| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2256007
![]()
DEVICE FOR PRODUCING THERMAL ENERGY, HYDROGEN AND OXYGEN
The name of the inventor: Kanarev F.М.
(RU); Tlishev A.I. (RU)
The name of the patent holder: Kuban State Agrarian University
Address for correspondence: 350044, Krasnodar, ul. Kalinin, 13, KGAU, PIO
Date of commencement of the patent: 2003.12.08
The invention relates to physical and chemical technologies for producing heat, hydrogen and oxygen. The device comprises a housing made of a dielectric material, a cover, and made of a dielectric material. The anode is made of a flat annular without holes and is installed under the dielectric cylindrical inflow of the anodic-cathode dielectric rod and is held by a stopping dielectric ring. The cathode is mounted in the upper enlarged part of the axial hole of the anodic-cathode dielectric rod, the anodic-cathode dielectric rod together with the planar annular anode and the cylindrical cathode is threaded into the axial hole of the bottom of the housing coaxially with the axial hole of the cover, into which the nozzle for the outlet of the heated solution is introduced and Gases, while the anode and the cathode are connected to a power source that generates pulses. The technical effect is an increase in the energy indicators of the device.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to physical and chemical technologies and techniques for producing heat, hydrogen and oxygen.
A technical solution is known (see Yakovlev SV, Krasnoborodko IG and Rogov VM "Technology of Electrochemical Water Purification., Leningrad: Stroy-izdat, 1987, p.207-211, 227-231), containing A body with branch pipes for supply and removal of the treated solution, an electric discharge chamber with a flat and needle electrode placed in it.
The technical solution described in SU 487665, 15.10.75, C 25 V 9/00, comprising a body, upper and lower covers, nozzles for input and output of a working solution, an anode connected to the positive pole of the power source, and a cathode connected to Negative pole of the power source.
And the technical solution described in Russian Patent No. 2,157,861 (prototype) is known for the production of thermal energy of hydrogen and oxygen, comprising a housing made of a dielectric material, a cover, and made of a dielectric material that has a cylindrical conical tide with a through hole forming, together with The anode is made flat, annular with holes, is located in the anode cavity and is connected to the positive pole of the power source, the cathode - in the form of a rod of refractory material, is inserted into the dielectric rod with external thread, by means of which it is inserted into the interelectrode chamber Through the threaded hole in the housing and is centered in the through-hole of the cover, and connected to the negative pole of the power source, the branch pipe for insertion of the working solution is located in the middle part of the anode cavity.
A disadvantage of the known inventions is that they have a low energy efficiency.
The technical solution of the problem is to improve the energy performance of the device.
The object is achieved by the fact that the device for obtaining the thermal energy of hydrogen and oxygen comprises a housing made of a dielectric material, a cover, and made of a dielectric material. The anode is made of a flat annular without holes and is installed under the dielectric cylindrical inflow of the anodic-cathode dielectric rod and is held by a stop dielectric ring, the cathode is mounted in the upper enlarged part of the axial hole of the anodic-cathode dielectric rod, the anodic-cathode dielectric rod together with the plane annular anode and the cylindrical cathode Is threaded into the axial hole of the bottom of the housing coaxially with the axial opening of the cover into which a branch pipe for the outlet of the heated solution and gases is introduced, the anode and the cathode being connected to a power source that generates pulses.
The novelty of the claimed proposal is due to the fact that the anode has a flat annular shape without holes, which allowed to increase the gap area between the dielectric bottom of the casing and the end surface of the dielectric cylindrical tide of the anode dielectric rod. Since polarization of water molecules and ions occurs in this gap, the increased area of this gap significantly increases the stability of the process of electrodynamic destruction and dissociation of water molecules and ions. Increasing the stability of the process eliminates the need to install automatic systems to regulate its parameters. All this increases the efficiency of the device for obtaining thermal energy, hydrogen and oxygen.
With such a device circuit, it is possible to select a resonant frequency of action on molecules and ions of water and thus dramatically reduce the energy costs for their destruction. In the subsequent synthesis of molecules and water ions destroyed by a resonant electromagnetic field, additional thermal energy is released. Thus, the device generates simultaneously thermal energy and a mixture of gases: hydrogen and oxygen.
According to the data of the patent-technical literature, a similar set of characteristics has not been found, which makes it possible to judge the inventive level of the proposal.
The essence of the invention is explained in the drawing, which shows a general view of the device.
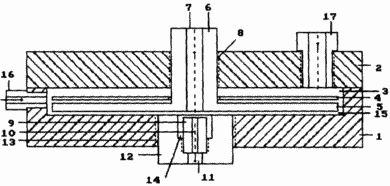 |
The device for obtaining thermal energy of hydrogen and oxygen contains a body 1 made of a dielectric material and having an axial hole in the bottom; Dielectric cover 2 and with an axial hole. The housing 1 and the cover 2 form an anode cavity 3. The flat annular anode 4 is located under the dielectric tide 5 of the anodic-cathode dielectric rod 6 and is held by the stop ring 7. The cylindrical cathode 8 is inserted into the axial hole 9 of the anodic-cathode dielectric rod 6 which, together with the anode 5 and the cathode 8 by the thread 10 is inserted into the axial hole at the bottom of the body 1. |
The cathode cavity 11 is formed by an enlarged portion of the axial hole 9 of the anodic-cathode dielectric rod 6. The gap 12 between the lower surface of the dielectric cover 2 and the end surface of the dielectric tide 5 on the anodic-cathode dielectric rod 6 changes the movement of the anodic-cathode dielectric rod 6 in the axial bore 1 by a thread 10. The branch pipe 13 for supplying a solution to the anode cavity 3 is mounted on the side wall of the housing 1. The oxygen outlet 14 is introduced into the axial opening of the cover 2 by the thread 15. | |
The device works as follows. The set flow rate of the solution passing through the device is set. The power supply is turned on and the set voltage is set. In a few minutes the process acquires an established character. After this, the required pulse frequency is set and the process of fixing the solution, voltage, current and temperature difference of the solution at the input and output of the device begins (Table). In this case, the solution enters the anode cavity 3, and then into the gap 12, where the polarization of water molecules and ions occurs under the action of electrical pulses. After the destruction of their chemical bonds and subsequent dissociation, the heated solution and gases exit through the axial aperture 16 of the nozzle 14.
| Table | ||||
| Indicators | 1 | 2 | 3 | Avg. |
| 1-mass of the solution passed through the device m, kg. | 0.352 | 0.342 | 0,242 | 0.312 |
| 2-temperature of the solution at the reactor inlet t 1 , deg. | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| 3-temperature of the solution at the outlet of the device t 2 , deg. | 85 | 83 | 94 | 80.3 |
| 4-temperature difference of solution |
65 | 63 | 74 | 67.3 |
| 5-duration of the experiment |
300 | 300 | 300 | 300 |
| 6-voltmeter readings V, V | 5.5 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.17 |
| 7-readings of ammeter I, A | 1.90 | 1.90 | 1.50 | 1.77 |
| 8-power consumption E 1 = I · V · |
3.14 | 2.85 | 2.25 | 2.75 |
| 9 is the energy of the heated solution, E 2 = 4.19 · m · |
98.59 | 90.28 | 75.03 | 87.97 |
| 10-indicator of the efficiency of the device K = E 2 / E 1 | 31.40 | 31.68 | 33.35 | 32.14 |
CLAIM
A device for producing thermal energy, hydrogen and oxygen, comprising a housing made of a dielectric material, a cover made of a dielectric material, an anode, a cathode and a branch pipe for introducing a working solution, characterized in that the anode is flat, annular without holes and is installed under a dielectric cylindrical tide anodically Cathode dielectric rod, and the cathode is mounted in the upper enlarged part of the axial hole of the anodic-cathode dielectric rod, the anode-cathode dielectric rod together with the planar annular anode and the cylindrical cathode is threaded into the axial hole of the bottom of the housing coaxially with the axial hole of the cover , In which a branch pipe for the outlet of the heated solution and gases is introduced, the anode and the cathode being connected to a power source generating pulses.
print version
Date of publication 02.03.2007гг




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.