| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2096888
![]()
Method of controlling the reactive power
AND DEVICE FOR ITS IMPLEMENTATION
Name of the inventor: Kanter I.I .; Mityashin NP .; Golembiovskiy YM .; Tomaszewski JB .; Sumaneev G.E .; Rezchikov AF
The name of the patentee: Saratov State Technical University
Address for correspondence:
Starting date of the patent: 1996.04.08
The invention relates to a converter technology and can be used for work in the distribution networks of industrial enterprises for power factor correction of loads. The inventive performance improvement and expansion of the control range of reactive power sources are provided by changing the voltage value on the storage capacitor in a controlled voltage converter. This is achieved by calculating the voltage on the capacitor that provides the desired reactive power value and its stabilization by charging and discharging the storage capacitor by independent circuits. Implementation of the method the source of reactive power by introducing a controlled rectifier and inverter driven network connected to the network through the power transformers, voltage increases enables to reduce the proportion of higher harmonics in the current waveform generated.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to a converter technology and can be used for work in the distribution networks of industrial enterprises for power factor correction of loads.
Known reactive power control method thyristor reactive power compensator (TKRM) [1] is to organize the pulse width modulation voltage to crush the charge-storage capacitor discharge process.
Known TKRM comprising a three-phase bridge thyristors with cut-off diodes and switching capacitors and feedback diodes, a storage capacitor interconnected by busses DC voltage from the phase terminals bridges are connected via switching reactors [1] Thus, due to the pulse width modulation voltage and increase frequency switching valves thyristor bridge is crushed process, the storage capacitor charge-discharge.
However, the known method and device allow to obtain an acceptable value nonsinusoidality ns coefficient K only in a narrow range of reactive power control. By increasing the range of the current control curve is sharply non-sinusoidal character and nonsinusoidality ratio is at best 30-40%
The closest to the technical nature of the invention is a method of controlling the reactive power [2] based on the change in the storage capacitor charge voltage by changing the charging current pulse width by changing the time of the switching thyristor in the controller DC (RPN), which is incorporated between the storage capacitor and the output phase rectifier.
The closest to the claimed device the technical essence is a source of reactive power (IRM) [2] containing controlled voltage converter with input reactors and the storage capacitor in the DC link current of the inverter.
The disadvantage of the known method and device is provided that are operative in the charge storage capacitor, a reactive power control over a wide range and must also ensure its operational discharge. One recharging the storage capacitor does not provide high-speed regulation of reactive power IWW, determining its narrow range. This continuous change of the reactive power can be achieved only outstripping nature.
The object of the invention is to improve the performance and expand the reactive power control range.
This object is achieved by the fact that the reactive power control method, by changing the voltage value on the storage capacitor connected to the output of the controllable voltage converter, calculate the voltage value on it, providing the required amount of reactive power, and stabilize its voltage at a calculated level, performing recharging and discharging the storage capacitor on the independent circuits.
The task is achieved by the fact that the source of reactive power, comprising a controllable voltage converter with input reactors and the storage capacitor of the DC converter according to the invention is equipped with a sensor of reactive power and voltage, a computing device for determining the voltage on the basis of providing the necessary quantities of reactive power, Compare node, two power transformers controlled rectifier and the slave inverter with a system of pulse-phase control corresponding conclusions DC rectifier and inverter voltage are connected in parallel storage capacitor and the voltage sensor, the reactive power output of the sensor forms an input of a computing device, which output is connected to a respective node input by comparison, the other input connected to the output voltage of the sensor, and the output to the input pulse-phase control system, two control outputs which are connected to a controllable rectifier and inverter driven network connected to the network through the power transformers.
It is the use of a controlled rectifier and inverter driven network, carrying out operational respectively charge and discharge the storage capacitor with the calculation of the voltage value it provides in accordance with a method of stabilizing the voltage at a calculated level corresponding to the required value of the reactive power, and thus the goal of the inventions. This leads to the conclusion that the claimed invention interconnected single inventive concept.
The figure shows a functional diagram of the IWW, which implements the method of regulation of reactive power and device for its implementation.
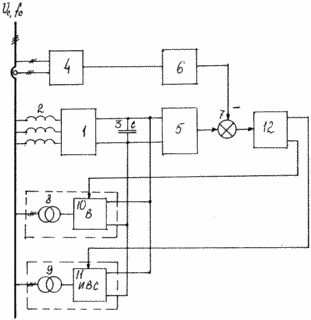 |
As a control parameter received the value of the storage capacitor voltage 3. Voltage-controlled inverter 1 with input reactor 2 by acting on the thyristor control angle provides a predetermined amount ratio non-sinusoidal current waveform. As it can be used stand-alone voltage inverter (VSI) with a reverse diode bridge. Reactive power control is performed as follows. The output of reactive power sensor 4 a signal proportional to the consumption of reactive power generated or is supplied to a computing device 6 which computes the desired value |
Third-controlled charge and discharge circuits of the storage capacitor by introducing respectively controlled rectifier and inverter driven network, improves performance, and provides a wide range of reactive power regulation.
Increased performance is due to the fact that the maximum delay in regulating the capacitor voltage does not exceed 3 1/6 of a period of the mains voltage when increasing and decreasing, respectively, by using the rectifier 10 and inverter 11 driven.
IRM comprises a controllable voltage converter 1 with the input reactors 2 and a storage capacitor 3 connected to the output controlled voltage converter 1, the sensors of reactive power 4 and 5 V, the calculating unit 6 to determine the voltage on the basis of providing the necessary quantity of reactive power, the comparison unit 7, two transformers 8, 9, 10 controlled rectifier and inverter driven 11 to 12. In this case, IFSB conclusions DC rectifier 10 and the inverter 11 are connected in parallel storage capacitor 3 and the voltage sensor 5, the reactive power output of the sensor 4 forms the input of the computing device 6, the output It is connected to the corresponding input of the comparison unit 7, the other input connected to the output voltage of the sensor 5 and the output to the input IFSB 12, two control outputs which are connected to the controlled rectifier 10 and inverter 11, driven network connected to the network through the power transformers 8 and 9 respectively.
Device operates as follows
A signal proportional to the consumed (generated) reactive power, reactive power output from the sensor 4 is supplied to the calculating unit 6. In the latter can be used as a microprocessor with the requisite peripherals or single chip computer. Value ![]() * Calculated on the basis of providing the necessary reactive power value compared to the comparison unit 7 with the signal
* Calculated on the basis of providing the necessary reactive power value compared to the comparison unit 7 with the signal ![]() Proportional to the current value of the voltage on the capacitor 3. Then IFSB 12 based on the error signal
Proportional to the current value of the voltage on the capacitor 3. Then IFSB 12 based on the error signal ![]() generates the necessary control signals are respectively controlled rectifier 10 and driven by the inverter 11.
generates the necessary control signals are respectively controlled rectifier 10 and driven by the inverter 11.
Expansion of the control range, achieved by controlling the voltage on the storage capacitor, allows an increase in the voltage to reduce the proportion of higher harmonics in the current waveform generated.
Voltage curve at the output of the inverter bridge compensator 1 may be represented ![]()
where u (k 1) (t) the instantaneous voltage of the first harmonic;
u (k s) (t) the instantaneous voltage s-th harmonic.
Turning to the complexes have.
Let the relative change in the U K compared to the mains voltage is d. Then, the first harmonic current generated in the network is 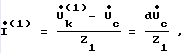
Where ![]() supply voltage;
supply voltage;
Z 1 impedance reactor on the inverter input 1.
Current s-th harmonic is 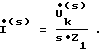
Finally a 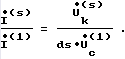
The relative content of higher harmonics in reduced times d. d mode ![]() 1 is provided with transformers 8 and 9, respectively.
1 is provided with transformers 8 and 9, respectively.
Thus, the IWW with a new way of regulation improves performance and provides a wide range of reactive power regulation.
CLAIM
1. A method for regulating the reactive power by changing the voltage level on the storage capacitor is switched to the output controlled voltage converter, characterized in that the calculated value of the voltage across it, providing necessary amount of reactive power and voltage of the storage capacitor is stabilized on a calculated level of carrying out incremental recharging or discharging capacitors of independent circuits.
2. Reactive power source voltage converter comprising a controllable reactor with inlet and a storage capacitor in the circuit current of the converter, characterized in that it is equipped with sensors of reactive power and voltage computing unit for determining the voltage based on providing the necessary reactive power values, the comparison unit , two power transformers controlled rectifier and the slave inverter with a system of pulse-phase control corresponding conclusions DC rectifier voltage and an inverter connected in parallel storage capacitor and the sensor voltage, reactive power output of the sensor forms an input of a computing device, the output of which is connected to the corresponding input of the comparison unit, other input connected to the output voltage of the sensor, and the output to the input pulse-phase control system, two control outputs which are connected to the control rectifier and inverter driven network connected to the network through the power transformers.
print version
Publication date 15.02.2007gg



 Proportional to the current value of the voltage on the capacitor 3 U C. The error signal
Proportional to the current value of the voltage on the capacitor 3 U C. The error signal 
Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.