| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2290730
![]()
DEVICE FOR PROTECTION OF ELECTRICITY CONSUMERS FROM
SHORT-TERM VOLTAGE PROCEDURES
The name of the inventor: Shpiganovich Alexander Nikolaevich (RU); Shlyakhov Nikolay Alexandrovich (RU); Zakharov Kirill Dmitrievich (RU); Zatsepin Evgeniy Petrovich (RU); Bosch Violetta Iosifovna
The name of the patent holder: Lipetsk State Technical University (LSTU)
Address for correspondence: 398600, Lipetsk, ul. Moscow, 30, LSTU, NIS
Date of commencement of the patent: 2005.05.20
The device of protection of consumers of the electric power from short-term voltage dips refers to the electrical engineering, namely to electrosupply at emergency modes of the consumers, not allowing short-term decrease in pressure. The technical result is to increase the trouble-free operation of consumers. The device assumes, in the presence of two switching devices through which the consumer is connected to two independent power sources, the introduction of reactive elements L and C into the circuit in parallel with the consumer, which, in the event of a power failure, will increase the time constant of the transient process and reduce the steepness of the voltage drop front due to the return to the network in advance Accumulated in the magnetic field of the coil and the electric field of the energy capacitor.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to electrical engineering, namely to power supply in emergency modes of consumers, which do not allow short-term voltage reduction, for example, for metallurgical enterprises.
There are known devices of fault-free power supply of the responsible consumers, including an electrical substation containing two transformers with load voltage regulation (RPN). Increasing the efficiency of electricity supply is provided, in addition to the presence of two power transformers, on-load tap-changers, the use of booster transformers or linear regulators. The main drawback of the known methods, as their long-term operation has shown, is the failure of the voltage, the duration of which is determined by the time of operation of the relay protection, automatic switching devices and switching equipment, and is on the order of 150-550 ms. This leads to the activation of the protection of electrical installations, the mismatch of devices controlling the operation of equipment, which does not correspond to the continuity of the technological process of the production of metallurgical enterprises.
The closest technical solution to the invention is a device for emergency switching to a standby power source having two switching devices through which consumers are connected to respective bus sections receiving power from two independent sources. Between the bus sections a sectional disconnector is included in such a way that the first source is reserved for consumers of the second and vice versa [1]. The disadvantage of this device is that at the time of the accident, the voltage on the consumer is up to 30-35%, and then rises to 92-94% of the nominal with a time delay of up to 0.55 s.
The aim of the invention is to ensure the reliability of power supply to the main consumers of electricity during short-term power failures by reducing the time and magnitude of the voltage failure by returning to the energy network, previously stored by reactive elements, to values sufficient for the functional power supply of the consumer until the nominal voltage level is restored.
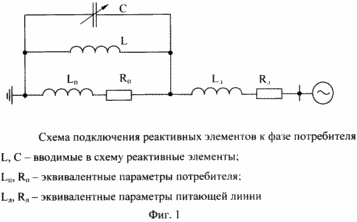 |
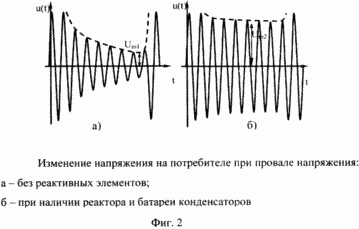 |
The claimed device, in addition to the presence of two independent power supplies and two switching devices, involves the introduction into the circuit in parallel with a consumer with an equivalent resistance R n and inductance L n of the reactor and a battery of variable capacitors (FIG. 1). The inductance of the reactor remains constant, and the battery capacity is selected so that in an emergency mode, which corresponds to a voltage drop to a level determined by the type, location and power of the short circuit in the supply network, maintain the voltage on the supply rails at a level not less than 0.9 · U N for a period equal to the voltage recovery time (FIG. 2). The main factors influencing the values of the electrical parameters of the elements are the control angle of the thyristor converters, the power of the transformer of the converter unit, the resistance of the distribution network, the engine power, its operating mode and the nature of the load. As is known, the consumer of most process units does not remain constant, but changes in time, depending on the mode of operation of the equipment and the requirements of the technological process. The values of equivalent parameters that characterize the load, and will vary depending on the technological process of production. In this case, it is necessary to change the values of the electrical parameters included in parallel with the load of the reactive elements, which is ensured by adjusting the capacity of the capacitor bank. Capacity changes according to the algorithm providing the "feeder line - consumer - reactive elements" closest to the resonant state of the electrical system. The connection scheme of the reactor and the capacitor bank is shown in Fig. 1, where R n and L n are the equivalent parameters of the consumer, R l and L l are the equivalent parameters of the supply line, L is the reactor, and C is the battery of capacitors of variable capacity. The capacitor bank acts as a controlled link in the electrical circuit. The value of the battery capacity varies depending on the process parameters.
As calculations and results of approbation showed, the values of the electrical parameters of the reactive elements necessary to reduce the voltage failures during the operation of the main equipment of steelmaking, steelmaking and sheet rolling plants lie within the limits in which, in normal operation, they allow additional compensation of the reactive power of the consumer. The parameters of the elements are chosen from the resonance condition of the voltages at the fundamental frequency. The physical essence consists in the periodic exchange of energy between the magnetic field of the inductance and the electric field of the capacitor, while the sum of the field energies and its variation in time are determined by the parameters of the reactive elements L and C. The power factor of the "feeder-consumer-reactive elements" system becomes close to unity , Which reduces electrical losses.
In the event of an accident (shutdown) of the mains, a transient process occurs in the system. The use of additional reactive elements and the adjustment of the system at the moment of switching off the resonant voltage at the fundamental frequency make it possible to increase the time constant of the circuit. At the same time, the energy stored in the magnetic field of the reactor and the electric field of the capacitor will be spent on making useful work by the technological equipment, as a result of which the slope of the voltage reduction front will decrease and the duration of the transient process will increase to values sufficient to maintain the system's operability within the voltage drop to 0 , 9 · U n (Fig. 2).
INFORMATION SOURCES
1. Knyazevsky B.A. Lipkin B.Yu. Power supply of industrial enterprises. - Moscow: Higher School, 1979, p.138-139.
CLAIM
The device protects consumers of electricity from short-term voltage dips using two independent power supplies, two switching devices through which consumers are connected to the corresponding sections of tires with independent power supplies and a sectional disconnector, characterized in that, in order to ensure the reliability of electricity supply to the main consumers of electricity, in parallel They include a battery of static capacitors and a controlled reactor, and the inductance of the reactor varies depending on the process so that the device provides a constant tuning of the "feeder-consumer-reactive system" system to the resonance mode of the main frequency voltage.
print version
Publication date 17.02.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.