|
Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2088532
![]()
A METHOD FOR EXTRACTING PLATINUM AND / OR RARE FROM PROCESSED CATALYSTS
BASED ON MINERAL OXIDES
The name of the inventor: Bely A.; Zatolokina EV; N. Habibislamova; Radko DM; Duplyakin V.K.
The name of the patent holder: Omsk Branch of the Institute of Catalysis of the SB RAS
Address for correspondence:
Date of commencement of the patent: 1993.11.29
Use: extraction of precious metals from spent catalysts used in the oil refinery and petrochemical industry.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION: The pre-calcined spent catalyst is treated with a solution of hydrochloric and nitric acids with a total concentration of 0.1-1.0 mol / l and a molar ratio of 3: 1 to 7: 1 at a temperature of 70-90 ° C for 1-3 H , followed by a temperature increase of 150-300 ° C and a catalyst holding at this temperature in vapors, which are a product of evaporation of hydrochloric and nitric acids for 1-3 hours . The catalyst is then treated with hydrochloric acid at a concentration of 0.025-1.0 mol / l at 30-90 ° C for 0.5-3.0 hours .
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to methods for recovering platinum or platinum and rhenium from spent industrial catalysts used in the petroleum refining and petrochemical industries.
Various methods for the extraction of platinum or platinum and rhenium from spent catalysts are known. The essence of most of them consists in oxidation of the metal into soluble compounds with subsequent transfer to a solution, melt or gas phase.
The closest in technical essence to the present invention is a process for recovering platinum and rhenium from spent catalysts, including calcining the catalyst in a stream of air or other oxygen-containing gas at 300-500 ° C for 2-8 hours and treating with a concentrated solution ( 5.0 mol / L ) of hydrochloric acid or a mixture of hydrochloric and nitric acids at 20-90 ° C. The resulting solution is separated on columns with an ion exchanger.
A disadvantage of the known method is the strong destruction of the carrier matrix ( 30% by weight and more ), high processing costs, and large amounts of waste, processing waste.
The object of the invention is to develop an environmentally friendly process for the extraction of platinum, as well as rhenium from spent catalysts, which provides a degree of recovery of metals at a level of 99.0-99.8 wt. Reducing the consumption of raw materials and reagents, reducing waste, processing waste, storing the carrier matrix for subsequent use.
For this purpose, a method for processing catalysts is proposed by first treating them with a dilute aqueous solution containing hydrochloric and nitric acid with a total concentration of 0.1 to 1.0 mol / l and a molar ratio of 3: 1 to 7: 1 at temperatures of 70-90 o C for 1 to 3 hours , followed by an increase in the temperature of the catalyst to 150-300 ° C and holding at this temperature for 1-3 hours . The catalyst is then treated with a solution of hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 0.025-1.0 mol / l at a temperature of 30-90 ° C for 0.5-3.0 hours . The spent catalysts are calcined in air at a temperature of 400-500 ° C before removal to remove organic deposits.
Essential distinctive features of the invention are:
- Use of a dilute solution of hydrochloric and nitric acids (total concentration from 0.1 to 1.0 mol / l) with a molar ratio of 3: 1 to 7: 1 ;
- A subsequent increase in the temperature of the solution and aging of the catalyst at 150-300 ° C in vapors, which are the product of solution evaporation;
- Treatment with a solution of hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 0.025-1.7 mol / l at a temperature of 30-90 ° C.
The separation of platinum and rhenium from the hydrochloric acid solution is carried out by passing through anion-exchange columns, precipitation in the form of metals by hydrogen, precipitation in the form of sulfides with hydrogen sulfide. The complete release of metals is facilitated by the absence in the solution of large amounts of the components of catalyst carriers and other reagents used for the processing of catalysts by known methods. The invention is illustrated by the following examples. The subject of processing were monometallic ( AP series) and polymetallic (series КР ) industrial catalysts, used for oil refining and petrochemical processes. The catalysts contain from 0.1 to 0.6 wt . Platinum ( AP series), and platinum and rhenium ( CR series) on alumina-supported supports. The results are shown in Table 1. Determination of the content of platinum and rhenium in solution was carried out according to known methods.
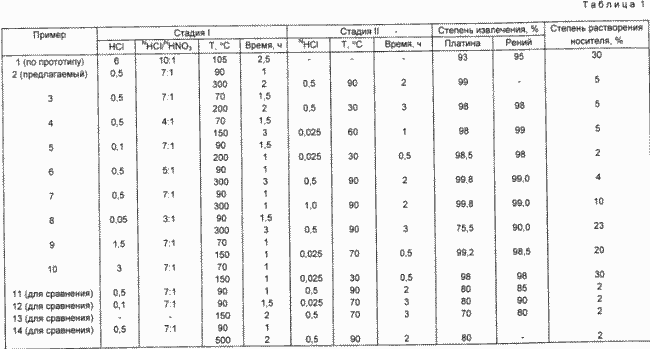
Example 1 (by prototype)
100 g of spent catalyst with a platinum content of 0.36% rhenium 0.2% pre-calcined at 500 ° C for 6 hours , treated with a solution containing 1000 ml of 6N hydrochloric acid and 50 ml of 58% nitric acid and refluxed for 2 , 5 hours
Degree of platinum recovery 93% rhenium 95% Degree of carrier dissolution 30%
Example 2 (according to the proposed method)
100 g pre-calcined at 500 ° C spent catalyst AP-64 with a platinum content of 0.6 wt . Is treated with a solution containing 77 ml of 0.5N hydrochloric acid . Hydrochloric acid and 10.5 ml of nitric acid at a temperature of 90 ° C. for 1.0 hour . Thereafter, the treated catalyst is placed in a drying oven at a temperature of 60 ° C. where it is held for 2 hours , then placed in a muffle furnace at a temperature of 300 ° C. and held at this temperature for 2 hours . After this, the catalyst is poured into 500 ml of 0.5 N HCl . Hydrochloric acid and refluxed at 90 ° C. for 2 hours . Degree of platinum recovery 99% degree of carrier dissolution 5%
Examples 3-10 are carried out under the conditions of Example 2, while varying the normality and the molar ratios of hydrochloric and nitric acids, the time and the normality of the acid for extraction.
Example 3
To treat the KR-104 catalyst with a platinum content of 0.34 wt.
Rhenium 0.2% a solution containing 77 ml of 05N hydrochloric acid is used .
Hydrochloric acid and 10.5 ml of nitric acid. The treatment time is 1.5 hours at 70 ° C and 2 hours at 200 ° C.
Extraction is carried out 0.5 N.
Solution of hydrochloric acid at a temperature of 30 ° C. for 3 hours . Degree of extraction of platinum 98% of rhenium 98% degree of dissolution of carrier 5%
Example 4
The KR-104 catalyst with a platinum content of 0.34% rhenium 0.2% is treated with a solution containing 72 ml of 0.5N H2O .
Hydrochloric acid and 18 ml of 0.5N hydrochloric acid .
Nitric acid at a temperature of 70 ° C for 1.5 hours . In the muffle, the catalyst is held for 3 hours at 150 ° C. for 1 hour . The results are obtained: the degree of extraction of platinum 98% of rhenium 99% degree of dissolution of the carrier 5%
Example 5
The KR-104 catalyst is treated with a 0.34% rhenium platinum content of 0.2% using a solution containing 77 ml of 0.1 N HCl.
Hydrochloric acid and 10.5 ml of 0.1N hydrochloric acid.
Nitric acid. The treatment time is 1.5 hours at a temperature of 90 ° C , soak in a muffle for 1 hour at a temperature of 200 ° C.
The extraction was carried out at 0.025N .
Solution of hydrochloric acid at a temperature of 30 ° C for 0.5 hour . Extraction rate for platinum 98.5% rhenium 98.0% degree of dissolution of carrier 2%
Example 6
The KR-104 catalyst is treated with a 0.34% rhenium 0.2% platinum content using a solution containing 73 ml of 0.5N H2O .
Hydrochloric acid and 14.6 ml of 0.5N hydrochloric acid.
Nitric acid. The treatment temperature was 90 ° C. for 1 hour , held in a muffle of 300 ° C. for 3 hours. The extraction was carried out with 0.5 N HCl . Solution of hydrochloric acid at a temperature of 90 ° C. for 2 hours . The degree of extraction of platinum 99.8% of rhenium 99.0% The degree of dissolution of the carrier 4%
Example 7
The catalyst KR-104 is treated. A solution containing 77 ml of 0.5N hydrochloric acid was used. And 10.5 ml of 0.5N hydrochloric acid.
Nitric acid, treatment temperature 90 ° C. for 1 hour , soak in a muffle at 300 ° C. for 1 hour . The extraction was carried out 1.0N.
Solution of hydrochloric acid at a temperature of 90 ° C. for 2 hours . Extraction rate of platinum 99.8% rhenium 99.0% degree of dissolution of carrier 10%
Example 8
The catalyst KR-110 with a platinum content of 0.34% rhenium 0.21%, which is treated with a solution containing 66 ml of 0.05 N , is treated .
Hydrochloric acid and 22 ml of 0.05N.
Nitric acid at a temperature of 90 ° C for 1.5 hours . Holding in a muffle at 90 ° C for 1.5 hours . Degree of platinum recovery 75.5% rhenium 90.0% degree of dissolution of carrier 2%
Example 9
The catalyst KR-110 is treated with a solution containing 77.0 ml of 1.5N . Hydrochloric acid and 10.8 ml of 1.5N hydrochloric acid.
Nitric acid at a temperature of 70 ° C for 1 hour , holding in a muffle at 150 ° C for 1 hour . The metals are extracted with 0.025N .
Solution of hydrochloric acid at 70 ° C for 0.5 h . Extraction rate of platinum 99.2% of rhenium 98.5% degree of dissolution of carrier 20%
Example 10
The KR-104 catalyst with a 0.34% rhenium platinum content of 0.2% was treated with a solution containing 77 ml of 3N hydrochloric acid.
Hydrochloric acid and 10.8 ml of 3N hydrochloric acid.
Nitric acid at a temperature of 70 ° C. for 1 hour , holding in a muffle at 150 ° C. for 1 hour . Extraction is carried out at 0.025N .
Solution of hydrochloric acid at a temperature of 30 ° C for 0.5 hour . Extraction rate of platinum 98% of rhenium 98% degree of dissolution of carrier 30%
Example 11 (for comparison)
100 g of KP-110 catalyst, pre-calcined at 400 ° C , is treated with a solution containing 77 ml of 0.5 N HCl.
And 10.8 ml of 0.5N hydrochloric acid.
Nitric acid at a temperature of 90 ° C for 1 hour . The metals are extracted with 0.5N HCl.
Hydrochloric acid at a temperature of 90 ° C. for 1 hour . Extent of extraction of platinum 80% of rhenium 85% degree of destruction of the carrier 2%
Example 12 (for comparison)
Carry out under the conditions of Example 11 , but use a solution containing 77 ml of 0.1N hydrochloric acid.
Hydrochloric acid and 10.9 ml of 0.1N hydrochloric acid.
Nitric acid. The treatment is carried out at a temperature of 90 ° C for 1.5 hours . Extraction is carried out at 0.025N .
Hydrochloric acid at a temperature of 70 ° C. for 3 hours . Extraction rate of platinum 80% of rhenium 90% degree of dissolution of carrier 2%
Example 13 (for comparison)
It is carried out under the conditions of Example 12 , but the stage of treatment with a dilute solution of hydrochloric and nitric acids is excluded, and the catalyst is held in a muffle at a temperature of 150 ° C. for 2 hours . The extraction was carried out with 0.5N HCl.
Solution of hydrochloric acid at a temperature of 70 ° C. for 3 hours . Extraction rate of platinum 70% rhenium 80% degree of destruction of the carrier 2%
Example 14 (for comparison)
It is carried out under the conditions of Example 2 , but the catalyst is kept in the muffle at a temperature of 500 ° C. for 2 hours . The degree of extraction of platinum 80% degree of destruction of the carrier 2%
As can be seen from the presented data, the proposed method has the following advantages:
- The degree of metal recovery is 99.0- 99.8% by weight.
- Provides a significant reduction in the costs of raw materials and reagents;
- Provides a reduction in waste and sewage processing ( Table 2 );
- Ensures the storage of the carrier matrix for subsequent use.
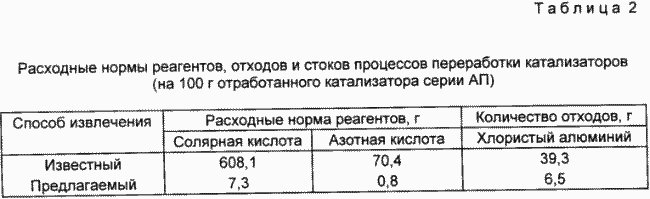
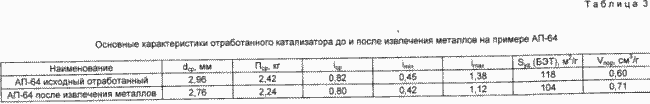
The possibility of reusing the carrier matrix is one of the significant technological results. In Table. 3 shows the basic texture characteristics and adsorption properties of the catalyst after the removal of the plate and rhenium. From Table. 3 it can be seen that, according to its basic characteristics, the spent catalyst carrier meets the requirements of the technical specifications for the quality indicators of aluminum oxide used as a gas dryer. For these reasons, the catalyst support can be used as a commercial product.
CLAIM
A method for recovering platinum and / or rhenium from spent catalysts based on mineral oxides, comprising calcining the catalyst, treating it with an aqueous solution of hydrochloric and nitric acids at 70-90 ° C , characterized in that the treatment is carried out with a solution of hydrochloric and nitric acids with a total concentration of 0.1 -1.0 mol / l and a molar ratio of 3: 1 to 7: 1 , after which the temperature is increased and the catalyst is maintained in the vapor, which is the evaporation product of hydrochloric and nitric acids at 150-300 ° C , and then treated with a solution of hydrochloric acid with With a concentration of 0.025-1.0 mol / l at 30-90 ° C.
The process according to claim 1, characterized in that the catalyst is kept in the vapor, which is a product of evaporation of hydrochloric and nitric acids at 150-300 ° C , for 1 3 hours .
The method according to claim 1, characterized in that the treatment with a solution of hydrochloric acid is carried out for 0.5-3.0 hours .
print version
Date of publication 07.11.2006гг




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.