| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2167211
![]()
Environmentally friendly way to recovery of precious metals
OF MATERIALS CONTAINING THEM
Name of the inventor: Vladimir Gurov
The name of the patentee: Vladimir Gurov; Yuri Dorofeev Nikanorovich; Koltsov Vasily Yurevich; Snigir Alexander
Address for correspondence:
Starting date of the patent: 2000.10.26
The invention relates to metallurgy, in particular to methods for the recovery of precious metals.
Method of extracting precious metals from materials containing them, materials include leaching solution containing chloride ions, introducing in the leaching solution of sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide productive subsequent processing solution with the extraction of precious metals and returning recycled leaching solution. Thus sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide is introduced into the leaching solution as a mixture, the mixing is performed by introducing hydrogen peroxide to sulfuric acid at a molar ratio of 2SO 4: H 2 O 2> 1, and cooling. The use of the invention reduces reagent consumption and improve environmental safety and cleanliness of the process.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to metallurgy, in particular to methods for producing the precious metals, and can be used to extract gold, silver and platinum group metals from ores, concentrates, cinders, tails, spent catalysts, electronic scrap, etc.
The method for extracting precious metals from ores, concentrates, waste and recycled solution containing ions H, Cl and NO 3, for example a solution containing 50-350 g / l and NCl 3-50% HNO 3 at a temperature of 20-110 o C . After separation of metals from the spent solution is recycled solution (DE 2418441).
The disadvantages of the method is the high consumption of nitric acid because for the efficiency of the process, it must be a high concentration, and low and environmentally friendly way in view of obtaining as waste nitrogen oxide.
Chosen as the prototype a method of extracting precious metals from materials containing them comprising treating materials circulating leach solution mixture of hydrochloric and sulfuric acid with the addition of hydrogen peroxide followed by processing productive solution ( "Rh, Pt and Pd Recovery from New and Apent Automative Catalysts" / / Wu Koo Ying et. al. Precious Metals, 1993, N 17, p. 343-349).
In this method, the addition of hydrogen peroxide to a solution of hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid will result in an increased consumption of reagents that increases the probability of formation and release of elemental (gaseous) chlorine in reducing amount of process safety and environmental purity.
Object of the invention is to reduce the consumption of reagents and increased environmental safety and cleanliness of the process.
This object is achieved by a method for the recovery of noble metals from materials containing them, comprising leaching the materials with a solution containing chloride ions, introducing in the leaching solution of sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide, subsequent processing productive solution with the extraction of precious metals, and return the processed solution leaching, sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide is introduced into the leaching solution as a mixture, the mixing is performed by introducing hydrogen peroxide to sulfuric acid at a molar ratio of H 2 SO 4: H 2 O 2> 1, and cooling.
Summary of the invention is as follows. When introduced into the leach solution containing chloride ions and sulfuric acid as cold or by heating a mixture of sulfuric and hydrochloric acid by reacting
2Cl - + H 2 SO 4 = SO 42- + 2HCl (1)
The oxidative action of hydrogen peroxide is described by half-reaction
H 2 O 2+ 2H + + 2e = 2H 2 O, (2)
the value of the standard oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) which is + 1.776 in.
Reactions dissolving noble metals such as gold and platinum, with hydrochloric acid and hydrogen peroxide will have the form
2Au + 3H 2 O 2 + 8HCl = 2HAuCl 4 + 6H 2 O (3)
Pt + 2H 2 O 2 + 6HCl = H 2 PtCl 6 + 4H 2 O (4)
In this standard AFP gold dissolution in a chloride medium (1.0 in), and platinum (0.7 in), significantly lower the ORP of hydrogen peroxide. However, the actual oxidising activity of hydrogen peroxide is shown only at high pH and significant concentrations of hydrogen peroxide and chloride ions in the solution. However, if the pre-mix hydrogen peroxide and concentrated sulfuric acid, the sulfuric acid and part of hydrogen peroxide and permonosulphuric form persulfuric acid by the reactions
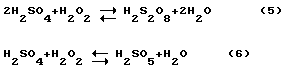
Persulfuric acid and permonosulphuric are much stronger and more active oxidants than hydrogen peroxide (ORP = 2.12 in). Reactions (5, 6), both reversible and markedly persulfuric acid and decompose at elevated temperature and dilution, as well as hydrogen peroxide. However, if a mixture of hydrogen peroxide and concentrated sulfuric acid while cooling in cook temperature range 0-30 o C and used immediately after preparation, most of the hydrogen peroxide is converted into permonosulphuric acid.
In addition, the order of mixing is set to hydrogen peroxide and sulfuric acid. If administered in sulfuric acid, hydrogen peroxide, that by mixing dilution water generated persulfuric acids and their decomposition is observed initially to hydrogen peroxide, and then to oxygen. The result will be unproductive loss of hydrogen peroxide used. If administered hydrogen peroxide in sulfuric acid, the persulfuric acid will be diluted sulfuric acid, which increases their resistance. As a result, the conversion of peroxide to persulfuric acid will be much more complete. For the same reasons, the molar concentration of sulfuric acid in the final mixture should be greater than the molar concentration of hydrogen peroxide. In other words, the finished mixture is to contain a molar excess of sulfuric acid according to reaction (6), i.e. It must be observed ratio of H 2 SO 4: H 2 O 2> 1
When introduced into the leaching solution of hydrogen peroxide in a mixture of sulfuric acid, persulfuric acid obtained decomposed, but significantly slower than hydrogen peroxide itself. Moreover, hydrogen peroxide decomposes into oxygen and water, and persulfuric acid largely decompose ozone. If oxygen under these conditions is not an oxidizing agent for the noble metal and the resulting ozone is an oxidizing agent, and a stronger and more active than hydrogen peroxide. As a result of pre-mixing hydrogen peroxide with sulfuric acid leads to the simultaneous activation and stabilization of hydrogen peroxide. The consequence of this fact is a real opportunity to maintain a significantly lower concentration of the oxidizing agent, acid and chloride ions in the leaching solution, while providing the dissolution of precious metals. As a result of reduced consumption.
AFP formation of elemental chlorine is set to 1.36 and ORP values is between noble metals and hydrogen peroxide. Half reaction formation of chlorine has the form
Cl 2+ 2e = 2Cl - (7)
Although the half-reaction of (7) it follows that the probability of formation of elemental chlorine is dependent only on the concentration of chloride ions, in fact it depends on the acidity of the solution. The fact that the elemental chlorine is hydrolyzed to form hypochlorous acid having ORP is significantly greater than that of chlorine (1.63 in), and increased acidity inhibits hydrolysis and facilitates the oxidation of chloride ions to elemental chlorine. Therefore, if the lead leaching at high acidity and the concentration of chloride ions, the probability of formation of elemental chlorine increases. Conversely, at a lower concentration of acid and chloride ions decreases this probability. Thus, the ability to maintain lower concentrations of oxidant, acid and chloride ions by adding hydrogen peroxide in a mixture reduces the probability of formation of elemental chlorine and improves process safety and environmental purity.
All the introduced hydrogen peroxide may be mixed with a portion of the entire injected sulfuric acid, when the acidity is necessary to maintain relatively high, such as platinum leaching. In this case, the other part is introduced into the sulfuric acid leach solution prior to addition of the peroxide mixture. In case of need to maintain a low pH, for example in the leaching of gold ore, all the peroxide is mixed with the sulfuric acid all input and both reactants are added to the leaching solution only in a mixture. The ratio of hydrogen peroxide and sulfuric acid can vary quite widely in admixture: depending on the concentrations of the reactants in the starting reagents, but also reduction of the acid and leachable ores and container materials. Important to and during mixing, and after a final mixture ensured molar excess of sulfuric acid. Preferably, the hydrogen peroxide contained in the source reagent in the range of 30-60%, and the sulfuric acid - in the range 92-98%. When the agitation process embodiment peroxide mixture may be dispensed directly into the leach slurry as cold or by heating. In the case of heap leaching and underground precious metal mixture of hydrogen peroxide and sulfuric acid can be added to the leaching solution before it is fed directly from the leaching of ores. The source of chloride ions in the leach solution can serve as the chlorides of alkaline and alkaline earth metals and hydrochloric acid, and aluminum chloride and other chlorides. Processing of a production solution made by traditional methods: sorption, electrolysis or cementation, with the return of working solution leaching.
According to the well-known and offers the option to carry out processing platinum-alumina catalyst with a leach solution containing aluminum chloride. The treatment was carried out under stirring on a magnetic stirrer and a temperature of 80 o C in a hermetically sealed glass vessels. The vessels were equipped with devices for dispensing reagents and exhaust through hydraulic locks filled with a solution of potassium hydroxide 200 g / l. According to an embodiment of a known concentration of the solution were: Cl - 8M, H 2 SO 4 - 2.5 M, 30% hydrogen peroxide is dosed within 1 hour a number of different calculation from 10 to 100 g per 1 kg of catalyst.
According to an embodiment of the proposed concentration were: Cl - 2M, H 2 SO 4 - 0.5M. A mixture of 30% hydrogen peroxide and 92% sulfuric acid was prepared from the calculation: 1 volume sulfuric acid and 1 volume of hydrogen peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide introduced into sulfuric acid zaholozhennoy cooling water while maintaining the mixture temperature of 15 o C. The molar concentration of sulfuric acid in the mixture was - 8.6 M, the hydrogen peroxide - 5 M, that is, the mixture contains a considerable molar excess of sulfuric acid. And the resulting mixture was dosed during 1 hour various amounts based on hydrogen peroxide of from 5 to 15 g per 1 kg of catalyst. At the end of the pulp on both treatment options were filtered out in the solutions were determined by the concentration of sulfuric acid and platinum, is used to calculate the recovery rate and the proportion of sulfuric acid. Thus in solutions of potassium hydroxide in water trap defined active chlorine and calculates the specific yield of chlorine gas during processing. The results are shown in the table.
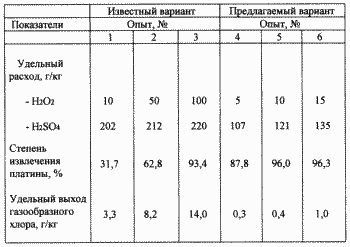
From the table it follows that the known embodiment, a high degree of extraction of 93.4% of platinum is achieved only if the specific consumption of hydrogen peroxide in 100 g / kg of catalyst and sulfuric acid 220 g / kg. In this specific yield of chlorine gas was 14 g / kg. According to an embodiment already proposed in the specific consumption of hydrogen peroxide - 10 g / kg, and sulfuric acid - 121 g / kg of 96% platinum recovered and specific yield of chlorine gas was only 0.4 g / kg. Thus, according to the proposed variant significantly reduces reagent consumption and environmental safety and cleanliness of the process increased.
CLAIM
Method of extracting precious metals from materials containing them, comprising leaching the materials with a solution containing chloride ions, introducing in the leaching solution of sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide, subsequent processing productive solution with the extraction of precious metals and returning the processed solution to the leaching, characterized in that the sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide is introduced into the leaching solution as a mixture, the mixing is performed by introducing hydrogen peroxide to sulfuric acid at a molar ratio of H 2 SO 4: H 2 O 2> 1, and cooling.
print version
Publication date 07.11.2006gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.