| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2006526
![]()
Electrolyzer to produce a mixture of oxygen and hydrogen
Name of the inventor: Matafonov AG
The name of the patentee: Association "Ecology and charity" ( "ECOM")
Address for correspondence:
Starting date of the patent: 1991.06.03
The invention relates to electrochemistry, in particular to a device for the electrolytic production of oxygen-hydrogen mixture - detonating gas which, when used for combustion flame technologies in a number of industries. The new design is that the steel electrodes are made in the form of discs with an annular groove, each of which has at the top a cutout in the form of a sector or one of the sides of the disc in the upper half coated with alkali-resistant insulation, which is preferable because of better heat dissipation. The electrodes are located between the front and rear boards are separated by a dielectric spacers. The front plate formed of transparent dielectric deposited scale to determine the level of electrolyte and the current regulation by rotating electrolyzer around its longitudinal axis on a stationary base.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the construction of the apparatus the electrolytic production of hydrogen-oxygen mixture by the electrolysis of water and aqueous solution which is formed during combustion of the explosive mixture gas flame used for flame technologies in a number of industries.
As a prototype selected electrolyzer structure consisting of electrodes provided in the trough-shaped with one side facing cavities where dielectric spacers mounted on the perimeter of the depressions.
The disadvantage of the known electrolysis cells is much complexity electrode design is not providing power regulation unit, large dimensions and weight.
The aim of the invention is to simplify the structure of the electrodes, providing power control capabilities of the cell with significant compactness and reliability, t. E. The portability of the device.
This object is achieved in that in an electrolytic cell consisting of electrodes separated by dielectric spacers, electrodes are formed as steel disks with annular grooves, each of which in its upper part has a cutout in the form of a sector or one side coated alkali-resistant insulator that It allows for the entire cell is rotated about the longitudinal axis to change the contact area with the electrolyte, thus control the power machine.
 |
 |
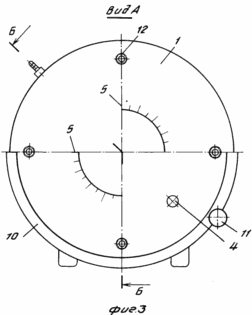 |
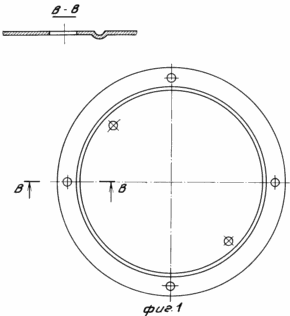
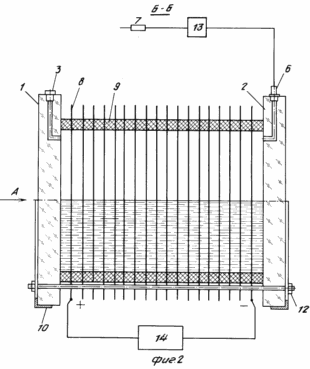
FIG. 1 shows the proposed structure of the electrode; FIG. 2 - a cell for producing hydrogen and oxygen mixture gas, longitudinal section; FIG. 3 - view along arrow A in Fig. 2. The cell comprises a board made of a transparent dielectric disk. The front plate is set in aspic 1 3 4 and the drain plug, and 5, and applied scale to determine the level of the electrolyte and power control. The back plate 2 is set fitting 6 through which the gas mixture exits and enters the burner 7. Electrodes 8 are made of steel plate disks with annular grooves in each of which the upper part has a sector cut-out on one side or coated with alkali-resistant insulator. The electrodes are located between the front and rear boards are separated by a dielectric spacers 9, forming a sealed container. The cell is mounted on a stationary base 10 and can rotate it about its longitudinal axis by a shaft 11 is frictionally connected with the boards of the cell. The board and all the electrode plates have holes for the tie rods 12. The burner is fitted with a rubber balloon filled with water, to extinguish the flame. Before burner installed water gate 13, provided with two non-return valves through which the gas is bubbled. For operation of the cell using a constant current source 14 with the necessary voltage. |
Experimental studies carried out with the claimed device cutting metal with the following parameters. Circular electrodes with annular recesses made of mild steel with a thickness of 0.3-0.5 mm, a diameter of 192 mm. The number of electrodes 112 pcs. The thickness of the rubber ring gaskets 6 mm. The 22% is used as the electrolyte, ie. E. Normal aqueous NaOH solution. Test voltage of the power supply of 220 V. The highest direct current - 13 A, the lowest - 2 A. Maximum power consumption of 2.86 kW. The lowest power consumption of 0.44 kW. The diameter of the burner nozzle, used in stainless steel cutting 1.2 mm. The flame obtained with a current of 6-8 A, allows cutting of stainless steel 3 mm thick. Weight of 6.0 kg. Dimensions: diameter 240 mm, length 700 mm.
Experimental work conducted with the electrolytic cutting and welding low carbon and high-alloy steels, the results are positive, ie. E. Available as welding and cutting steel sheet with a thickness of 0.1 to 6.0 mm.
The unit is environmentally friendly, since the combustion of detonating gas generated superheated steam. Burner nozzle diameter of 0.1 to 1.5 mm. The device is virtually fireproof, t. To. The water seal reliably separates the lighted torch from the electrolytic tank. Due to the rotation around the longitudinal axis of the cell capacity is infinitely adjustable, allowing you to choose the desired mode of combustion. Electrodes made of steel plates in the form of discs, are simple to manufacture, and provide a portable apparatus with considerable reliability and compactness.
The device operates as follows. Electric power is supplied from the battery or other DC source. The electrolyte is an aqueous alkaline solution NaOH. In aqueous solution, except in the electrolysis of electrolyte ions Na + and OH - ions exist, which are products of water dissociation of H + and OH -. In the electric field of hydrogen ions move to the cathode, and the ions OH - -.. The anode, ie, the cathode is discharged as the electrolyte cations and hydrogen cations. On inert electrodes in the electrolysis of aqueous solutions of alkali electrochemical reduction of water occurs with evolution of hydrogen and the electrochemical oxidation of water to produce oxygen.
In an alkaline environment, the equation is as follows: 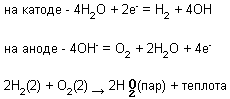
Released during the reaction of hydrogen with oxygen, heat is used to heat the metal in welding and cutting.
The most important conditions of electrolysis include the composition of the solution, temperature and current density. Current density is the ratio of current to the working electrode area. According to the invention, the electrodes are in the upper portion of the disk sectorial notch or alkali-resistant coating with improved insulator heat sink. Availability sectoral recess or coatings allow when turning the entire cell about the longitudinal axis to change the contact area with the electrolyte, thus changing the current. Power control apparatus on a scale marked on the front plate of the cell. Selection of the working area of the electrodes, current, electrolyte composition determined by calculation and experiment depending on the application - welding or metal cutting different thicknesses and properties of the steel.
The proposed electrolyzer advantageously differs from the known as continuous adjustment of current value of the surface area of the electrodes creates an ease of operation and high performance of the cell. (56) Author's certificate USSR N 1023001, cl. With 25 1/04 in 1983.
CLAIM
Electrolyzer to produce a mixture of oxygen and hydrogen, including end plates between which are placed electrodes strapped fasteners vent device, the electrolyte feed pipe, dielectric spacers that separate the electrodes, characterized in that, in order to enable controlling the amount of the mixture, the cell is provided with a shaft and rotatably mounted, the electrodes are in the form of disks, each of which is provided with a cutout in the form of a sector or at each of the electrodes is coated with an insulator in the form schelochnoupornogo sector.
print version
Publication date 26.02.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.