| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2084121
![]()
METHOD OF GROWING SHRUBBY berries
Name of the inventor: Beshnov GV
The name of the patentee: All-Russia Selection-Technological Institute of Horticulture and Nursery
Address for correspondence:
Starting date of the patent: 1995.07.07
Usage: The invention relates to agriculture, in particular for gardening, and can be used during the laying of high-berry plantings. The inventive method: Each graft harvested from the mother plant, prior to planting bent into a ring, the ends of which are connected to each other by means provided with a thread permanent split annular permanent magnets worn on said ends of the cutting and planting is performed by penetration of the ring into the soil, so that, at least one kidney was cutting on the soil surface, and the other - on the last level. The combined ends bent in the cutting ring are immersed into the soil at an acute angle to its surface. After rooting cuttings, part of the ring, located above the soil, cut and processed garden pitch, and the permanent magnets are removed from the soil.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to agriculture, and can be used for laying high-berry plantings.
There is a method of preparation and planting of cuttings in autumn with aisles of 60 cm private landing strip or the distances between the centers of 80 to 90 cm between the distances in the series of 5 to 8 cm. [1]
The disadvantage of this method is the low survival rate of cuttings of 60% and 85 bulging and cuttings from the soil in winter and spring due to sudden fluctuations in temperature, which leads to their death.
Known and method tab plantings of horticultural crops, according to which the cuttings, such as blackcurrant length of 35 cm and a diameter of 45 base 5 to 10 mm obliquely planted in a hole in the place of their permanent growth [2]
The disadvantage of this method is undoubtedly a progressive need to use to produce positive results cuttings, cut out 2-year-olds branches.
The closest technical solution known is the method of growing shrub berries, according to which the cuttings are planted in their place of permanent growth [3] Before planting cuttings are fastened in pairs at the bottom and top ends are bred during landing. To create a closed drills planting stapled cuttings planted in a number of planes. To create in wide spaces stapled cuttings are planted across the series.
A disadvantage of this known method is the possibility of infection through the open ends of the upper portions of pairs of planted cuttings prior to their rooting. Furthermore, when diluted in the upper parts of the soil planted cuttings recessed gap is not excluded in the kidneys from the soil cuttings, the number of which is not so large, and their loss may reduce the survival rate of the cuttings.
The task to be solved by the invention is the elimination of infection in the planted cutting and increasing the likelihood of its survival, by creating more favorable conditions.
The problem is solved by the fact that in the process of growing shrub berries, which includes harvesting cuttings from parent plants and the subsequent rows of landing a permanent place, each cutting before planting folded into the ring, the ends of which are connected to each other by means provided with drinking permanent split ring of permanent magnets, worn ends to said handle, a landing ring is manufactured by burying in the soil, so that at least one cutting kidney was above the soil surface and the other at the last level.
The problem is solved, and the fact that the soil is immersed joined together in the bent ends of the cutting ring.
The problem is solved by the fact that bent into the ring shank bury into the soil at an acute angle to the surface of the soil.
Besides, the task set is solved by the fact that after rooting cuttings, part of a ring, located above the ground, cut and processed garden pitch, and the permanent magnets are removed from the soil.
Arranged in a ring kidney graft has a higher water intake surface and carries a large number of kidneys that provides a high probability of the healing it, and the lack of open end all over the surface of the soil reduces the penetration of infection inside the handle, increasing its resilience during rooting.
In order to create in wide planting soil before planting in the lower parts connecting the two rings bent in the cuttings and the tops of the last landing bred and stalks bent into a ring connected, twisting them together.
Comparative analysis of the inventive solutions with the prototype shows that the proposed method differs from the known fact that each cutting before planting bent into a ring, the ends of which are joined by means provided with a thread split annular permanent magnets have been put onto the ends of the cutting and planting is performed by penetration ring in the soil, so that at least one cutting kidney was above the soil surface and the other at the level of the latter, and the soil was immersed joined together in the bent ends of the cutting ring.
Thus, the claimed method of the invention meets the criterion of "novelty".
The claimed technical solution has inventive and not obvious to those skilled in the field of agriculture. Although known method of reproduction of horticultural crops elongated handle, but a way to burying it in soil traditional [2]
The proposed method is, despite its apparent simplicity, the source of the information we do not know and in practice has not been applied.
The proposed method of growing shrub berries very technologically as harvesting and cuttings, and bending them in the ring, m stacking them in the soil can easily be mechanized using existing hardware.
 |
 |
 |
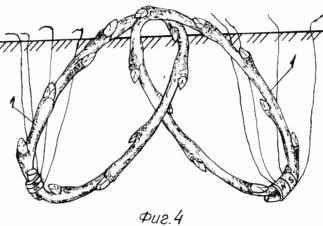 |
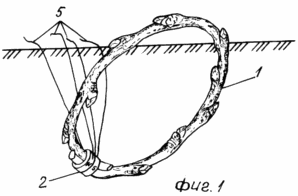
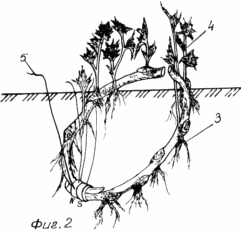
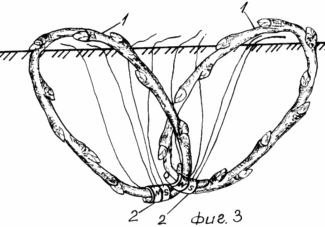
The invention is illustrated by a drawing, where FIG. 1 shows a planted in the soil in a bent stalk ring; FIG. 2 shows a rooted cutting to cut the upper part; FIG. 3 landing joined together at the bottom of the cuttings bent in a ring; FIG. 4 landing interconnected in the upper parts of cuttings in a bent ring.
Method is as follows
With hardwood cuttings harvested in the autumn of 50 cm long leaves are removed. Branching in cuttings and removed. Cuttings put in plastic bags and covered them with wet sawdust. Cuttings are stored prior to planting, they can be stored in a cool place not more than 30 days. It is best to harvest and plant the cuttings in early autumn, in the 2nd and 3rd decade of September. September period of harvesting cuttings preferable others because it provides the beginning of root formation in cuttings in autumn, when the soil temperature is much higher than the spring planting. Cuttings harvested in a few days when the kidney, for example, currants already entered into rest, and not wake up. Spring rooting hardwood cuttings after winter storage in Prikope often accompanied by intense gray mold (Botrytis cinerea). This leads to the death of 40 to 90% of the cuttings.
The soil on the site of the landing of the cuttings should be loose and moist, richly seasoned with organic and mineral fertilizers. So for planting cuttings currants digging trenches or pits 50 cm deep and fill them with a mixture of soil with fertilizers. Fertilizers contribute 1 per hole: 3-6 kg of humus, superphosphate granulated 0.5-1 kg of potassium sulfate 20-30 g
Handle 1 is folded before landing on a mandrel (not shown) in the ring, with the ends of a handle connected to each other by means of detachable annular magnets 2, worn by said cutting ends. Then, in place of constant growth the plant by, for example, a shovel made inclined at an angle of 45 o to the surface of the soil slot, which is placed folded into the ring shank, thus it is necessary to ensure that the soil was immersed ends joined together by a handle, and at least one kidney is above the soil surface, and the other at the level of the final surface. Then a gap in it stowed handle is closed or simple pressing of the soil layer, dry or pre-poured harvested substrate with mineral additives and growth substances, so that there were no voids. Then planted cuttings watered and sprinkle organic material.
During the week and a half after landing in cuttings appear adventitious roots 3, in the spring of their growth continues, and in the first decade of May, the plant has a large number of branched roots, and aided by the impact of the magnetic field of the permanent magnets in the soil. Cuttings are well acclimatized and in that time, part of the ring, located above the soil surface is cut and the cut processed garden pitch. With laid at an acute angle to the surface of the soil in the ring bent stalk touched in the vertical growth of 4 March 4. Over the summer, escape completely root stalk and branch shoots. Permanent magnets with flexible filaments 5 if necessary is extracted from the soil for reuse.
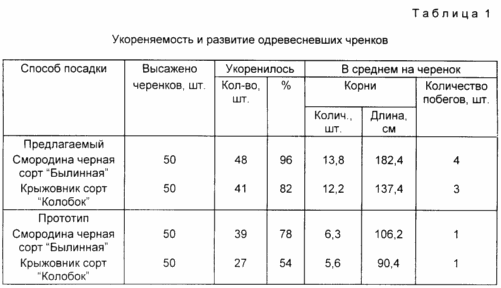
Thus, in the first year on the site of the permanent growth of the stalk bent in a ring formed by a full bush currants. Since the upper part of the bent in the cutting ring, located above the surface of the soil, the whole winter and early spring period was uncut, the possibility of infection from outside to inside of the cutting has been ruled out, and the great length of the cutting in the soil, with a lot more than traditional technology number kidneys, allowing the plant to develop a greater number of roots and contributed to the emergence of new shoots from the buds on the recess portion bent into a ring handle, and create a more productive bush (Table. 1).
In order to create in wide spaces, before planting into the soil the lower part of the two bent to connect the ring shanks, twisting them together, and the upper bred.
The stalks bent to the ring, most of which is in the soil is less susceptible to bulging in the winter and spring, and constant exposure to the magnetic fields of the permanent magnets to accelerate biochemical processes and the development of roots, total length 1.5 times longer than the control. The nutrients in the soil, under the action of the magnetic field and will better assimilated by plants, with their smaller loss due to leaching with water.
The ground under the influence of the magnetic field changes its physico-chemical properties, it enhanced microbiological processes and activates decomposition of organic matter and increases the solubility of mineral salts.
Thus, the method enables the operational management of growth and development of plants to accelerate root formation before the onset of winter and the vegetative growth in the spring and summer.
For the manufacture of magnets using waste products (block ring ferrites). The field strength of not more than 2000 Oe.
USED BOOKS
1. Polikarpov Ya Ya et al. Guidelines for the production of healthy planting material technology blackcurrant. M. 1978, p. 31, 58, 60.
2. Kondrashov VT The new technology of sea buckthorn plantations bookmarks and other horticultural crops. // Reports Rosselhozakadenii, 1994, N 6, p. 13 o C 15.
3. Author's certificate USSR N 1782446. The process of growing shrub berries. M. Cl. A 01 G 1/00, 08.10.90 priority was published. 23.12.92 Mr. Bull. N 47 prototype.
CLAIM
1. A method of growing shrub berries including cuttings from the workpiece parent plants and their subsequent rows on the landing place of their constant growth, characterized in that each shank is bent before planting in the ring, the ends of which are connected to each other by means of thread split ring equipped with permanent magnets, worn by the cutting ends and the landing is performed by burial in soil of the ring so that at least one cutting kidney was above the soil surface and the other
at the last level.
2. A method according to claim 1, characterized in that the soil is immersed joined together in the bent ends of the cutting ring.
3. The method of claim 1 or 2, characterized in that a bent stem ring bury in the ground under an acute angle to the soil surface.
4. The method of claims 1 to 3, characterized in that after rooting of the cutting part of a ring, located above the ground, cut, and the permanent magnets are removed from the soil.
5. The method according to claim 1, characterized in that, in order to create in wide spaces, in the soil before planting the lower connecting portions of the two shanks bent into rings, and the upper parts of the last landing diluted.
6. The method of claim 1 or 5, characterized in that the bent connecting ring shanks, twisting them together.
print version
Publication date 06.03.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.