| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2078152
![]()
FOTOLIZER to decompose water
Name of the inventor: Mishin Alexander
The name of the patentee: Mishin Alexander
Address for correspondence:
Starting date of the patent: 1992.04.24
Use: the decomposition of water into hydrogen and oxygen. The inventive fotolizer comprises a cell with a lens membrane made two-layer catalyst in the form of a truncated cone facing smaller base to the lens from the lens diaphragm is formed as a cathode plate and the opposite side - in the form of an anode made of hafnium, the anode and the cathode are welded together, and their surface layers are dispersed.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to a device for the decomposition of water into hydrogen and oxygen and may be used in devices for detecting infrared radiation sources (II). Known semiconductor photocatalytic systems combine electrical properties of solar cells and a device for electrolysis of water.
Such apparatus comprises an electrolyte, a semiconductor photoanode, a metal cathode. Light energy is converted into electricity by the internal photoelectric effect. It uses the visible part of the solar spectrum with an efficiency of up to 1.5% photoanode masloustoychiv in acid-alkaline environments, as corrodes.
The closest to the claimed device is a device for photolysis of water, comprising a cell filled with a solution of NaOH, divided into an anode and a cathode compartment equipped with an anode of the semiconductor photocatalyst "P" type nickel electrode and coated nickel monoxide. Instead of nickel can be used a platinum cathode.
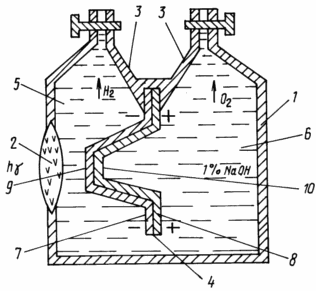 |
FIG. 1 shows a cross-section of fotolizera decomposition of water. Fotolizer mounted in the housing 1 with a transparent window for infrared radiation with biconvex fluorite lens 2 and filled with 1% sodium hydroxide. The upper part of the body is made in the form of overturned funnels with cranes for Evolved Gas 3: O 2 and H 2. The electrolyte membrane is divided catalyst 4 to the cathode 5 and the anode portion 6. The diaphragm portion is made of four plates welded together: platinum cathode 7 side and the anode side hafnium 8. Membrane 4 has the shape of a truncated cone whose apex is cut off as close to 9 fluorite lens 2 for reducing the thickness of the aqueous electrolyte solution as water absorbs almost all of the infrared spectrum. Cut the top of the cone 9 is covered with a layer of platinum dispersed, while the opposite side 10 is covered with a layer of hafnium dispersed. |
Electrochemical closed circuit of two inert metal is soldered greatest external contact potential difference of 1% alkaline electrolyte. Infrared light is irradiated towards a negatively charged redox cathode catalyst portion formed of platinum. Catalytic membrane surface must have a "tip" or needle "mustache" obtained in the process of recovery of metal oxides with hydrogen or by electrolytic deposition of, for example platinized plate gafnirovanny hafnium. In the case of a minor shock of the positive potential of the voltage at the point of increase of more than 30,000 volts / cm, and an electron runoff. This field emission or non-self-discharge in the presence of an external "ionizer" infrared radiation. Catalytic membrane has energy in the form of contact potential difference (IF) and establishes electrical contact between the layers of hydrated oppositely charged ion, the cathode and anode in the form of two series-connected capacitors.
![]()
Infrared radiation / and. and. / digidratiruemymi absorbed by molecules of water and creates the ion potential difference plates 2, 2B, causing potential drop between the capacitor plates in the tens of millions of volts / cm. There is a cold emission of electrons from the cathode to the positive ion and a negative ion discharge at the anode.
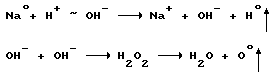
Externally, the unmodified catalyst ![]() changes in synchronism with the frequency of its infrared (IF) of 1.8 to "0" and in the electron work function of Pt from 5.3 V to 4.4 V, Hf of from 3.5 to 4.4 B and transfers an electron from a negative to a positive ion.
changes in synchronism with the frequency of its infrared (IF) of 1.8 to "0" and in the electron work function of Pt from 5.3 V to 4.4 V, Hf of from 3.5 to 4.4 B and transfers an electron from a negative to a positive ion.
Analogs of the invention operate on a semiconductor photoanode and formed in the inventive device, the electron-hole current decomposes water. Their efficiency and 1.5% in 30% fotolizera
CLAIM
Fotolizer for decomposition of water containing a cell with the lens separated membrane on the anode and cathode spaces respectively with the anode and the cathode, and pipes oxygen O and hydrogen, the light source, wherein the membrane is a bilayer catalyst frustoconical facing smaller base to lens from the lens diaphragm is formed as a platinum cathode and the opposite side of the anode in the form of hafnium, with an anode and a cathode are welded to each other, and their surface layers are dispersed.
print version
Publication date 27.02.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.