| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2283899
![]()
METHOD FOR MOLECULAR HYDROGEN
Name of the inventor: Adam Gregory E. (RU); Goldobin Igor Stepanovich (RU); Grebennikov Evgeny Petrovich (RU); Devyatkov Alexander G. (RU)
The name of the patentee: Adam Gregory E. (RU); Goldobin Igor Stepanovich (RU); Grebennikov Evgeny Petrovich (RU); Devyatkov Alexander G. (RU)
Address for correspondence:. 103009, Moscow, Middle Kislovskiy Lane, 7/10, kv.26, AS Popov, reg. number 694
Starting date of the patent: 2005.05.31
The invention relates to the field of electrochemistry, and can be used to produce molecular hydrogen by electrolysis of water by the energy of sunlight without an external source of electric current. A method of producing molecular hydrogen involves the decomposition of water by passing an electric current between placed in water electrodes at combination of the conductor and the continuous light, sunlight one electrode, which is in the form of a porous permeable to hydrogen conductive substrate coated with a film oriented in one direction of purple membrane containing bacteriorhodopsin molecules that carry targeting of hydrogen ions - protons. The invention allows to create a technologically simple, environmentally friendly and safe method of producing hydrogen.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of electrochemistry, and can be used to produce molecular hydrogen by electrolysis of water by the energy of sunlight without an external source of electric current.
The prior art discloses a method for producing hydrogen decomposition of water by an electric current when subjected to submerged electrodes from an external power source DC voltage higher than the electrochemical potential expansion (Chemical Encyclopedia, ed., "Soviet Encyclopedia", Moscow, 1998, article "Hydrogen "" hydrogen "section). As a result of electrolysis the recovered hydrogen is released at the cathode and the anode - oxygen.
The disadvantage of this method is the necessity of using an electrolyte, for example a concentrated aqueous KOH solution, the electrolysis process flow at high pressure and the presence of externally applied electric source.
The invention is directed to a technologically simple, environmentally friendly and safe method of producing hydrogen using sunlight energy without an external source of electric current.
The solution of this problem is provided by the fact that the method of producing the molecular hydrogen by decomposing water with an electric current between placed in water the electrodes according to the invention an electric current is generated between the electrodes when the connection of the conductor and the continuous light, sunlight one electrode, which is in the form of a porous permeable hydrogen conductive substrate coated with a film oriented in one direction of purple membrane containing bacteriorhodopsin molecules that carry targeting hydrogen - ion proton.
The ability to produce molecular hydrogen by the claimed "bioelektroliza" water without external electric power source due to the basic property of bacteriorhodopsin - the light-sensitive protein halobacteria Halobacterium salenarium, in cell membranes called purple membranes where it is incorporated, to carry out directional proton transfer - hydrogen ions - from the inside out on endoplasmic side of the purple membrane during natural photocycle under the influence of sunlight energy.
The drawing schematically shows a general view of the installation for realization of the claimed method.
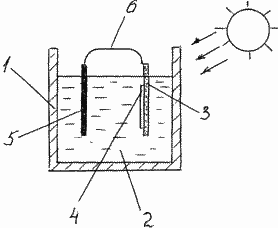 |
Apparatus for producing molecular hydrogen by decomposing water comprises an electrochemical cell 1 of transparent material such as glass filled with water 2, in which the submerged electrode 3 made of a porous permeable to hydrogen conductive substrate (e.g., a porous platinum plate or a glass substrate coated with a layer of tin oxide doped oxide indium) coated with a film 4 are oriented in one direction of purple membrane containing bacteriorhodopsin molecules and the electrode 5 arranged in the form of platinum or nickel plate, the electrodes 3 and 5 are interconnected by an external conductor 6 . The orientation of purple membrane and respectively bacteriorhodopsin molecules which are orderly arranged relative to each other in a two-dimensional crystal structure of the latter in the same direction, namely to the endoplasmic side surface conductive electrode substrate 3 can be carried out, for example by electrophoretic deposition. For oriented film purple membrane suspension is an aqueous bacteriorhodopsin D96N strain with a concentration of 3 mg / ml. |
A method of producing molecular hydrogen by decomposing water as follows.
When illuminated by sunlight deposited on a porous conductive substrate electrode 3 film 4 oriented purple membrane and accordingly bacteriorhodopsin molecules in the process of natural photocycle under the action of light energy in the absorption band of the ground state of the half-width of 130 nm with a maximum at 570 nm photochromic protein bacteriorhodopsin begins to implement targeting of hydrogen ions - protons - from the inside outwards on the side of the endoplasmic purple membrane, resulting in the accumulation of ions at the electrode 3 and between the two submerged electrodes 3 and 5, a potential difference. With the closure of the conductor 6 of the electrodes 3 and 5 between them in water 2 electric current flows and there are processes of electrochemical reduction - oxidation with allocation on a porous conductive electrode substrate 3 of hydrogen and oxygen, respectively, on the electrode 5.
Thus, the inventive method allows the production of hydrogen by electrolysis of water by solar energy without an external source of electric current, with the bacteriorhodopsin - an environmentally friendly material that does not require maintenance and replacement during operation, resulting in simple and reliable method.
CLAIM
A method of producing molecular hydrogen by decomposing water with an electric current between placed in water the electrodes, characterized in that electric current occurs between the electrodes when the connection of the conductor and the continuous light, sunlight one electrode, which is in the form of a porous permeable to hydrogen conductive substrate, oriented film coated on one side of purple membrane containing bacteriorhodopsin molecules that carry targeting hydrogen - ion proton.
print version
Publication date 23.11.2006gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.