| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2219274
![]()
METHOD FOR PRODUCING VODORODOPOGLOTITELNYH alloys of complex composition
Name of the inventor: Patrickeyev JB .; Buzlov AV .; Badovskiy VV
The name of the patentee: Federal State Unitary Enterprise State Research and Design Institute of Rare Metal Industry "Giredmet"
Address for correspondence:. 109017, Moscow, B. Tolmachevsky Lane 5, "Giredmet" OPiII
Starting date of the patent: 2002.05.27
The invention relates to metallurgy, in particular to the production of alloys, whose composition allows the absorption and release of hydrogen. The process is carried out at least four remelting the ingot with subsequent crystallization rate of less than 0.6 mm / s, and the final remelting - followed ingot solidification rate of 0.6 mm / s. The invention enables standard equipment to increase productivity of the process on the basis of receipt of REM alloys by 2.5 times and provides alloys with high performance, stable properties for use as components of heat pumps, hydrogen batteries.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to ferrous metallurgy, in particular to producing alloy whose composition allows the absorption and release of hydrogen.
Known alloys - hydrogen scavengers are made on the basis of the type AB 5 compounds, which suck the alloying components are added. They are used in chemical power sources, electrochemical generators, hydrogen, batteries, heat pumps.
The main technical feature that defines the quality of alloys is their working hydrogen capacity, expressed as a percentage by weight, which shows how much hydrogen can be stripped in a given alloy at a given temperature range of pressures. The use of a composition of the alloy determines the possibility of expanding the range of the pressure and temperature.
The process for obtaining hydrogen scavengers alloys consists of two major steps: melting the initial charge and components ingot crystallization. The fusion is carried out, usually in the induction or arc furnaces (B.V.Linchevsky, "Technology of metallurgical experiment", Moscow, "Metallurgy", 1979, p.16).
Induction furnaces for heating and melting may be open or closed. Vodorodopoglotitelnymi When working with alloys of the type AB 5 are in a closed melting induction furnace in an argon atmosphere due to the high oxidizing power of their constituent rare earth metals (REM). The power source furnaces are tube or engine generators of various capacities. alloy charge was placed in a crucible container, being located inside the coil. Number of REM included in the charge, with the excess charge based on carbon monoxide. Next, the furnace is evacuated, backfilled with argon and alloying is carried out batch materials. At the end of the melting current is turned off, the alloy is poured into a mold, where it is crystallization.
The disadvantages of induction melting should include chemical interaction of the melt with the crucible material, which leads to disruption of the chemical composition of the alloy and, as a consequence, to a decrease in the working of hydrogen capacity.
A method of obtaining vodorodopoglotitelnyh alloys of complex composition in arc furnaces with non-consumable electrodes. As used tungsten electrode. Furnaces operate in a neutral gas atmosphere (Argon). Molten metal (charge) in a cooled mold under the electrode. When the arc melted material, when you turn off the melt crystallizes, forming a metal ingot (alloy). remelting and crystallization operations carried out several times. As the mold material used copper (B.V.Linchevsky, "Metallurgical Engineering Experiment", Moscow, "Metallurgy", 1979, p.21).
Smelting furnaces of this type is obtained the chemical composition of homogeneous metal. This chemical interaction between the mold material and alloy no. Therefore, in terms of constancy of the arc melting purity alloy has an advantage over induction.
The disadvantage of the conventional method is the poor reproducibility of the results for hydrogen capacity alloys and implementation method exclusively on small batches of the initial charge.
The technical result of the claimed method for producing vodorodopoglotitelnyh alloys of complex composition in an arc furnace with a non-consumable electrode is to improve the cycle performance by increasing the mass of melted ingots and stable reception of increased hydrogen capacity alloys.
This is achieved by a method for producing alloys vodorodopoglotitelnyh complex composition comprising repeated melting and crystallization of the starting components in arc furnaces ingot from the casting mold cooled by a neutral gas atmosphere, according to the invention at least four subsequent remelting is carried out with the ingot crystallization rate less than 0.6 mm / sec, and a final remelting is carried out subsequent crystallization rate of 0.6 mm / sec.
The method consists in the fact that the claimed modes crystallization ceteris paribus (mothers, mold design, etc.) to provide a first remelting complete fusion blend components and chemical homogeneity of the alloy, and subsequent remelting of the final rate of crystallization of the ingot yields the optimum phase composition, microstructure and the necessary associated labor hydrogen capacity.
Currently, no published data on the effect on the crystallization conditions of the ingot and its technical characteristics, in particular hydrogen capacity. Meanwhile, in the step of crystallization is formed ingot necessary microstructure and phase composition of the alloy, to ensure its working hydrogen capacity.
For the main characteristic of the crystallization process, which determines all the other parameters of the alloy production process and at the same time lends itself well to production control and the mathematical description, select the speed of the ingot crystallization, expressed in mm / sec. The lack of information about such studies is accompanied in practice, unstable, poorly reproducible results or even low values of hydrogen capacity alloys.
The claimed preparation process parameters vodorodopoglotitelnyh alloys of complex composition are optimal because holding smelting under conditions in which the subsequent crystallization rate exceeding 0.6 mm / sec in the step 1-4 remelting be accompanied neproplavami chemical and lead to inhomogeneity of the ingot. Thus, the main task of 1-4 remelting - ensuring the chemical homogeneity of the ingot to its volume.
Crystallization fifth ingot after remelting at a rate of less than 0.6 mm / sec leads to disruption of the microstructure and phase composition of the alloy, and hence to reduce work hydrogen capacity (see. Table). The main task of this stage - to obtain the maximum possible working alloy hydrogen capacity.
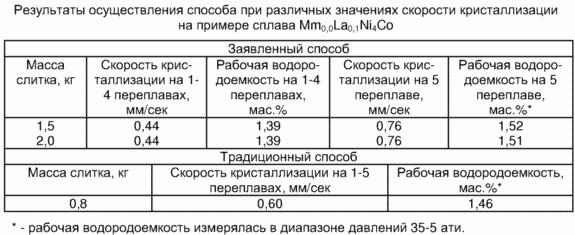
It should be noted that the ingot obtained by the conventional technique with the same process parameters (mold material and design of the arc parameters, etc.) has a smaller mass and labor hydrogen capacity. This is due to the fact that the crystallization rate constant at 1.5 remelting step creates the need to reduce the mass of melted ingot to provide both chemical homogeneity, and the maximum hydrogen capacity of the alloy.
Application of this method of smelting, as is evident from the table that allows you to raise the cyclic performance of 2.5 times, that is to provide the opportunity to increase 2.5 times the mass of melted ingot while maintaining its qualitative and quantitative characteristics. The claimed invention can be of the same technical result to be applicable to all known alloy compositions hydrogen scavengers.
An example of the process for producing the composition of complex alloys vodorodopoglotitelnyh
In a water-cooled copper mold alloy loaded charge Mm 0,9 La 0,1 Ni 4 Co. The mass of lanthanum and misch metal were taken from 3% excess, based on the burn. For ingot weighing 2 kg batch composition of the components is as follows: 600 g of mischmetal, Lanthanum 66 g, 1082 g of nickel, cobalt, 272 g Next, the furnace was evacuated to a residual gas pressure of 0.006 mmHg cleaned and filled with argon. The first four of remelting was performed under conditions allowing subsequent crystallization speed of 0.44 mm / sec (see. Table). smelting average current of 350 A at U = 60 V. Each ingot remelting overturned. After the fifth remelting the ingot crystallization is performed at a speed of 0.76 mm / sec. After cooling the alloy furnace was opened and dumped bullion. Working obtained ingot hydrogen capacity in the pressure range 35-5 atm was 1.52% by weight.
Thus, the claimed invention allows to improve the performance of standard process equipment getting vodorodopoglotitelnyh AB 5 type alloy, rare earth-based and by 2.5 times to ensure receipt of alloys with high performance, stable properties for use as components of heat pumps, hydrogen storage, chemical current sources.
CLAIM
A method of producing alloys vodorodopoglotitelnyh complex composition comprising multiple crystallization and remelt ingot in arc furnaces with cooled ingot mold in an atmosphere of neutral gas, characterized in that at least four subsequent remelting is carried out with the crystallization rate of the ingot at least 0.6 mm / s, and the final carry remelting followed ingot solidification rate 0.6 mm / s.
print version
Publication date 04.01.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.