| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2237334
![]()
METHOD OF INCREASING ELECTRIC ENERGY QUALITY
The name of the inventor: Mashkin AG (RU); Buglak N.Yu. (RU); Tan-Tsai VB (RU); Sapunov S.D.
The name of the patent holder: Mashkin Anatoly Gennadievich
Address for correspondence: 672039, Chita, ul. Aleksandro-Zavodskaya, 30, Chita State Technical University, Department of Intellectual Property
The effective date of the patent: 2002.11.25
The invention relates to the electric power industry and can be used to improve the quality of electrical energy in power supply systems, including power systems for electrified railways. The technical result is improvement of quality and reduction of unproductive losses of electric energy in power supply systems. The essence of the invention consists in separating the higher harmonics from the supply voltage, and the first harmonic, determined by the zero sequence voltage, obtaining from it a constant voltage and converting it into main harmonic voltage of the network and returning it to the network, thereby reducing the network asymmetry voltage and reducing the power consumption .
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the electric power industry and can be used to improve the quality of electrical energy in power supply systems, including power systems for electrified railways.
The appearance of unbalanced and non-linear loads in the network leads to deterioration in the quality of electrical energy in power supply systems, determined by the coefficient of unbalance of the voltage along the zero sequence K ou and the coefficient of nonsinusoidal K u (GOST 13109-97). Reducing these indicators is an urgent task.
A method for improving the quality of electrical energy is known, consisting in lowering the level of the higher harmonics and reducing the voltage of the asymmetry of the network; for this, a series circuit is tuned to the resonance of voltages along the 3rd harmonic and include a circuit in the network (see Markvart KG Electric supply of electrified railways. -M .: Transport, 1982, p.249-251).
The closest to the claimed is the method of improving the quality of electrical energy, consisting in reducing the level of higher harmonics and reducing the voltage of unbalanced network by tuning two groups of successive circuits to resonate voltages along the 5th and 7th harmonics and include these groups of circuits in the network (see Zhezhelenko IV, etc. The quality of electrical energy in industrial enterprises. - Kiev: Technics, 1981, p.134-135).
The main drawbacks of the known method is that, at low loads, the network voltage increases up to unacceptable values at the points of contour connection, and the fact that the decrease in the amplitudes of the higher harmonics is caused by the growth of active losses in the network due to a sharp increase in the current over those harmonics to resonance, (The resistance for these circuits sharply decreases, becoming purely active), and the electrical energy caused by the higher harmonics is irretrievably lost.
The technical result of the claimed method is to improve the quality of electrical energy, while the voltage in the network in the case of small loads does not increase and the active losses from the higher harmonics are sharply reduced.
This is achieved by the fact that in the method for improving the quality of electrical energy, which consists in decreasing the amplitudes of the voltage harmonics and reducing the asymmetry voltage, the higher voltage harmonics are extracted from the mains voltage, and the first harmonic determined by the asymmetry voltage rectifies the selected voltage harmonics, converts the rectified voltage into An alternating voltage with a frequency equal to the frequency of the first harmonic of the network, and return the alternating voltage to the electrical network.
The claimed method makes it possible to eliminate the main drawbacks inherent in the known method, namely, under the low load regime, the voltage will not increase, since the magnitude of the higher-harmonic amplitudes and the asymmetry voltage is insignificant and they will not straighten (rectifier rectifier operation in the initial sections) or the DC voltage will be Slightly in the "dead zone" of the converter and will not be converted into a variable. In the known method, the amplitudes of the higher harmonics are reduced by creating their drain circuits on the ground, and their energy is irretrievably lost as joule losses in the wires of the network, the reactor, the capacitor bank, and the ground. In the claimed method, by separating the higher harmonics and the first harmonic determined by the asymmetry of the circuit, rectifying them and converting them from a constant to an alternating voltage, and incorporating this voltage into the network, a significant portion of the energy of the harmonics listed above will return to the network.
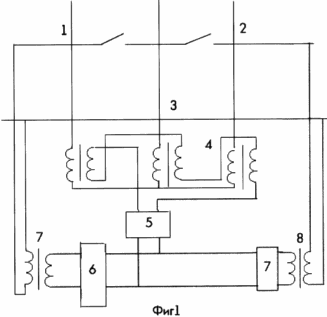
1 shows a diagram of one of the devices implementing the claimed method.
 |
 |
In Figures 1 and 2, respectively, the leading and trailing phases, 3 - the rail, 4 - the transformer whose primary winding is connected to the star, the secondary winding to the open triangle, 5 - the rectifier, 6, 7 - respectively, inverters driven by the network of the leading and Lagging phases, 8, 9 - single-phase transformers.
The method is carried out as follows. If there is no load in the contact network, there is no voltage at the output of the transformer 4, the rectifier 5, the inverters 6 and 7, thereby the voltage of the contact network does not increase in idle mode (in the known method the voltage increases). In the case of a load in phases 1 and 2, this load is usually asymmetrical and non-sinusoidal (due to a non-linear nature), this leads to the appearance of an asymmetric component of the zero sequence and higher harmonics in the voltage of the contact network, then at the output Transformer 4 there is a voltage of the first harmonic, whose amplitude is determined by the zero harmonic of the voltage of the asymmetry of the contact network, and all higher harmonics multiples of the third, this voltage rectifier 5 is converted into a constant voltage applied to the inputs of inverters 6, 7, with which the DC voltage is converted into A sinusoidal power frequency and returns to phases 1 and 2 as the fundamental harmonic energy through single-phase transformers 8 and 9.
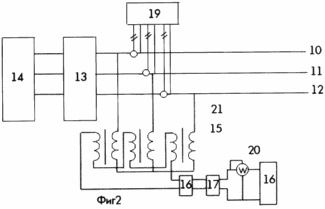
The modeling of the method was carried out according to the scheme of FIG. 2, where 10, 11, 12 are the phases of the network, 13 is the asymmetric adjustable section of the network, 14 is the non-linear adjustable load (for example, the 3-phase rectifier according to the Larionov scheme, the DC motor with a variable torque on the shaft ), 15 - 3-phase transformer with primary windings connected to the star, and secondary to the open triangle, 16 - bridge rectifier, 17 - inverter, 18 - adjustable load, 19 - power consumption analyzer and power quality meter AR.5M , 20 - the wattmeter, 21 - the switch.
The results of the simulation of the method yielded the following parameters: with the switch 21 turned off, the maximum asymmetry and nonlinearity of the model, the parameters of the quality of the electric energy were: K ou = 3.65%, K u = 18.2%, tq j = 1.02, : K ou = 0.02%, K u = 1.79%, tq j = 0.13, power in the load 18 was ~ 17% of the power consumption 13 and 14, which led to the conclusion that when implementing the claimed The method improves the quality of electrical energy and provides saving of electrical energy.
The claimed method can be implemented based on the use of known blocks in the contact network of electrified railways, as well as in power supply schemes for industrial enterprises.
CLAIM
A method for improving the quality of electrical energy, consisting in decreasing the amplitudes of the voltage harmonics and reducing the asymmetry voltage, characterized in that the higher voltage harmonics are extracted from the mains voltage, and the first harmonic determined by the asymmetry voltage rectifies the selected voltage harmonics, converts the rectified voltage by means of inverters , Driven by the leading and lagging phases of the network with load, into sinusoidal voltages with a frequency equal to the frequency of the first harmonic of the network, these voltages are returned to the respective phases of the network in the form of fundamental harmonic energy through the corresponding single-phase transformers.
print version
Date of publication 05.04.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.