuits with inductive windings are fixed in the grooves of the side and intermediate shields from falling out by means of squares with clamping bolts and are closed from the outside by a cylindrical insulating jacket consisting of two halves connected between By means of a threaded connection with bolts and a nut, and the rotor fixed to the shaft contains a group of rotors, each rotor is fixedly fixed to the shaft through the intermediate sleeves and consists of two disks assembled into the bag by means of a threaded connection where the discs are installed radially In grooves and fixed with clamps having a bolt hole, bracket shells made of ferroalloy, containing in the side view at the end a rectangular protrusion for fixing in the groove of the disc, and in the top view the arms have a cross-shaped shape and contain on one and the other side of the base The body of a ferroalloy cylindrical protrusion-core on which coils of electromagnets are mounted, where the electromagnet itself consists of a ferroalloy cylindrical core and two coils wound by a wire, connected in series, forming a single unified electromagnet, the brackets of the electromagnets mounted on the rotor are located on the rotor disk Radially at the same step distance, in proportion to the step distance between the guide grooves located on the stator, the coils of the electromagnets each have a series-on-counter connection, i.e., the end of the winding terminal of the first electromagnet is connected to the end of the winding of the second neighboring electromagnet, and the start of the winding of the second electromagnet is connected to The beginning of the output of the winding of the third electromagnet, and so on ... Thus, when power is supplied to the electromagnets, the magnetic poles of the electromagnets face each other with the same poles and form toroidal magnets on the rotors, the end ends of the terminals of the connected electromagnets are connected to the contact rings, To which the contact brushes are supplied, through which electric power is supplied to the electromagnets, in addition, the first carrier disc in the package of each individual rotor serves as a base that contains the hub and on the end plane of the disc there are through-through fixing holes and a circular base groove on the periphery of the first carrier disc, The second rotor disk serves as a matrix for the brackets and contains a shaft hole through the center of the disk, through holes and holes with a countersink for the screw heads, and endless grooves cut radially along the perimeter of the disk, equal in width to the brackets which are located at a uniform step distance proportional to the step The distance between the grooves located on the stator in the side bearings and in the intermediate panels, to all this, the pulsed electric power generator contains mounting supports and loading lugs, which are mounted on the studs, which tighten the bearing shields.
The invention, in my opinion, is new, because the pulsed electric energy generator consists of a group of pulsed electric energy generators in which the stators of the extreme, lateral pulse generators of electrical energy are located between the outer side bearing shields and the inner intermediate shields, and the average pulse generator of electrical energy Is located between two internal intermediate shields, the side bearing shields and internal intermediate panels are fixed to each other by spacer tubes and studs by threaded connection with nuts and washers; in addition, the bearing shields on the end face contain stiffeners, and on the inside, the bearing shields together with Intermediate shields on the lateral face surface contain a base ring stop and guides forming grooves that are located radially along the entire circumference of the stator circumference at the same step distance; in the guide grooves, radially the sections of the cores of the magnetic circuits forming radially inside the stator a toroidal arcuate cavity for free rotation of the rotor, Each separate section of the magnetic circuit body consists of side rails and two arcuate plates made of ferroalloy and fixed with each other by threaded connection with screws, the ferro-alloy cores are fixed inside the plates between the plates, the inductors connected in series are connected to the cores The end of the conductor of the first inductor is connected to the beginning of the conductor of the second inductor, and the end of the conductor of the second inductor is connected to the beginning of the conductor of the third inductor, and so on, forming a circular zigzag inductive circuit on the stator of a separate generator which is connected in parallel with the zigzag inductive circuits of neighboring generators , The extreme ends of the terminals of the group zigzag chain are connected to the contact terminals to which the consumers of electrical energy are connected, the cores of the magnetic circuits with inductive windings are fixed in the grooves of the side and intermediate shields from falling out by means of squares with clamping bolts and closed from the outside by a cylindrical insulating jacket consisting of two halves , Connected by a threaded connection with bolts and a nut, and the rotor fixed to the shaft contains a group of rotors, each rotor is fixedly fixed to the shaft through intermediate sleeves and consists of two disks assembled into a bag by means of a threaded joint, Disks are installed radially in the grooves and fixed with clamps having a bolt hole, shells of brackets made of ferroalloy, containing in the side view at the end a rectangular protrusion for fixing in the groove of the disc, and in the top view, the brackets have a cross-shaped shape and contain one and The other side of the base of the body is a ferroalloy cylindrical protrusion-core on which coils of electromagnets are mounted, where the electromagnet itself consists of a ferroalloy cylindrical core and two wire-wound coils connected in series to form a single electromagnet, the brackets of electromagnets mounted on the rotor are located on the disk Rotor radially at the same step distance, in proportion to the step distance between the guide grooves located on the stator, the coils of the electromagnets each have a series-on-counter connection, i.e., the end of the winding of the first electromagnet is connected to the end of the winding of the second neighboring electromagnet, and the start of the winding of the second electromagnet is connected With the beginning of the output of the winding of the third electromagnet, and so on, thus, when power is supplied to the electromagnets, the magnetic poles of the electromagnets face each other with the same poles and form toroidal magnets on the rotors, the terminal ends of the connected electromagnets are connected to the contact rings to which The contact brushes are fed through which the electric power is supplied to the electromagnets, in addition, the first carrier disc in the package of each individual rotor serves as a base that contains the hub and on the end plane of the disc there are through-through fixing holes and a circular base groove on the periphery of the first carrier disc, Rotor serves as a matrix for the brackets and contains a hole in the center for the shaft, through holes and holes with countersink for the screw heads, and cut radially along the perimeter of the disk through grooves equal in width to the brackets, which are located at a uniform step distance proportional to the step distance Between grooves located on the stator in the side bearings and in the intermediate panels, to all this, the pulsed electric power generator contains mounting supports and loading lugs, which are mounted on the studs, which tighten the bearing shields.
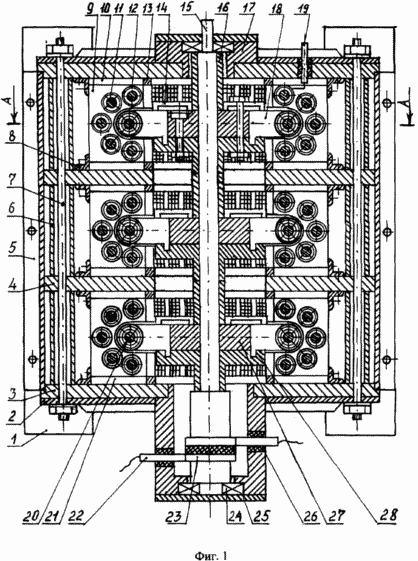 |
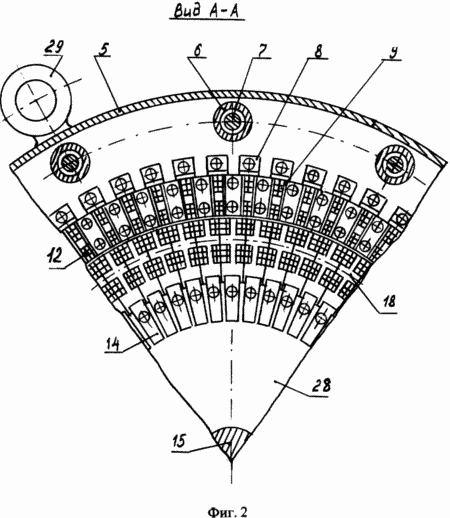
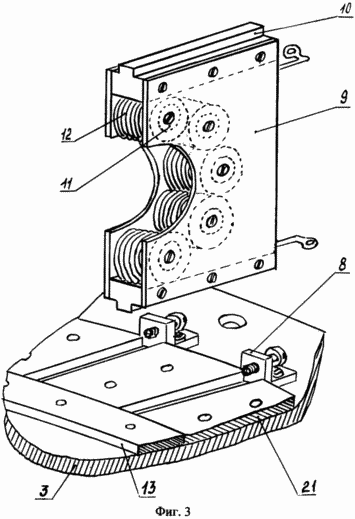
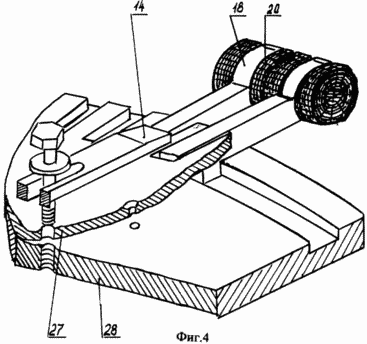
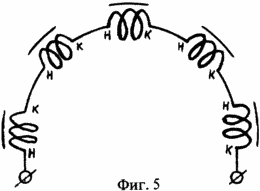
The proposed pulsed electric power generator is shown in FIG. 1, FIG. 2, a and, as shown in separate fragments of the nodes of FIG. 3, FIG. 4, which consists of: mounting supports 1, stiffeners 2, outer side bearing shields 3, The inner intermediate shields 4, the casing 5, the spacer sleeves between the shields 6, the tightening pins 7, the elbows with the clamping screws 8, the arcuate plates of the magnetic core 9, the slide 10, the cores of the magnetic core 11, the inductive windings 12, the thrust base rings 13, the clamps 14, the shaft 15 , Spacer sleeves for rotors 16, bearing housings 17, ferroalloy brackets 18, contact terminals 19, annular electromagnets 20, guides 21, contact brushes 22, contact rings 23, bearings 24, bearing caps 25, insulating housing 26, matrix disk 27, a carrier disc 28, loading lugs 29. |
 |
 |
 |
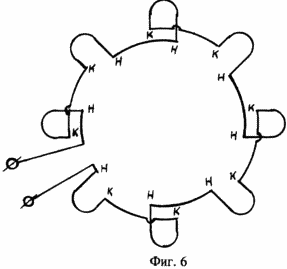 |
The pulsed electric energy generator works as follows. With the help of an external traction force, we begin to rotate the rotor shaft 15 of the generator. During rotation of the generator rotor shaft, we apply power to the electromagnets 20 of the rotor with the help of brushes 22 and contact rings 23 (the generator has independent excitation). As a result of the flow of electric current in the electromagnets of the rotor, along the perimeter of the rotor circumference, a constant magnetic field is formed in which the magnetic force lines of the transverse magnetic flux of each annular electromagnet are added to the transverse magnetic lines of force of another neighboring electromagnet and have the opposite direction in each step. When the rotor shaft rotates with electromagnets in the toroidal cavity of the stator, in the inductive windings 12 mounted on the stator, the direction of the magnetic flux will change periodically. As a result, an electric charge will be generated in the inductive windings of the stator 12. Since the inductors 12 are connected in the cores of the magnetic circuit (FIG. 5) and the stator (FIG. 6) in series, and they are excited simultaneously in the same phase, the total electric charge will be equal to the sum of all electric charges generated in each separately taken , The inductor, and the parallel connection of adjacent sections of the pulsed electric power generator increases the total power of the pulsed electric energy generator. The potential difference in the pulsed electric energy generator is removed directly from the stator, from the contact terminals 19, to which inductive windings are connected.
As a result of using such a design of a pulsed electric energy generator, the value of the induced charge and the power of the generator increase.
CLAIM
An electric power generator comprising a housing with a stator, with inductive windings, a rotor with electromagnets fixed to the shaft, characterized in that the pulsed electric energy generator consists of a group of pulsed electric energy generators in which the stators of the extreme lateral pulse generators of electrical energy are located between the outer side Bearing shields and internal intermediate shields, and the average pulse generator of electrical energy is located between two internal intermediate shields, the side bearing shields and internal intermediate shields are fixed to each other by spacer tubes and studs with threaded nuts and washers, in addition, the bearing shields are externally on the end shield The surfaces contain stiffeners, and on the inside, the bearing shields together with the intermediate shields on the lateral face surface comprise a base ring stop and guides forming grooves that are located radially at the same step distance along the whole circumference of the stator circumference, in the guide grooves, Magnetic cores forming inside the stator a toroidal arcuate cavity for free rotation of the rotor, each separate section of the magnetic circuit body consists of side rails and two arcuate plates made of ferroalloy and fixed with each other by threaded connection with screws, inside between the plates are fixed with screws ferroalloy cores, The coils are connected in series, that is, the end of the conductor of the first inductor is connected to the beginning of the conductor of the second inductor, and the end of the conductor of the second inductor is connected to the beginning of the conductor of the third inductor, and so on, in addition, each section of the casing The inductance coils are connected in series with the next adjacent section of the housing with the coils of inductance, forming a circular zigzag inductive circuit on the stator of a separate generator, which is connected in parallel with the zigzag inductive circuits of neighboring generators; the terminal ends of the group zigzag chain are connected to the contact terminals to which consumers of electrical energy , Cores of magnetic circuits with inductive windings are fixed in the slots of side and intermediate shields from falling out by means of angles with clamping bolts and closed from the outside by a cylindrical insulating casing consisting of two halves connected by a threaded connection with bolts and a nut, and a rotor fixed to the shaft , Contains a group of rotors, each rotor is fixedly fixed to the shaft through intermediate sleeves and consists of two disks assembled into the bag by means of a threaded connection where the discs are mounted radially and fixed in the grooves with the help of tackers having a bolt hole, , Made of ferroalloy, containing in the side view at the end a rectangular protrusion for fixing in the groove of the disc, and in the top view the arms have a cross-shaped shape and contain on each side of the base of the body a ferroalloy cylindrical protrusion-core on which coils of electromagnets are mounted, The electromagnet consists of a ferroalloy cylindrical core and two wound coils connected in series to form a single electromagnet, the brackets of the electromagnets mounted on the rotor are located radially on the rotor disk at the same step distance in proportion to the step distance between the guide grooves located on the stator of the winding Electromagnets with each other have a series-on-counter connection, i.e. конец вывода обмотки первого электромагнита соединен с концом вывода обмотки второго соседнего электромагнита, а начало вывода обмотки второго электромагнита соединено с началом вывода обмотки третьего электромагнита и так далее, таким образом, при подаче электропитания на электромагниты, магнитные полюса электромагнитов оказываются обращенными по отношению друг к другу одноименными полюсами и образуют на роторах тороидальные магниты, крайние концы выводов соединенных электромагнитов подсоединены к контактным кольцам, к которым подведены контактные щетки, через которые подводится электропитание к электромагнитам, кроме того, первый несущий диск в пакете каждого отдельного ротора служит основанием, которое содержит ступицу, а на торцевой плоскости диска-основания содержатся сквозные крепежные отверстия и круговая базовая канавка на периферии первого несущего диска, второй диск ротора служит матрицей для кронштейнов и содержит по центру диска отверстие для вала, сквозные крепежные отверстия и отверстия с зенковкой под головки винтов, а и нарезанные радиально по периметру диска сквозные пазы, равные по ширине кронштейнам, которые располагаются радиально на равномерном шаговом расстоянии, соразмерном шаговому расстоянию между пазами, расположенными на статоре в боковых подшипниковых и в промежуточных щитах, ко всему этому импульсный генератор электрической энергии содержит установочные опоры и погрузочные проушины, которые установлены на шпильках, стягивающих подшипниковые щиты.
print version
Дата публикации 23.12.2006гг




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.