| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2203215
![]()
METHOD FOR PRODUCING A hydrogen rich gas
Name of the inventor: NIELSEN Poul Erik Heylund (DK); Lerman Peter (DK); Blom Nils Ergen (DK)
The name of the patentee: Haldor TOPSЁE A / S (DK)
Address for correspondence: 103064, Moscow, ul. Kazakova, 16, NIIR-Office, "Patent attorneys Kvashnin, Sapelnikov and partners", pat.pov. V.P.Kvashninu, Identification No 0004
Starting date of the patent: 1996.07.19
The invention relates to the production of hydrogen-containing gas from hydrocarbons, more particularly, to a method for producing a hydrogen-rich gas from the DME. A method for producing a hydrogen rich gas comprises contacting the dimethyl ether with steam in the presence of a solid catalyst and the solid acid in the reactor. The process is carried out in a fixed bed consisting of a mixture of a solid catalyst and the solid acid in a weight ratio respectively equal 1:5 ÷ 5:1, while as the solid catalyst is a metal-catalyst, and the process is carried out at a temperature of 225-450 o C and a pressure 1-100 bar. The invention improves the yield of the desired product with high selectivity for the formation of hydrogen and carbon oxides.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the production of hydrogen gas from hydrocarbons, more particularly, to a method for producing a hydrogen-rich gas from the DME.
A method of producing hydrogen rich gas by contacting dimethyl ether with steam in the presence of a solid catalyst and the solid acid in the reactor, and by contacting the feedstock with steam occur hydration and expansion of the resulting methanol (See. Patent GB 2805314, B 01 J 23 / 78, 04/28/1982).
Occurring in the known method illustrated by the following reaction scheme: 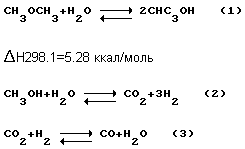
Both reactions can be carried out both in the gas and liquid phase.
The object of the invention is a method for producing a hydrogen rich gas, which is highly efficient due to the high reaction rate.
The problem is solved in a method for producing hydrogen rich gas by contacting dimethyl ether with steam in the presence of a solid catalyst and the solid acid in the reactor due to the fact that the process is carried out in a fixed bed consisting of a solid catalyst mixture and a solid acid in a weight ratio respectively equal to 1: 5 ÷ 5: 1, and as the metal catalyst is a solid catalyst, and the process is carried out at a temperature of 225 - 450 o C and a pressure of 1-100 bar.
It has been found that the overall reaction of dimethyl ether (DME) until the hydrogen rich gas according to the following reaction: 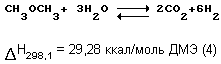
proceeds with satisfactory conversion, high yield of the desired product, high selectivity for the formation of hydrogen and carbon oxides unless limitation to the equilibrium reaction (1) hydration of dimethyl ether is eliminated by the conversion of methanol at the time of its formation to hydrogen and carbon oxides according to the above reactions (2) and (3).
As the metal-containing catalyst used is preferably copper and zinc on alumina.
It can be used in any solid acid as the solid acid. A preferred catalyst is selected from the group consisting of zeolites, in particular zeolite ZSM-5 grade in aqueous form and / or Siral-5, alumina silicates, alumina and silica and mixtures thereof.
The process is preferably carried out at a temperature of 225-240 o C and a pressure of 2-50 bar.
Prior to contacting with the starting raw material gas is converted into the active catalyst form. For example, the active form of the solid acid is the hydrogen form obtained by ion exchange as a result of contacting the catalyst with a proton donor solution. The metal catalyst is typically activated by contacting with a reducing gas.
Catalysts usually employed in the form of extrudates, pellets, granules, etc. solid forms which are suitable for forming fixed bed.
The proposed method is carried out by the fact that the starting dimethyl ether with steam in a molar ratio of 1: 1 ÷ 1: 10, preferably 1: 2 ÷ 1: 5 is fed to a fixed bed BMU. Consisting of dimethyl ether and steam gas is passed through the catalyst layer at 1: 100 bar and a space velocity of 1000-5000 h -1.
At a reaction temperature exceeding 225 o C, preferably 250 o C, conversion of DME to hydrogen and carbon oxides is substantially complete at the above conditions.
The following examples further illustrate the present invention.
example 1
The reactor tube is placed a fixed bed consisting of a mixture of 3.00 g of catalyst, which is a commercial product MDK-20 company Haldor Topsoe A / S, DK (copper-zinc-aluminum catalyst), and a commercial product of company Siral-5 kondeem, DE (silica and alumina), taken in a weight ratio of 1: 1. The mixture consists of both catalysts granule size of 0.1-1.0 mm.
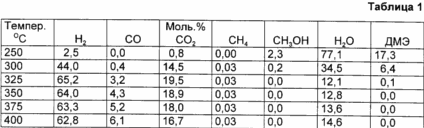
Consisting of dimethyl ether and water in a molar ratio of 0.25: 1 gas is supplied to the reactor in an amount of 1.6 g DME / h and at a pressure of 1.2 bar. The process is carried out at temperatures isometrically shown in table 1, in which the results of this example are summarized.
example 2
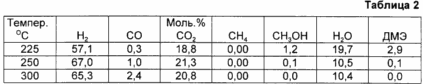
Example 1 was repeated with the only difference that dimethyl ether is converted to hydrogen rich gas at the temperature given in Table 2. In this example, the reactor comprises a mixture of the activated catalyst consisting of 3.0 g of MPC-20 trade product, which is a decomposition catalyst methanol, and zeolite ZSM-5 grade. The weight ratio of the two catalysts is 1: 1. The catalyst mixture has a particle size of 0.5-1 mm.
The results of this example and are summarized in Table 2.
CLAIM
1. A method for producing hydrogen rich gas by contacting dimethyl ether with steam in the presence of a solid catalyst and the solid acid in a reactor, characterized in that the process is carried out in a fixed bed consisting of a solid catalyst and the solid acid mixture in a weight ratio respectively equal to 1: 5 ÷ 5: 1, wherein the metal used in the catalyst, and the process is carried out as a solid catalyst at a temperature of 225-450 o C and a pressure of 1-100 bar.
2. The method of claim. 1, wherein the solid acid is selected from the group consisting of zeolites, alumina silicates, alumina and silica and mixtures thereof.
3. A method according to claim 1, characterized in that as solid acid zeolite ZSM-5 grade in the hydrogen form and / or Siral-5.
4. A method according to claim 1, characterized in that the process is carried out at a temperature of 225-240 o C and a pressure of 2-50 bar.
print version
Publication date 01.03.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.