| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2277599
![]()
METHOD extract silver from waste sorbents containing iodine-129
Name of the inventor: Equal Sergey Ivanovich (RU); Pyatin Nikolai Petrovich (RU); Istomin Igor
The name of the patentee: Federal State Unitary Enterprise "Production Association" Mayak "
Address for correspondence: 456780, Chelyabinsk Region, Ozersk, Lenina, 31, FSUE "PO" Mayak ", TVE..
Starting date of the patent: 2004.05.26
The invention relates to the field of recycling and disposal of radioactive solid waste reprocessing nuclear industry, in particular to a method for immobilizing Iodine-129 and silver recovery from spent sorbents which can be used for producing iodine absorber. Silver-treated sorbent heated to 75-80 ° C with an alkaline solution of hydrazine nitrate with a concentration of alkali of 30 to 100 g / l of hydrazine and - from 15 to 50 g / l. The solution was kept for at least 60 minutes and poured into a separate container for the concentration of iodine-129 has. Washing was performed with water sorbent. sorbent was then treated with nitric acid with a concentration from 3 to 10 mol / L, warmed to 80 ° C for 30 minutes. The technical result is the re-use of silver from the spent sorbent and increase the life of the unit iodine treatment in the processing of irradiated nuclear fuel with minimal cost.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of recycling and disposal of radioactive solid waste reprocessing nuclear industry, namely to a method for immobilizing Iodine-129 and silver recovery from spent sorbents which can be used for producing iodine absorber.
Production process for the processing of irradiated nuclear fuel (SNF) power reactors and transport systems are inextricably linked to gas-aerosol cleaning waste from the long-lived iodine-129 (T 1/2 = 1,57 · 10 7 years). The sorbent used for the recovery thereof, for example, the active gamma alumina impregnated with silver nitrate. During operation associated with the silver and partly iodine with chlorine and fluorine. Thus, in industrial waste sorbent to 70% of silver associated with iodine (iodine-127, 129). The remainder of the silver is mainly as fluoride and chloride, and in the form of nitrate.
After several cycles of regeneration sorbent destroyed and much of it turns into dust-like fraction, which excludes its further use in gas and aerosol waste treatment technology [I.A.Istomin. Development and implementation of treatment technologies with iodine-129 in the processing of irradiated nuclear fuel from power reactors. Thesis for scientific degree of candidate of technical sciences. - Ozersk, FSUE "PO" Mayak "-. 2003 C - 105].
Given the fact that silver is in short supply and expensive reagent, there is the need to develop methods to extract silver from spent "silver" filters containing iodine-129, for the purpose of using it to prepare the new filter material.
Regeneration method known solid iodine filter containing silver iodide, silver iodate, physically adsorbed molecular iodine by [GB 2390219 A (IPC G 21 F 9/30, publ. 31.12.2003)], in which is provided a method to extract silver from spent sorbent, iodine-129 containing. The essence of the method consists in bringing the solid filter into contact with an aqueous solution of a reducing agent selected from hydroxylamine, hydroxylamine salts, ascorbic acid, salts of ascorbic acid, ascorbyl esters, sodium borohydride, sodium hypophosphite, formaldehyde, urea, formic acid and salts thereof for the desorption of iodine a filter and dissolved in an aqueous solution. Silver extraction is carried out by immersing the filter containing reduced silver in nitric acid solution having a concentration of from two to six moles per liter.
The distinguishing features of the invention as compared to the closest analogue are as follows.
1. The use in the removal of the spent sorbent radioiodine as a reducing alkali solution of hydrazine nitrate.
2. Increased nitric acid concentration range up to 10 mol / l in the process of recovery of silver from spent sorbent.
The technical result of the invention is to simplify the operation and optimization of iodine sorbent by reusing technical silver obtained in the form of silver nitrate solution, suitable for the manufacture of a new sorbent.
Technical result is achieved by way of silver recovery from spent sorbents containing iodine-129, comprising the reduction of silver to its transfer to the metallic state by treatment with an alkaline agent solution, washing with water sorbent processing sorbent containing metallic silver with nitric acid, which according to the invention, the silver recovery are alkali solution of hydrazine nitrate, hydrazine at a concentration of 15-50 g / l and alkali 30-100 g / l during at least 60 minutes at a temperature of 75-80 ° C, processing sorbent containing metallic silver with nitric acid is carried out with a concentration of 3 -10 mol / l, warmed to 80 ° C for 30 minutes.
Implementation of the proposed method consists of the following steps
1. The spent sorbent containing iodine-129, treated with alkaline solution, hydrazine nitrate with a concentration of alkali of from 30 to 100 g / l and hydrazine - from 15 to 50 g / l at a temperature of from 75 to 80 ° C and the duration of the process does not less than 60 minutes to convert all the silver to the metallic state.
2. The sorbent was washed with water to remove traces of hydrazine and alkali.
3. The device containing the washed sorbent is poured preheated to 80 ° C with a nitric acid concentration of 3 to 10 mol / l. The system is maintained for 30 minutes after which the solution is discharged to a separate tank. The basis of the sorbent is washed with water to remove residues of silver. The solutions were combined and used for the manufacture of a sorbent by impregnating a new framework.
example 1
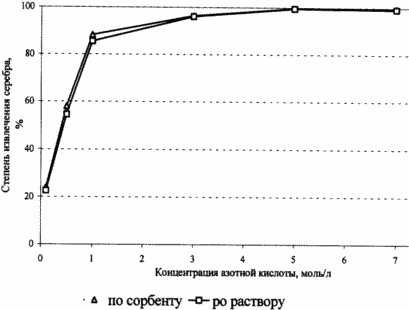
Several batches of sorbent containing metallic silver were treated with a solution of nitric acid with a concentration of from 0.1 to 7.0 mol / l at 80 ° C for 30 minutes. The degree of extraction of silver was determined as a residual content in the sorbent, and on its concentration in the solution. The dependence of the degree of the sorbent to extract silver from a nitric acid concentration is given in FIG. As can be seen the maximum extraction efficiency of silver ions in solution is observed in the range of nitric acid concentrations of 3 mol / l and above.
example 2
Several portions of the silver-containing sorbent (pellets as cylinders d = 3 to 5 mm and h = 10 to 15 mm) based on alumina containing sparingly soluble silver compound (AgI, AgCl, AgF) was treated with pre-heated to 80 ° C caustic hydrazine nitrate solution with a concentration of alkali of 30 g / l of hydrazine and 15 g / l for at least 60 minutes. After the extraction process iodine adsorbent was washed with distilled water until neutral reaction of wash solution, dried and weighed. The solutions were formed during regeneration (regenerates and flushing) were analyzed for their content of iodine. Results of iodine removal from the sorbent are shown in Table 1.
| Table 1 Extraction of iodine from waste sorbent | ||||
| Room experience | Mass sorbent mg | The mass of iodine in solution, mg | Efficiency of extraction of iodine,% | |
| to iodine extraction | after extraction of iodine | |||
| 1 | 4952 | 4642 | 310 | 98.1 |
| 2 | 4926 | 4628 | 298 | 98.7 |
| 3 | 4946 | 4649 | 294 | 98.9 |
| 4 | 5047 | 4762 | 312 | 99.1 |
| 5 | 4960 | 4667 | 299 | 97.4 |
| 6 | 4993 | 4697 | 315 | 96.9 |
| 7 | 5030 | 4735 | 321 | 97.3 |
| 8 | 4985 | 4698 | 309 | 97.2 |
| 9 | 4953 | 4674 | 307 | 99.4 |
| 10 | 5000 | 4711 | 305 | 97.1 |
| Average | 4979,2 ± 27,5 | 4b87,2 ± 29.5 | 292,0 ± 4,8 | 98,0 ± 0,7 |
It was further carried out the extraction of silver from the sorbent. Samples of the sorbent treated with nitric acid with a concentration of 5 mol / L for 30 minutes at 80 ° C. After the process of uterine and washes were analyzed for content of silver. Experimental results are presented in Table 2.
| table 2 Extract from the sorbent silver | ||||
| Room experience | Mass sorbent mg | The weight of silver in solution, mg | The efficiency of extraction of silver,% | |
| Before extracting Ag | After removing the Ag | |||
| 1 | 4642 | 4322 | 321 | 98.8 |
| 2 | 4628 | 4310 | 318 | 98.2 |
| 3 | 4649 | 4334 | 316 | 97.1 |
| 4 | 4762 | 4440 | 321 | 96.3 |
| 5 | 4667 | 4343 | 322 | 98.5 |
| 6 | 4697 | 4377 | 318 | 96.7 |
| 7 | 4735 | 4410 | 320 | 96.5 |
| 8 | 4698 | 4382 | 317 | 96.4 |
| 9 | 4674 | 4360 | 324 | 99.0 |
| 10 | 4711 | 4391 | 322 | 97.6 |
| Average | 97,4 ± 0,6 | |||
Thus, the efficiency of silver recovery from all portions of the sorbent was (97,4 ± 0,6)%.
 |
The advantage of the proposed method is an integrated approach to the issue of disposal of the sorbent saturated with iodine-129, in which is possible after completion of the use of the sorbent to remove him from the radioactive iodine for its subsequent disposal with subsequent extraction of silver for its further use (production of a new sorbent). Application of a chemical agent (nitric acid) to extract silver, and a decrease in nitric acid concentration provides a solution of silver nitrate, suitable for re-use it in the processing technology of irradiated nuclear fuel. |
CLAIM
Method of recovering silver from spent sorbents containing iodine-129, comprising reducing the silver with its transfer to the metallic state by treatment with an alkaline agent solution, washing the adsorbent with water and processing of the sorbent containing metallic silver with nitric acid, characterized in that the reduction of silver are alkali solution of hydrazine -nitrata with hydrazine concentration of 15-50 g / l and alkali 30-100 g / l during at least 60 minutes at a temperature of 75-80 ° C, processing sorbent containing metallic silver with nitric acid is carried out with a concentration of 3.10 mol / l, heated to 80 ° C for 30 min.
print version
Publication date 14.03.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.