| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2168061
![]()
ELECTRIC POWER INSTALLATION
The name of the inventor: Korotya Boris Viktorovich (UA); Kryzhov Harold Petrovich
The name of the patent holder: Korotya Boris Viktorovich (UA); Kryzhov Harold Petrovich
Address for correspondence:
Date of commencement of the patent: 1999.06.15
The invention relates to the field of electric power and is intended for the production of electricity using non-traditional sources, namely the radiant energy of the sun and air flows. The technical result, which consists in expanding the field of application and independence of the installation from the presence of winds, is provided by the fact that in an electric power plant containing a unit for converting mechanical energy into electric power with an associated electric generator and a unit for converting sun radiant energy into a mechanical energy through a thermal energy source, The second of the blocks is made in the form of a vertically installed pipe of variable cross-section, with expansion in the upper and lower sections and a narrowing in the middle part of the pipe, the pipe is made of two different materials docked along the longitudinal section of the pipe, one of them transparent and the other with an inner surface with The unit for converting mechanical energy into electric energy is in the form of a frame with blades of the windmill and is located in the most narrowed part of the tube with the orientation of the blades perpendicular to the axis of the tube, while the installation as a whole is installed in the place with the most favorable conditions for lighting the tube with the sun And is oriented with a transparent part towards the rays of the sun.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of electric power and is intended for the production of electricity using non-traditional sources, namely the radiant energy of the sun and air flows.
Known are devices that use solar energy, for example, a solar heater, the data of which are given in the USSR copyright certificate No. SU 1615484 A1 (MKI-5 F 24 J 2/10), which is intended for the use of solar energy for heating purposes. It contains a stationary hemispherical mirror reflector and a stationary heat receiver and a counter-monitor in the form of a spherical segment.
However, such a device can not directly be used as a power plant.
And there are known power plants that convert the energy of natural air (wind) flows into electric power, the data of which are given in Ukrainian patents and copyright certificates of the USSR. For example, five patents of the same author (Budrevich Cheslav-Konstantin Albinovich) No. 1594 (MKI-4 F03D 1/06, Wind engine) were published in the Bulletin of Ukraine "Industrial Property" No. 2-94; N 1597 (MKI-5 F 03 D 3/02, Wind-powered device); N 1592 (MKI-4 F 03 D 5/02, Wind engine of Ch.-KABudrevich); N 1598 (MKI-4 F 03 D 7/02, Wind motor); And No. 1593 (MKI-4 F 03 D 5/02, Wind engine) and others.
An electric power plant is known for converting the energy of natural air (wind) flows into electric energy, described in Ukrainian patent No. 21028 A, IPC-5 F 03 D 1/00. The electric power plant contains a wind wheel, kinematically connected to a power take-off shaft connected to an electric generator and a reducer located on a column or mast.
In all of these devices, a wind turbine is used to convert wind power to electric, which includes a supporting mast, a fairing located thereon and a frame with blades or a wind wheel, kinematically connected to a power take-off shaft connected to an electric generator. These devices are one of the main components of a power plant that uses wind energy as a natural air flow, but such a device is cumbersome and largely dependent on the presence of wind and openness of the terrain.
And it is known to use ventilation devices to create an air exchange (ventilation). Such devices are described in many literary and patent sources, in particular in the Official Bulletin "Promyslov Vlastnost" No. 2-94 and No. 3-94 (entered in the State Register of Ukraine). For example, data are given on a ventilation device containing an exhaust pipe, an exhaust hood installed above it, having a radial ejector channels (patent of Ukraine No. 1554, MKI-4 F 24 F 7/02., Ventilation device), or a flexible air duct containing separate sections , Each of which has a framework and an elastic shell (patent of Ukraine No. 1556, MKI-4 F 24 F 13/02., Ventilation flexible air line).
However, these devices are designed to create ventilation and can not directly be used as a power plant.
Known are devices designed to enhance thrust, for example, accepted for review and published in Bulletin of Ukraine No. 3-94, application No. 94020502, MKI-5 F 02 K 1/00, F 02 K 9/00 on the Centrifugal thrust amplifier of Engineer Prokhvatilov I .G., Which consists of a fluid flow source with a nozzle.
However, this device itself requires an additional inflow of energy and can not be directly used as a power plant.
The closest technical solution to the claimed technical solution is the power plant according to the German patent (see DE 4104770 A1, cl. F 03 D 9/00, 20.08.1992), which contains a unit for converting mechanical energy into electric power with an associated electric generator and A unit for converting the radiant energy of the sun into a mechanical one through a thermal one, made in the form of solar cell elements.
This device, like the previous ones, uses, first of all, natural air currents (wind), and for less dependence on the presence of wind in a given area and its closeness, the radiant energy of the sun through solar batteries. However, this device does not give complete independence from wind currents, which leads to a certain limitation of their application.
In addition, all the above-mentioned devices are mainly intended for industrial facilities. At the same time, there is a great need for sources of electricity that could be used and at the household level, for example, for feeding small estates, garden plots, etc.
The basis for the claimed technical solution is the task of creating a resource-saving electric power plant that provides electricity generation by using non-traditional energy sources and can be used in industry and household use or as a backup power source for electricity consumers. In this case, compared with the prototype, the task arises of expanding the field of application, completely regardless of the presence of winds in a given area and its closeness.
The object is achieved in that the electric power plant comprises a unit for converting mechanical energy into electric power with an associated electric generator, and a sun radiant energy conversion unit made in the form of a vertically installed variable-section pipe with an expansion in the upper and lower sections and a narrowing in the middle part of the tube , The pipe is made of two different materials docked along the longitudinal section of the tube, one of them is transparent, and the other with an inner surface with the highest degree of absorption of radiant energy. The unit for converting mechanical energy into electric is in the form of a frame with blades and is located in the narrowest part of the tube with the orientation of the blades perpendicular to the axis of the tube. The installation as a whole is installed in a place where the most favorable conditions for lighting the tube with the sun are provided, while it is oriented by the transparent part towards the rays of the sun.
In addition, for maximum efficiency of the installation, the lower part of the pipe is covered with a bottom with a surface made of a material similar to the material of the opposite transparent part of the tube, namely, the material with the highest absorption of radiant energy. From the lower edge of the transparent part of the pipe, an opening is formed formed between the bottom and the cross-section of the pipe with an inclination in the direction from the top of the hole from the side of the transparent part of the pipe down the side of the opposite part of the pipe. The greatest efficiency can be obtained by tilting at an angle of 30-40 o . In addition, on the side of the corner apex (the bottom of the part of the tube opposite the transparent part), the absorbing surface is made in the form of one or more sites located approximately perpendicular to the direction of the sun's rays.
In addition, for a more efficient use of the unit in under-heated hours with sunlight, especially at night, a burner can be additionally installed at the bottom of the pipe, which can additionally increase the draft in the pipe.
 |
 |
 |
The essence of the invention is explained by the drawing, which shows: |
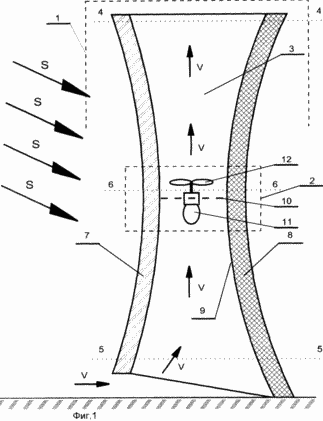
In Fig. 1 shows a general view of an electric power plant that comprises a solar energy conversion unit 1 and a mechanical energy conversion unit 2 to an electrical unit. The block 1 is made in the form of a vertically installed pipe 3 of variable cross-section with expansion in the upper 4 and lower 5 section and narrowing in the middle 6 of the pipe 3. The pipe 3 is made of two parts 7 and 8 joined to the longitudinal section of the pipe 3.
Part 7 is made of a transparent material, for example glass or transparent glass fiber reinforced plastic, and the other part 8 is provided with an inner surface 9 with the highest absorption of radiant energy, for example, painted with black paint, and the like. The unit 2 converts the mechanical energy into an electrical one in the most narrowed part 6 of the tube 3. The unit 2 consists of a base 10 in the form of a frame on which an electric generator 11 is mounted to which the blades of the windmill 12 are connected to the shaft of the wind turbine 12. The windmill 12 is oriented in such a way So that the blades are installed perpendicular to the axis of the pipe 3. The installation is generally installed in a place where the most favorable conditions for lighting the tube by the sun are provided, while it is oriented by the transparent part 7 towards the sun's rays, which are depicted in the form of arrows S.
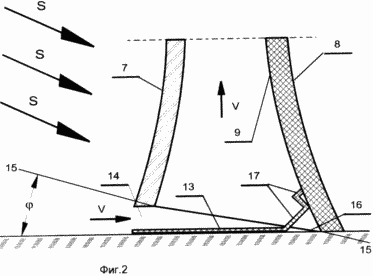
In Fig. 2 shows an embodiment of the lower part of the installation in a section where pipe 3 (with transparent part 7 and opaque - 8) is covered with bottom 13 with a surface of the material with the highest degree of absorption of radiant energy; From the lower edge of the transparent part 7 of the pipe 3, an opening 14 is formed between the bottom 13 and the cross-section of the pipe 15-15 with an inclination in the direction from the top of the opening from the side of the transparent part of the pipe down the side of the opposite part of the pipe at an angle ![]() , The most optimal value of which lies in the range of 30-40 ° , and from the vertex side of the corner 16, the absorbing surface is made in the form of one or more pads 17 arranged approximately perpendicular to the direction of the sun's rays S.
, The most optimal value of which lies in the range of 30-40 ° , and from the vertex side of the corner 16, the absorbing surface is made in the form of one or more pads 17 arranged approximately perpendicular to the direction of the sun's rays S.
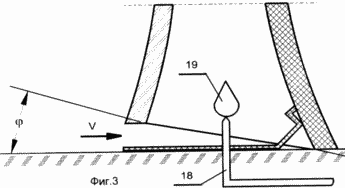
In Fig. 3 shows a possible version of the lower part of the installation when a burner 18 is additionally installed in the lower part of the pipe.
The operation of the proposed device is explained in FIG. 1. The rays of the sun (shown as arrows S) illuminate the tube 3 and through its transparent part 7 pass to the inner part of the tube 3. Reaching the surface 9 of the opposite part 8 of the tube 3, the sun's rays are absorbed, so that the sun's radiant energy is converted into thermal energy. The surface 9 is heated, which, in turn, heats the ambient air inside the pipe. Heated air in the pipe leads to a flow in the direction along the pipe 3 from the bottom up (indicated by the arrows V). Thus, radiant solar energy is converted into mechanical energy of air movement (the so-called furnace draft). The unit 2 senses the energy of the air flow and, by means of the blades of the windmill 12, drives the electric generator 11. As a result, the proposed electric power plant makes it possible to generate electricity using non-traditional energy sources, in particular, the energy of air movement in the tubes (thrust), amplified by the action of radiant energy Of the sun. The power of such an installation depends on the dimensions of the pipe (its height and cross-section) and the intensity of the sun's rays that fall on the active surface of the absorbing part of the pipe.
The operation of the additional elements located at the bottom of the plant is explained in FIG. 2. When overlapping the lower part of the pipe, the bottom 13 with a radiant-absorbing surface increases the active surface. For the same purpose, the pads 17 are constructed which, on the one hand, close the ineffective acute angle near the point 16, and on the other hand, when these sites are installed perpendicular to the sun's rays, they increase the concentration of sun rays in this part of the surface, thereby increasing their temperature. This contributes to the efficiency of the installation. At the same time, air is supplied through the opening 14, which, with increasing angle ![]() Will be large, which will reduce the resistance at the entrance. However, the effective height of the pipe decreases, which leads to a reduction in the power of the installation. Optimum is the value of the angle of inclination
Will be large, which will reduce the resistance at the entrance. However, the effective height of the pipe decreases, which leads to a reduction in the power of the installation. Optimum is the value of the angle of inclination ![]() Within 30-45 o , when a further increase in the input section slightly affects the increase in efficiency, and a decrease in the effective height of the pipe is not yet significant.
Within 30-45 o , when a further increase in the input section slightly affects the increase in efficiency, and a decrease in the effective height of the pipe is not yet significant.
In addition, for a more efficient use of the unit in under-heated hours with sunlight, especially at night, the installation can be supplemented with a burner located at the bottom of the pipe, which can further strengthen the draft in the pipe. The operation of the additional elements is explained in FIG. 3, where it is shown that when the heating from the sun's side is insufficient, to increase the power of the air stream (thrust) through the burner 18, it is possible to feed in small amounts of fuel, which is set on fire (the flame is shown under the numeral 19), and the thrust is strengthened.
Thus, the proposed electric power plant allows generating electricity using non-traditional sources of energy for this, and at the same time it can be used both in industry and for domestic needs. Particularly useful is its use for powering consumers located at a distance from existing power grids, or as a means of backup power consumers.
CLAIM
1. An electric power plant comprising a unit for converting mechanical energy into electric power with an associated electric generator and a unit for converting the radiant energy of the sun into a mechanical one through a thermal one, characterized in that the second of the blocks is made in the form of a vertically installed tube of variable cross-section with an expansion in the upper and lower sections And narrowing in the middle part of the pipe, the pipe is made of two different materials docked along the longitudinal section of the tube, one of them is transparent, and the other with the inner surface with the highest degree of absorption of radiant energy, the unit for converting mechanical energy into electric is in the form of a frame with blades Wind turbine and is located in the most narrowed part of the tube with the orientation of the blades perpendicular to the axis of the tube, while the installation as a whole is installed in the place with the most favorable conditions for lighting the tube with the sun and is oriented by the transparent part towards the sun's rays.
2. The device according to claim 1, characterized in that the lower part of the pipe is overlapped with the surface of the material with the highest absorption of radiant energy, and on the lower edge side of the transparent part of the pipe, an opening is formed between the bottom and the cross-section of the tube with an inclination in the direction from The top of the opening from the side of the transparent part of the pipe down the side of the opposite part of the pipe at an angle of 30-40 °, and from the side of the top of the corner the absorbing surface is made in the form of one or several sites located approximately perpendicular to the direction of the sun's rays.
3. The device according to claim 1, characterized in that in the lower part of the pipe there is a burner for strengthening the thrust in the hours of insufficient heating by the sun's rays.
print version
Published on February 14, 2007




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.